Adnane Boukhayma
GTAvatar: Bridging Gaussian Splatting and Texture Mapping for Relightable and Editable Gaussian Avatars
Dec 09, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in Gaussian Splatting have enabled increasingly accurate reconstruction of photorealistic head avatars, opening the door to numerous applications in visual effects, videoconferencing, and virtual reality. This, however, comes with the lack of intuitive editability offered by traditional triangle mesh-based methods. In contrast, we propose a method that combines the accuracy and fidelity of 2D Gaussian Splatting with the intuitiveness of UV texture mapping. By embedding each canonical Gaussian primitive's local frame into a patch in the UV space of a template mesh in a computationally efficient manner, we reconstruct continuous editable material head textures from a single monocular video on a conventional UV domain. Furthermore, we leverage an efficient physically based reflectance model to enable relighting and editing of these intrinsic material maps. Through extensive comparisons with state-of-the-art methods, we demonstrate the accuracy of our reconstructions, the quality of our relighting results, and the ability to provide intuitive controls for modifying an avatar's appearance and geometry via texture mapping without additional optimization.
TextureSplat: Per-Primitive Texture Mapping for Reflective Gaussian Splatting
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Gaussian Splatting have demonstrated remarkable novel view synthesis performance at high rendering frame rates. Optimization-based inverse rendering within complex capture scenarios remains however a challenging problem. A particular case is modelling complex surface light interactions for highly reflective scenes, which results in intricate high frequency specular radiance components. We hypothesize that such challenging settings can benefit from increased representation power. We hence propose a method that tackles this issue through a geometrically and physically grounded Gaussian Splatting borne radiance field, where normals and material properties are spatially variable in the primitive's local space. Using per-primitive texture maps for this purpose, we also propose to harness the GPU hardware to accelerate rendering at test time via unified material texture atlas.
Anti-Aliased 2D Gaussian Splatting
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) has recently emerged as a promising method for novel view synthesis and surface reconstruction, offering better view-consistency and geometric accuracy than volumetric 3DGS. However, 2DGS suffers from severe aliasing artifacts when rendering at different sampling rates than those used during training, limiting its practical applications in scenarios requiring camera zoom or varying fields of view. We identify that these artifacts stem from two key limitations: the lack of frequency constraints in the representation and an ineffective screen-space clamping approach. To address these issues, we present AA-2DGS, an antialiased formulation of 2D Gaussian Splatting that maintains its geometric benefits while significantly enhancing rendering quality across different scales. Our method introduces a world space flat smoothing kernel that constrains the frequency content of 2D Gaussian primitives based on the maximal sampling frequency from training views, effectively eliminating high-frequency artifacts when zooming in. Additionally, we derive a novel object space Mip filter by leveraging an affine approximation of the ray-splat intersection mapping, which allows us to efficiently apply proper anti-aliasing directly in the local space of each splat.
SparSplat: Fast Multi-View Reconstruction with Generalizable 2D Gaussian Splatting
May 04, 2025Abstract:Recovering 3D information from scenes via multi-view stereo reconstruction (MVS) and novel view synthesis (NVS) is inherently challenging, particularly in scenarios involving sparse-view setups. The advent of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enabled real-time, photorealistic NVS. Following this, 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) leveraged perspective accurate 2D Gaussian primitive rasterization to achieve accurate geometry representation during rendering, improving 3D scene reconstruction while maintaining real-time performance. Recent approaches have tackled the problem of sparse real-time NVS using 3DGS within a generalizable, MVS-based learning framework to regress 3D Gaussian parameters. Our work extends this line of research by addressing the challenge of generalizable sparse 3D reconstruction and NVS jointly, and manages to perform successfully at both tasks. We propose an MVS-based learning pipeline that regresses 2DGS surface element parameters in a feed-forward fashion to perform 3D shape reconstruction and NVS from sparse-view images. We further show that our generalizable pipeline can benefit from preexisting foundational multi-view deep visual features. The resulting model attains the state-of-the-art results on the DTU sparse 3D reconstruction benchmark in terms of Chamfer distance to ground-truth, as-well as state-of-the-art NVS. It also demonstrates strong generalization on the BlendedMVS and Tanks and Temples datasets. We note that our model outperforms the prior state-of-the-art in feed-forward sparse view reconstruction based on volume rendering of implicit representations, while offering an almost 2 orders of magnitude higher inference speed.
Sparfels: Fast Reconstruction from Sparse Unposed Imagery
May 04, 2025Abstract:We present a method for Sparse view reconstruction with surface element splatting that runs within 3 minutes on a consumer grade GPU. While few methods address sparse radiance field learning from noisy or unposed sparse cameras, shape recovery remains relatively underexplored in this setting. Several radiance and shape learning test-time optimization methods address the sparse posed setting by learning data priors or using combinations of external monocular geometry priors. Differently, we propose an efficient and simple pipeline harnessing a single recent 3D foundation model. We leverage its various task heads, notably point maps and camera initializations to instantiate a bundle adjusting 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) model, and image correspondences to guide camera optimization midst 2DGS training. Key to our contribution is a novel formulation of splatted color variance along rays, which can be computed efficiently. Reducing this moment in training leads to more accurate shape reconstructions. We demonstrate state-of-the-art performances in the sparse uncalibrated setting in reconstruction and novel view benchmarks based on established multi-view datasets.
D-Garment: Physics-Conditioned Latent Diffusion for Dynamic Garment Deformations
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Adjusting and deforming 3D garments to body shapes, body motion, and cloth material is an important problem in virtual and augmented reality. Applications are numerous, ranging from virtual change rooms to the entertainment and gaming industry. This problem is challenging as garment dynamics influence geometric details such as wrinkling patterns, which depend on physical input including the wearer's body shape and motion, as well as cloth material features. Existing work studies learning-based modeling techniques to generate garment deformations from example data, and physics-inspired simulators to generate realistic garment dynamics. We propose here a learning-based approach trained on data generated with a physics-based simulator. Compared to prior work, our 3D generative model learns garment deformations for loose cloth geometry, especially for large deformations and dynamic wrinkles driven by body motion and cloth material. Furthermore, the model can be efficiently fitted to observations captured using vision sensors. We propose to leverage the capability of diffusion models to learn fine-scale detail: we model the 3D garment in a 2D parameter space, and learn a latent diffusion model using this representation independent from the mesh resolution. This allows to condition global and local geometric information with body and material information. We quantitatively and qualitatively evaluate our method on both simulated data and data captured with a multi-view acquisition platform. Compared to strong baselines, our method is more accurate in terms of Chamfer distance.
Few-Shot Multi-Human Neural Rendering Using Geometry Constraints
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:We present a method for recovering the shape and radiance of a scene consisting of multiple people given solely a few images. Multi-human scenes are complex due to additional occlusion and clutter. For single-human settings, existing approaches using implicit neural representations have achieved impressive results that deliver accurate geometry and appearance. However, it remains challenging to extend these methods for estimating multiple humans from sparse views. We propose a neural implicit reconstruction method that addresses the inherent challenges of this task through the following contributions: First, we propose to use geometry constraints by exploiting pre-computed meshes using a human body model (SMPL). Specifically, we regularize the signed distances using the SMPL mesh and leverage bounding boxes for improved rendering. Second, we propose a ray regularization scheme to minimize rendering inconsistencies, and a saturation regularization for robust optimization in variable illumination. Extensive experiments on both real and synthetic datasets demonstrate the benefits of our approach and show state-of-the-art performance against existing neural reconstruction methods.
ProKeR: A Kernel Perspective on Few-Shot Adaptation of Large Vision-Language Models
Jan 19, 2025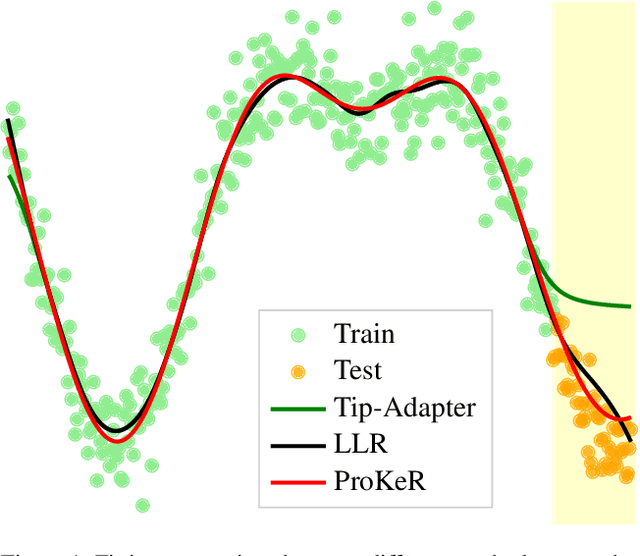
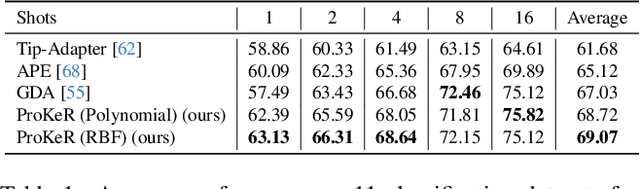
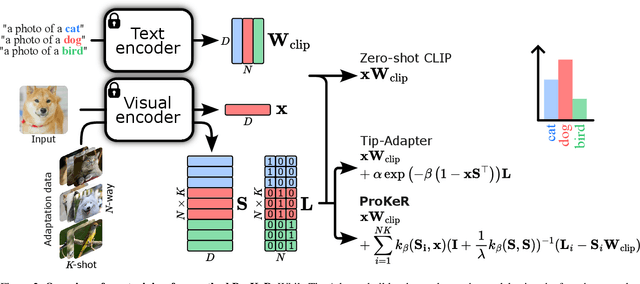
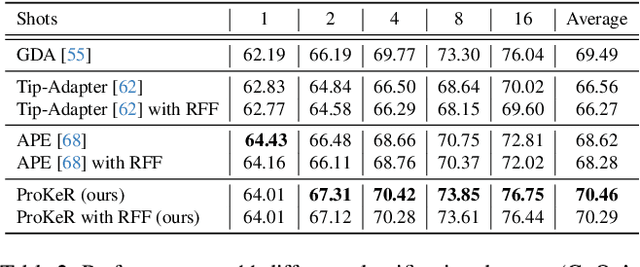
Abstract:The growing popularity of Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) has led to its widespread application in various visual downstream tasks. To enhance CLIP's effectiveness and versatility, efficient few-shot adaptation techniques have been widely adopted. Among these approaches, training-free methods, particularly caching methods exemplified by Tip-Adapter, have gained attention for their lightweight adaptation without the need for additional fine-tuning. In this paper, we revisit Tip-Adapter from a kernel perspective, showing that caching methods function as local adapters and are connected to a well-established kernel literature. Drawing on this insight, we offer a theoretical understanding of how these methods operate and suggest multiple avenues for enhancing the Tip-Adapter baseline. Notably, our analysis shows the importance of incorporating global information in local adapters. Therefore, we subsequently propose a global method that learns a proximal regularizer in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) using CLIP as a base learner. Our method, which we call ProKeR (Proximal Kernel ridge Regression), has a closed form solution and achieves state-of-the-art performances across 11 datasets in the standard few-shot adaptation benchmark.
Toward Robust Neural Reconstruction from Sparse Point Sets
Dec 20, 2024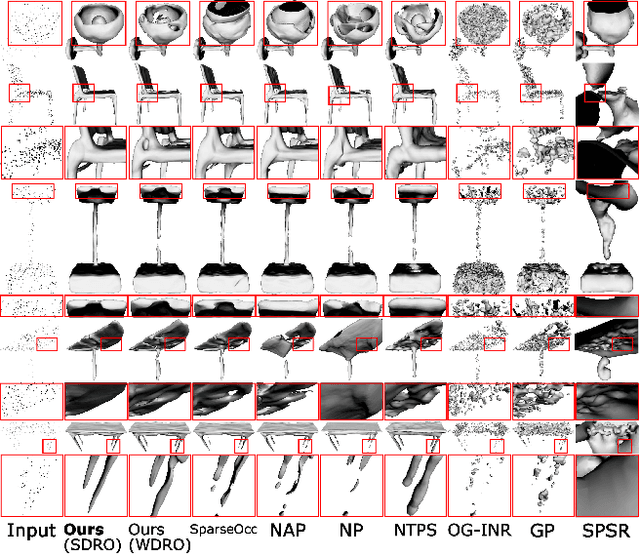
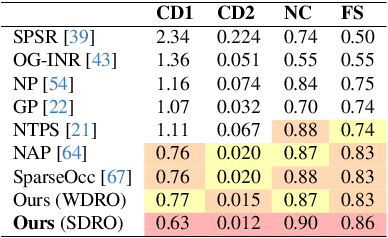
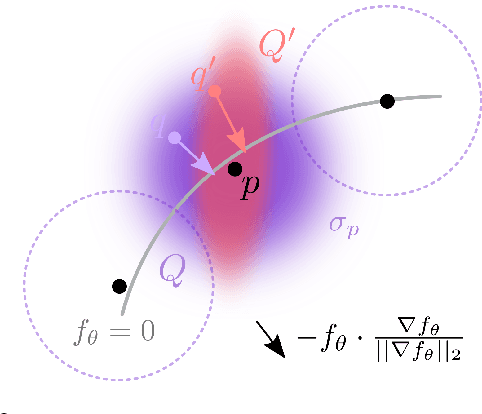
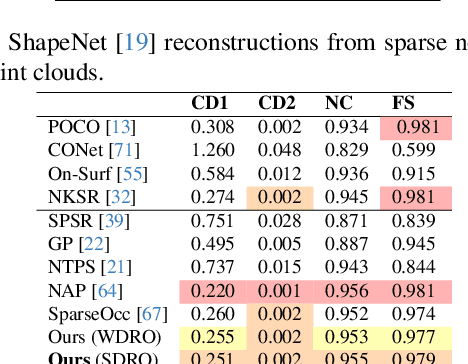
Abstract:We consider the challenging problem of learning Signed Distance Functions (SDF) from sparse and noisy 3D point clouds. In contrast to recent methods that depend on smoothness priors, our method, rooted in a distributionally robust optimization (DRO) framework, incorporates a regularization term that leverages samples from the uncertainty regions of the model to improve the learned SDFs. Thanks to tractable dual formulations, we show that this framework enables a stable and efficient optimization of SDFs in the absence of ground truth supervision. Using a variety of synthetic and real data evaluations from different modalities, we show that our DRO based learning framework can improve SDF learning with respect to baselines and the state-of-the-art methods.
SPARK: Self-supervised Personalized Real-time Monocular Face Capture
Sep 12, 2024
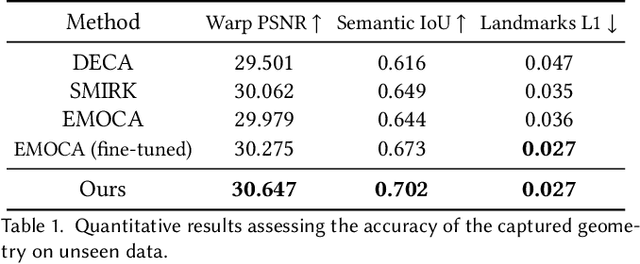
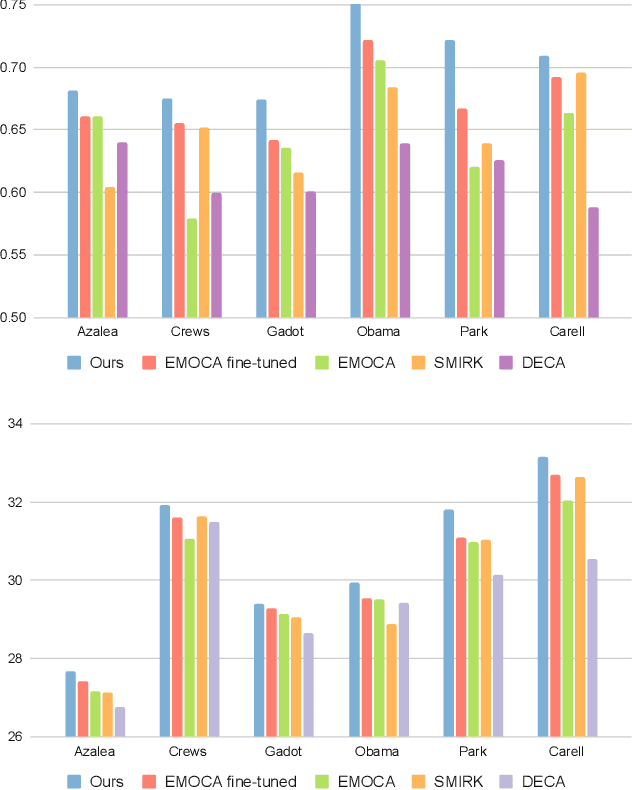
Abstract:Feedforward monocular face capture methods seek to reconstruct posed faces from a single image of a person. Current state of the art approaches have the ability to regress parametric 3D face models in real-time across a wide range of identities, lighting conditions and poses by leveraging large image datasets of human faces. These methods however suffer from clear limitations in that the underlying parametric face model only provides a coarse estimation of the face shape, thereby limiting their practical applicability in tasks that require precise 3D reconstruction (aging, face swapping, digital make-up, ...). In this paper, we propose a method for high-precision 3D face capture taking advantage of a collection of unconstrained videos of a subject as prior information. Our proposal builds on a two stage approach. We start with the reconstruction of a detailed 3D face avatar of the person, capturing both precise geometry and appearance from a collection of videos. We then use the encoder from a pre-trained monocular face reconstruction method, substituting its decoder with our personalized model, and proceed with transfer learning on the video collection. Using our pre-estimated image formation model, we obtain a more precise self-supervision objective, enabling improved expression and pose alignment. This results in a trained encoder capable of efficiently regressing pose and expression parameters in real-time from previously unseen images, which combined with our personalized geometry model yields more accurate and high fidelity mesh inference. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluation, we showcase the superiority of our final model as compared to state-of-the-art baselines, and demonstrate its generalization ability to unseen pose, expression and lighting.
* SIGGRAPH Asia 2024 Conference Paper. Project page: https://kelianb.github.io/SPARK/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge