Adam Wróbel
Personalized Interpretability -- Interactive Alignment of Prototypical Parts Networks
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Concept-based interpretable neural networks have gained significant attention due to their intuitive and easy-to-understand explanations based on case-based reasoning, such as "this bird looks like those sparrows". However, a major limitation is that these explanations may not always be comprehensible to users due to concept inconsistency, where multiple visual features are inappropriately mixed (e.g., a bird's head and wings treated as a single concept). This inconsistency breaks the alignment between model reasoning and human understanding. Furthermore, users have specific preferences for how concepts should look, yet current approaches provide no mechanism for incorporating their feedback. To address these issues, we introduce YoursProtoP, a novel interactive strategy that enables the personalization of prototypical parts - the visual concepts used by the model - according to user needs. By incorporating user supervision, YoursProtoP adapts and splits concepts used for both prediction and explanation to better match the user's preferences and understanding. Through experiments on both the synthetic FunnyBirds dataset and a real-world scenario using the CUB, CARS, and PETS datasets in a comprehensive user study, we demonstrate the effectiveness of YoursProtoP in achieving concept consistency without compromising the accuracy of the model.
This looks like what? Challenges and Future Research Directions for Part-Prototype Models
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:The growing interest in eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has prompted research into models with built-in interpretability, the most prominent of which are part-prototype models. Part-Prototype Models (PPMs) make decisions by comparing an input image to a set of learned prototypes, providing human-understandable explanations in the form of ``this looks like that''. Despite their inherent interpretability, PPMS are not yet considered a valuable alternative to post-hoc models. In this survey, we investigate the reasons for this and provide directions for future research. We analyze papers from 2019 to 2024, and derive a taxonomy of the challenges that current PPMS face. Our analysis shows that the open challenges are quite diverse. The main concern is the quality and quantity of prototypes. Other concerns are the lack of generalization to a variety of tasks and contexts, and general methodological issues, including non-standardized evaluation. We provide ideas for future research in five broad directions: improving predictive performance, developing novel architectures grounded in theory, establishing frameworks for human-AI collaboration, aligning models with humans, and establishing metrics and benchmarks for evaluation. We hope that this survey will stimulate research and promote intrinsically interpretable models for application domains. Our list of surveyed papers is available at https://github.com/aix-group/ppm-survey.
OMENN: One Matrix to Explain Neural Networks
Dec 03, 2024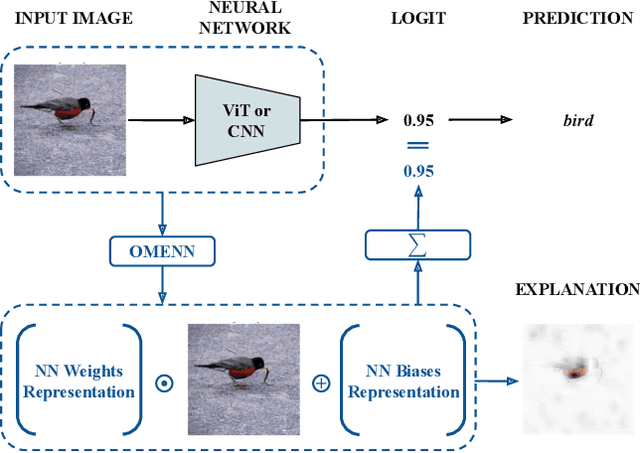
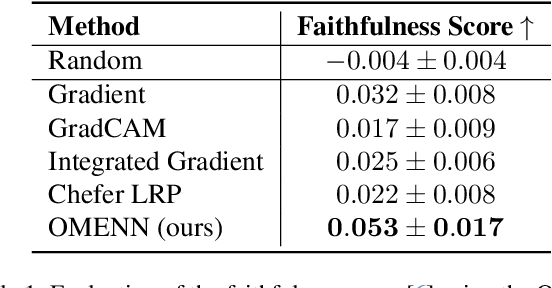
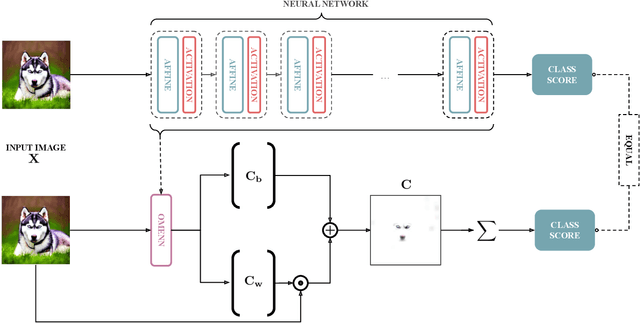
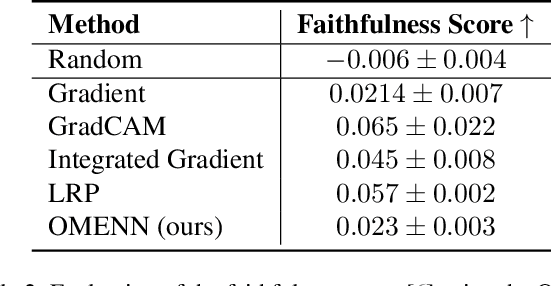
Abstract:Deep Learning (DL) models are often black boxes, making their decision-making processes difficult to interpret. This lack of transparency has driven advancements in eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI), a field dedicated to clarifying the reasoning behind DL model predictions. Among these, attribution-based methods such as LRP and GradCAM are widely used, though they rely on approximations that can be imprecise. To address these limitations, we introduce One Matrix to Explain Neural Networks (OMENN), a novel post-hoc method that represents a neural network as a single, interpretable matrix for each specific input. This matrix is constructed through a series of linear transformations that represent the processing of the input by each successive layer in the neural network. As a result, OMENN provides locally precise, attribution-based explanations of the input across various modern models, including ViTs and CNNs. We present a theoretical analysis of OMENN based on dynamic linearity property and validate its effectiveness with extensive tests on two XAI benchmarks, demonstrating that OMENN is competitive with state-of-the-art methods.
Avaya Conversational Intelligence: A Real-Time System for Spoken Language Understanding in Human-Human Call Center Conversations
Sep 02, 2019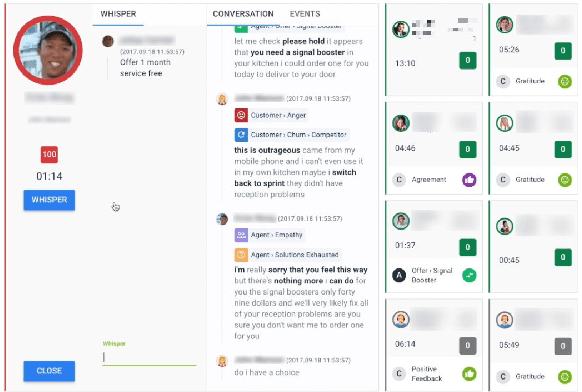

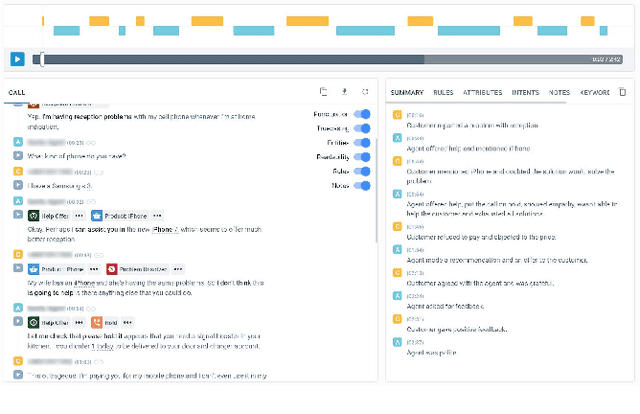
Abstract:Avaya Conversational Intelligence(ACI) is an end-to-end, cloud-based solution for real-time Spoken Language Understanding for call centers. It combines large vocabulary, real-time speech recognition, transcript refinement, and entity and intent recognition in order to convert live audio into a rich, actionable stream of structured events. These events can be further leveraged with a business rules engine, thus serving as a foundation for real-time supervision and assistance applications. After the ingestion, calls are enriched with unsupervised keyword extraction, abstractive summarization, and business-defined attributes, enabling offline use cases, such as business intelligence, topic mining, full-text search, quality assurance, and agent training. ACI comes with a pretrained, configurable library of hundreds of intents and a robust intent training environment that allows for efficient, cost-effective creation and customization of customer-specific intents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge