Shishir Reddy Vutukur
SparSplat: Fast Multi-View Reconstruction with Generalizable 2D Gaussian Splatting
May 04, 2025Abstract:Recovering 3D information from scenes via multi-view stereo reconstruction (MVS) and novel view synthesis (NVS) is inherently challenging, particularly in scenarios involving sparse-view setups. The advent of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enabled real-time, photorealistic NVS. Following this, 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) leveraged perspective accurate 2D Gaussian primitive rasterization to achieve accurate geometry representation during rendering, improving 3D scene reconstruction while maintaining real-time performance. Recent approaches have tackled the problem of sparse real-time NVS using 3DGS within a generalizable, MVS-based learning framework to regress 3D Gaussian parameters. Our work extends this line of research by addressing the challenge of generalizable sparse 3D reconstruction and NVS jointly, and manages to perform successfully at both tasks. We propose an MVS-based learning pipeline that regresses 2DGS surface element parameters in a feed-forward fashion to perform 3D shape reconstruction and NVS from sparse-view images. We further show that our generalizable pipeline can benefit from preexisting foundational multi-view deep visual features. The resulting model attains the state-of-the-art results on the DTU sparse 3D reconstruction benchmark in terms of Chamfer distance to ground-truth, as-well as state-of-the-art NVS. It also demonstrates strong generalization on the BlendedMVS and Tanks and Temples datasets. We note that our model outperforms the prior state-of-the-art in feed-forward sparse view reconstruction based on volume rendering of implicit representations, while offering an almost 2 orders of magnitude higher inference speed.
Alignist: CAD-Informed Orientation Distribution Estimation by Fusing Shape and Correspondences
Sep 10, 2024
Abstract:Object pose distribution estimation is crucial in robotics for better path planning and handling of symmetric objects. Recent distribution estimation approaches employ contrastive learning-based approaches by maximizing the likelihood of a single pose estimate in the absence of a CAD model. We propose a pose distribution estimation method leveraging symmetry respecting correspondence distributions and shape information obtained using a CAD model. Contrastive learning-based approaches require an exhaustive amount of training images from different viewpoints to learn the distribution properly, which is not possible in realistic scenarios. Instead, we propose a pipeline that can leverage correspondence distributions and shape information from the CAD model, which are later used to learn pose distributions. Besides, having access to pose distribution based on correspondences before learning pose distributions conditioned on images, can help formulate the loss between distributions. The prior knowledge of distribution also helps the network to focus on getting sharper modes instead. With the CAD prior, our approach converges much faster and learns distribution better by focusing on learning sharper distribution near all the valid modes, unlike contrastive approaches, which focus on a single mode at a time. We achieve benchmark results on SYMSOL-I and T-Less datasets.
SABER-6D: Shape Representation Based Implicit Object Pose Estimation
Aug 11, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel encoder-decoder architecture, named SABER, to learn the 6D pose of the object in the embedding space by learning shape representation at a given pose. This model enables us to learn pose by performing shape representation at a target pose from RGB image input. We perform shape representation as an auxiliary task which helps us in learning rotations space for an object based on 2D images. An image encoder predicts the rotation in the embedding space and the DeepSDF based decoder learns to represent the object's shape at the given pose. As our approach is shape based, the pipeline is suitable for any type of object irrespective of the symmetry. Moreover, we need only a CAD model of the objects to train SABER. Our pipeline is synthetic data based and can also handle symmetric objects without symmetry labels and, thus, no additional labeled training data is needed. The experimental evaluation shows that our method achieves close to benchmark results for both symmetric objects and asymmetric objects on Occlusion-LineMOD, and T-LESS datasets.
NeRF-Feat: 6D Object Pose Estimation using Feature Rendering
Jun 19, 2024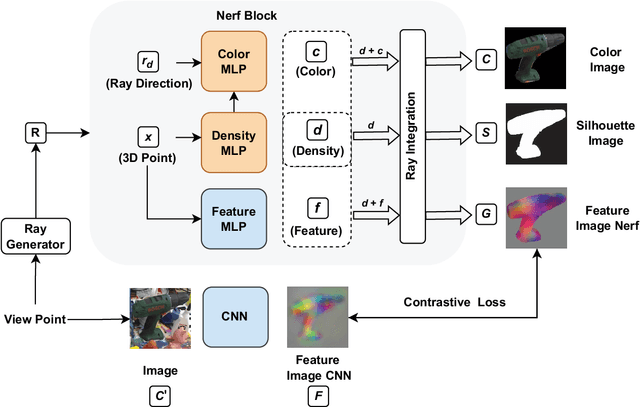

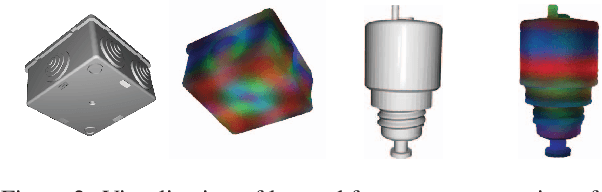
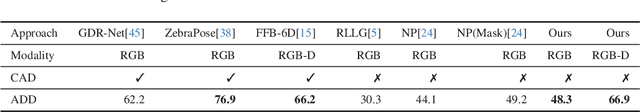
Abstract:Object Pose Estimation is a crucial component in robotic grasping and augmented reality. Learning based approaches typically require training data from a highly accurate CAD model or labeled training data acquired using a complex setup. We address this by learning to estimate pose from weakly labeled data without a known CAD model. We propose to use a NeRF to learn object shape implicitly which is later used to learn view-invariant features in conjunction with CNN using a contrastive loss. While NeRF helps in learning features that are view-consistent, CNN ensures that the learned features respect symmetry. During inference, CNN is used to predict view-invariant features which can be used to establish correspondences with the implicit 3d model in NeRF. The correspondences are then used to estimate the pose in the reference frame of NeRF. Our approach can also handle symmetric objects unlike other approaches using a similar training setup. Specifically, we learn viewpoint invariant, discriminative features using NeRF which are later used for pose estimation. We evaluated our approach on LM, LM-Occlusion, and T-Less dataset and achieved benchmark accuracy despite using weakly labeled data.
* 3DV 2024
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge