Abid Ali
AM Flow: Adapters for Temporal Processing in Action Recognition
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:Deep learning models, in particular \textit{image} models, have recently gained generalisability and robustness. %are becoming more general and robust by the day. In this work, we propose to exploit such advances in the realm of \textit{video} classification. Video foundation models suffer from the requirement of extensive pretraining and a large training time. Towards mitigating such limitations, we propose "\textit{Attention Map (AM) Flow}" for image models, a method for identifying pixels relevant to motion in each input video frame. In this context, we propose two methods to compute AM flow, depending on camera motion. AM flow allows the separation of spatial and temporal processing, while providing improved results over combined spatio-temporal processing (as in video models). Adapters, one of the popular techniques in parameter efficient transfer learning, facilitate the incorporation of AM flow into pretrained image models, mitigating the need for full-finetuning. We extend adapters to "\textit{temporal processing adapters}" by incorporating a temporal processing unit into the adapters. Our work achieves faster convergence, therefore reducing the number of epochs needed for training. Moreover, we endow an image model with the ability to achieve state-of-the-art results on popular action recognition datasets. This reduces training time and simplifies pretraining. We present experiments on Kinetics-400, Something-Something v2, and Toyota Smarthome datasets, showcasing state-of-the-art or comparable results.
Loose Social-Interaction Recognition in Real-world Therapy Scenarios
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:The computer vision community has explored dyadic interactions for atomic actions such as pushing, carrying-object, etc. However, with the advancement in deep learning models, there is a need to explore more complex dyadic situations such as loose interactions. These are interactions where two people perform certain atomic activities to complete a global action irrespective of temporal synchronisation and physical engagement, like cooking-together for example. Analysing these types of dyadic-interactions has several useful applications in the medical domain for social-skills development and mental health diagnosis. To achieve this, we propose a novel dual-path architecture to capture the loose interaction between two individuals. Our model learns global abstract features from each stream via a CNNs backbone and fuses them using a new Global-Layer-Attention module based on a cross-attention strategy. We evaluate our model on real-world autism diagnoses such as our Loose-Interaction dataset, and the publicly available Autism dataset for loose interactions. Our network achieves baseline results on the Loose-Interaction and SOTA results on the Autism datasets. Moreover, we study different social interactions by experimenting on a publicly available dataset i.e. NTU-RGB+D (interactive classes from both NTU-60 and NTU-120). We have found that different interactions require different network designs. We also compare a slightly different version of our method by incorporating time information to address tight interactions achieving SOTA results.
Weakly-supervised Autism Severity Assessment in Long Videos
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a diverse collection of neurobiological conditions marked by challenges in social communication and reciprocal interactions, as well as repetitive and stereotypical behaviors. Atypical behavior patterns in a long, untrimmed video can serve as biomarkers for children with ASD. In this paper, we propose a video-based weakly-supervised method that takes spatio-temporal features of long videos to learn typical and atypical behaviors for autism detection. On top of that, we propose a shallow TCN-MLP network, which is designed to further categorize the severity score. We evaluate our method on actual evaluation videos of children with autism collected and annotated (for severity score) by clinical professionals. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of behavioral biomarkers that could help clinicians in autism spectrum analysis.
P-Age: Pexels Dataset for Robust Spatio-Temporal Apparent Age Classification
Nov 04, 2023



Abstract:Age estimation is a challenging task that has numerous applications. In this paper, we propose a new direction for age classification that utilizes a video-based model to address challenges such as occlusions, low-resolution, and lighting conditions. To address these challenges, we propose AgeFormer which utilizes spatio-temporal information on the dynamics of the entire body dominating face-based methods for age classification. Our novel two-stream architecture uses TimeSformer and EfficientNet as backbones, to effectively capture both facial and body dynamics information for efficient and accurate age estimation in videos. Furthermore, to fill the gap in predicting age in real-world situations from videos, we construct a video dataset called Pexels Age (P-Age) for age classification. The proposed method achieves superior results compared to existing face-based age estimation methods and is evaluated in situations where the face is highly occluded, blurred, or masked. The method is also cross-tested on a variety of challenging video datasets such as Charades, Smarthome, and Thumos-14.
JOADAA: joint online action detection and action anticipation
Sep 12, 2023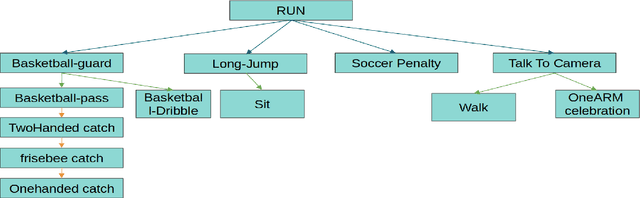
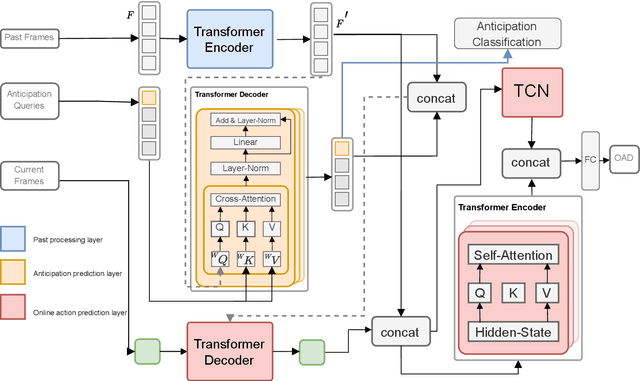
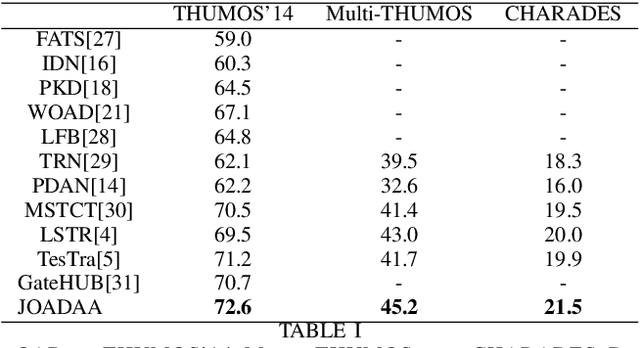
Abstract:Action anticipation involves forecasting future actions by connecting past events to future ones. However, this reasoning ignores the real-life hierarchy of events which is considered to be composed of three main parts: past, present, and future. We argue that considering these three main parts and their dependencies could improve performance. On the other hand, online action detection is the task of predicting actions in a streaming manner. In this case, one has access only to the past and present information. Therefore, in online action detection (OAD) the existing approaches miss semantics or future information which limits their performance. To sum up, for both of these tasks, the complete set of knowledge (past-present-future) is missing, which makes it challenging to infer action dependencies, therefore having low performances. To address this limitation, we propose to fuse both tasks into a single uniform architecture. By combining action anticipation and online action detection, our approach can cover the missing dependencies of future information in online action detection. This method referred to as JOADAA, presents a uniform model that jointly performs action anticipation and online action detection. We validate our proposed model on three challenging datasets: THUMOS'14, which is a sparsely annotated dataset with one action per time step, CHARADES, and Multi-THUMOS, two densely annotated datasets with more complex scenarios. JOADAA achieves SOTA results on these benchmarks for both tasks.
Intelligent 3D Network Protocol for Multimedia Data Classification using Deep Learning
Jul 23, 2022



Abstract:In videos, the human's actions are of three-dimensional (3D) signals. These videos investigate the spatiotemporal knowledge of human behavior. The promising ability is investigated using 3D convolution neural networks (CNNs). The 3D CNNs have not yet achieved high output for their well-established two-dimensional (2D) equivalents in still photographs. Board 3D Convolutional Memory and Spatiotemporal fusion face training difficulty preventing 3D CNN from accomplishing remarkable evaluation. In this paper, we implement Hybrid Deep Learning Architecture that combines STIP and 3D CNN features to enhance the performance of 3D videos effectively. After implementation, the more detailed and deeper charting for training in each circle of space-time fusion. The training model further enhances the results after handling complicated evaluations of models. The video classification model is used in this implemented model. Intelligent 3D Network Protocol for Multimedia Data Classification using Deep Learning is introduced to further understand spacetime association in human endeavors. In the implementation of the result, the well-known dataset, i.e., UCF101 to, evaluates the performance of the proposed hybrid technique. The results beat the proposed hybrid technique that substantially beats the initial 3D CNNs. The results are compared with state-of-the-art frameworks from literature for action recognition on UCF101 with an accuracy of 95%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge