Ziquan Fang
Moon: A Modality Conversion-based Efficient Multivariate Time Series Anomaly Detection
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Multivariate time series (MTS) anomaly detection identifies abnormal patterns where each timestamp contains multiple variables. Existing MTS anomaly detection methods fall into three categories: reconstruction-based, prediction-based, and classifier-based methods. However, these methods face two key challenges: (1) Unsupervised learning methods, such as reconstruction-based and prediction-based methods, rely on error thresholds, which can lead to inaccuracies; (2) Semi-supervised methods mainly model normal data and often underuse anomaly labels, limiting detection of subtle anomalies;(3) Supervised learning methods, such as classifier-based approaches, often fail to capture local relationships, incur high computational costs, and are constrained by the scarcity of labeled data. To address these limitations, we propose Moon, a supervised modality conversion-based multivariate time series anomaly detection framework. Moon enhances the efficiency and accuracy of anomaly detection while providing detailed anomaly analysis reports. First, Moon introduces a novel multivariate Markov Transition Field (MV-MTF) technique to convert numeric time series data into image representations, capturing relationships across variables and timestamps. Since numeric data retains unique patterns that cannot be fully captured by image conversion alone, Moon employs a Multimodal-CNN to integrate numeric and image data through a feature fusion model with parameter sharing, enhancing training efficiency. Finally, a SHAP-based anomaly explainer identifies key variables contributing to anomalies, improving interpretability. Extensive experiments on six real-world MTS datasets demonstrate that Moon outperforms six state-of-the-art methods by up to 93% in efficiency, 4% in accuracy and, 10.8% in interpretation performance.
Causal Spatio-Temporal Prediction: An Effective and Efficient Multi-Modal Approach
May 23, 2025Abstract:Spatio-temporal prediction plays a crucial role in intelligent transportation, weather forecasting, and urban planning. While integrating multi-modal data has shown potential for enhancing prediction accuracy, key challenges persist: (i) inadequate fusion of multi-modal information, (ii) confounding factors that obscure causal relations, and (iii) high computational complexity of prediction models. To address these challenges, we propose E^2-CSTP, an Effective and Efficient Causal multi-modal Spatio-Temporal Prediction framework. E^2-CSTP leverages cross-modal attention and gating mechanisms to effectively integrate multi-modal data. Building on this, we design a dual-branch causal inference approach: the primary branch focuses on spatio-temporal prediction, while the auxiliary branch mitigates bias by modeling additional modalities and applying causal interventions to uncover true causal dependencies. To improve model efficiency, we integrate GCN with the Mamba architecture for accelerated spatio-temporal encoding. Extensive experiments on 4 real-world datasets show that E^2-CSTP significantly outperforms 9 state-of-the-art methods, achieving up to 9.66% improvements in accuracy as well as 17.37%-56.11% reductions in computational overhead.
FedTDP: A Privacy-Preserving and Unified Framework for Trajectory Data Preparation via Federated Learning
May 08, 2025Abstract:Trajectory data, which capture the movement patterns of people and vehicles over time and space, are crucial for applications like traffic optimization and urban planning. However, issues such as noise and incompleteness often compromise data quality, leading to inaccurate trajectory analyses and limiting the potential of these applications. While Trajectory Data Preparation (TDP) can enhance data quality, existing methods suffer from two key limitations: (i) they do not address data privacy concerns, particularly in federated settings where trajectory data sharing is prohibited, and (ii) they typically design task-specific models that lack generalizability across diverse TDP scenarios. To overcome these challenges, we propose FedTDP, a privacy-preserving and unified framework that leverages the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) for TDP in federated environments. Specifically, we: (i) design a trajectory privacy autoencoder to secure data transmission and protect privacy, (ii) introduce a trajectory knowledge enhancer to improve model learning of TDP-related knowledge, enabling the development of TDP-oriented LLMs, and (iii) propose federated parallel optimization to enhance training efficiency by reducing data transmission and enabling parallel model training. Experiments on 6 real datasets and 10 mainstream TDP tasks demonstrate that FedTDP consistently outperforms 13 state-of-the-art baselines.
Effective and Efficient Cross-City Traffic Knowledge Transfer A Privacy-Preserving Perspective
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:Traffic prediction targets forecasting future traffic conditions using historical traffic data, serving a critical role in urban computing and transportation management. To mitigate the scarcity of traffic data while maintaining data privacy, numerous Federated Traffic Knowledge Transfer (FTT) approaches have been developed, which use transfer learning and federated learning to transfer traffic knowledge from data-rich cities to data-scarce cities, enhancing traffic prediction capabilities for the latter. However, current FTT approaches face challenges such as privacy leakage, cross-city data distribution discrepancies, low data quality, and inefficient knowledge transfer, limiting their privacy protection, effectiveness, robustness, and efficiency in real-world applications. To this end, we propose FedTT, an effective, efficient, and privacy-aware cross-city traffic knowledge transfer framework that transforms the traffic data domain from the data-rich cities and trains traffic models using the transformed data for the data-scarce cities. First, to safeguard data privacy, we propose a traffic secret transmission method that securely transmits and aggregates traffic domain-transformed data from source cities using a lightweight secret aggregation approach. Second, to mitigate the impact of traffic data distribution discrepancies on model performance, we introduce a traffic domain adapter to uniformly transform traffic data from the source cities' domains to that of the target city. Third, to improve traffic data quality, we design a traffic view imputation method to fill in and predict missing traffic data. Finally, to enhance transfer efficiency, FedTT is equipped with a federated parallel training method that enables the simultaneous training of multiple modules. Extensive experiments using 4 real-life datasets demonstrate that FedTT outperforms the 14 state-of-the-art baselines.
Estimator: An Effective and Scalable Framework for Transportation Mode Classification over Trajectories
Dec 11, 2022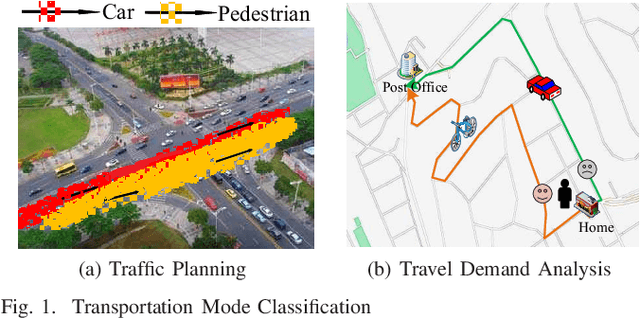
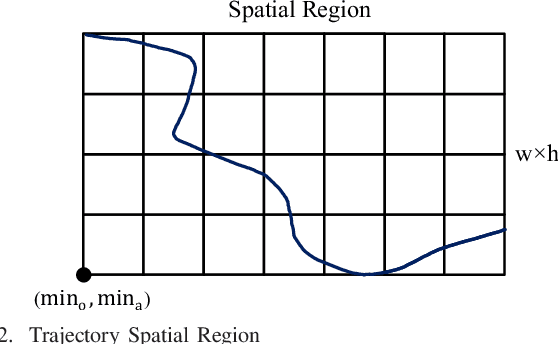
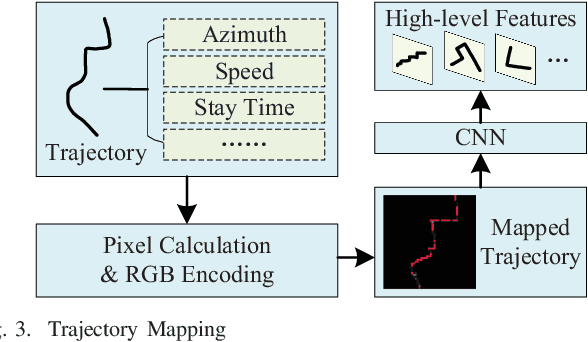
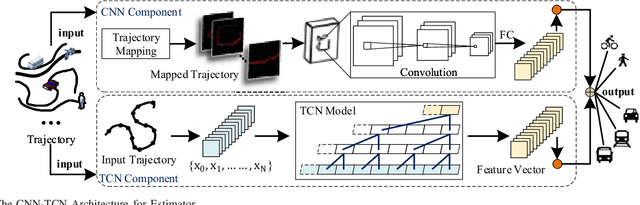
Abstract:Transportation mode classification, the process of predicting the class labels of moving objects transportation modes, has been widely applied to a variety of real world applications, such as traffic management, urban computing, and behavior study. However, existing studies of transportation mode classification typically extract the explicit features of trajectory data but fail to capture the implicit features that affect the classification performance. In addition, most of the existing studies also prefer to apply RNN-based models to embed trajectories, which is only suitable for classifying small-scale data. To tackle the above challenges, we propose an effective and scalable framework for transportation mode classification over GPS trajectories, abbreviated Estimator. Estimator is established on a developed CNN-TCN architecture, which is capable of leveraging the spatial and temporal hidden features of trajectories to achieve high effectiveness and efficiency. Estimator partitions the entire traffic space into disjointed spatial regions according to traffic conditions, which enhances the scalability significantly and thus enables parallel transportation classification. Extensive experiments using eight public real-life datasets offer evidence that Estimator i) achieves superior model effectiveness (i.e., 99% Accuracy and 0.98 F1-score), which outperforms state-of-the-arts substantially; ii) exhibits prominent model efficiency, and obtains 7-40x speedups up over state-of-the-arts learning-based methods; and iii) shows high model scalability and robustness that enables large-scale classification analytics.
Self-Guided Learning to Denoise for Robust Recommendation
Apr 14, 2022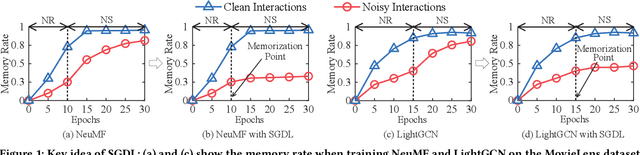
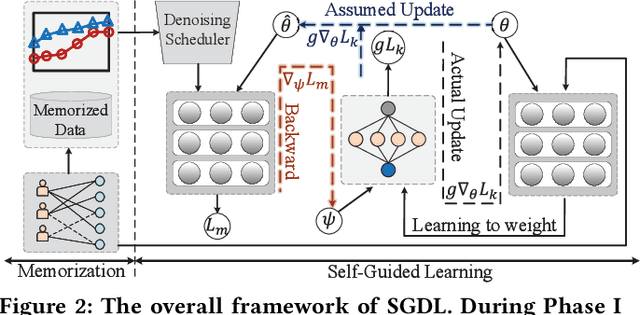
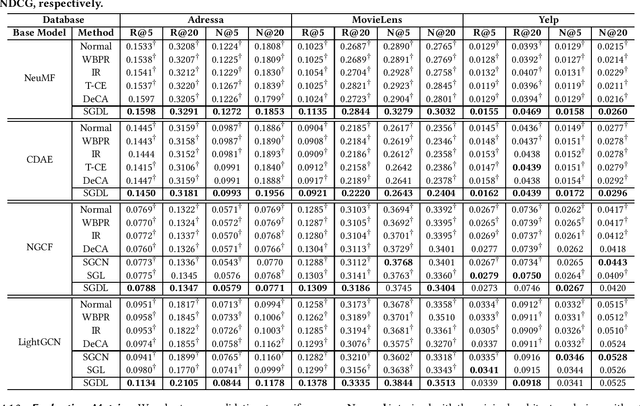
Abstract:The ubiquity of implicit feedback makes them the default choice to build modern recommender systems. Generally speaking, observed interactions are considered as positive samples, while unobserved interactions are considered as negative ones. However, implicit feedback is inherently noisy because of the ubiquitous presence of noisy-positive and noisy-negative interactions. Recently, some studies have noticed the importance of denoising implicit feedback for recommendations, and enhanced the robustness of recommendation models to some extent. Nonetheless, they typically fail to (1) capture the hard yet clean interactions for learning comprehensive user preference, and (2) provide a universal denoising solution that can be applied to various kinds of recommendation models. In this paper, we thoroughly investigate the memorization effect of recommendation models, and propose a new denoising paradigm, i.e., Self-Guided Denoising Learning (SGDL), which is able to collect memorized interactions at the early stage of the training (i.e., "noise-resistant" period), and leverage those data as denoising signals to guide the following training (i.e., "noise-sensitive" period) of the model in a meta-learning manner. Besides, our method can automatically switch its learning phase at the memorization point from memorization to self-guided learning, and select clean and informative memorized data via a novel adaptive denoising scheduler to improve the robustness. We incorporate SGDL with four representative recommendation models (i.e., NeuMF, CDAE, NGCF and LightGCN) and different loss functions (i.e., binary cross-entropy and BPR loss). The experimental results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of SGDL over the state-of-the-art denoising methods like T-CE, IR, DeCA, and even state-of-the-art robust graph-based methods like SGCN and SGL.
MetaKG: Meta-learning on Knowledge Graph for Cold-start Recommendation
Feb 08, 2022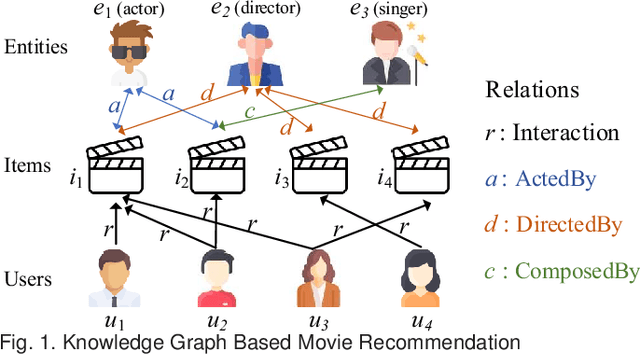
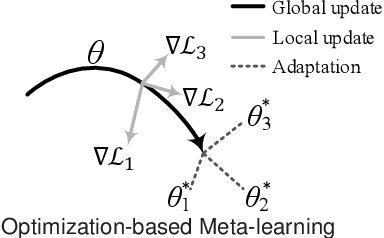
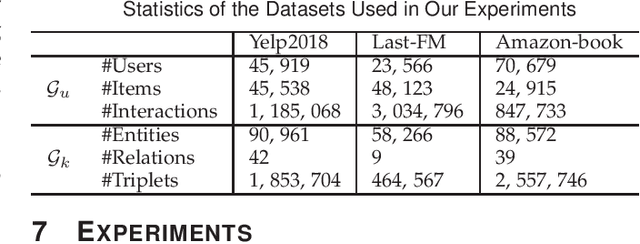
Abstract:A knowledge graph (KG) consists of a set of interconnected typed entities and their attributes. Recently, KGs are popularly used as the auxiliary information to enable more accurate, explainable, and diverse user preference recommendations. Specifically, existing KG-based recommendation methods target modeling high-order relations/dependencies from long connectivity user-item interactions hidden in KG. However, most of them ignore the cold-start problems (i.e., user cold-start and item cold-start) of recommendation analytics, which restricts their performance in scenarios when involving new users or new items. Inspired by the success of meta-learning on scarce training samples, we propose a novel meta-learning based framework called MetaKG, which encompasses a collaborative-aware meta learner and a knowledge-aware meta learner, to capture meta users' preference and entities' knowledge for cold-start recommendations. The collaborative-aware meta learner aims to locally aggregate user preferences for each user preference learning task. In contrast, the knowledge-aware meta learner is to globally generalize knowledge representation across different user preference learning tasks. Guided by two meta learners, MetaKG can effectively capture the high-order collaborative relations and semantic representations, which could be easily adapted to cold-start scenarios. Besides, we devise a novel adaptive task scheduler which can adaptively select the informative tasks for meta learning in order to prevent the model from being corrupted by noisy tasks. Extensive experiments on various cold-start scenarios using three real data sets demonstrate that our presented MetaKG outperforms all the existing state-of-the-art competitors in terms of effectiveness, efficiency, and scalability.
ST2Vec: Spatio-Temporal Trajectory Similarity Learning in Road Networks
Dec 17, 2021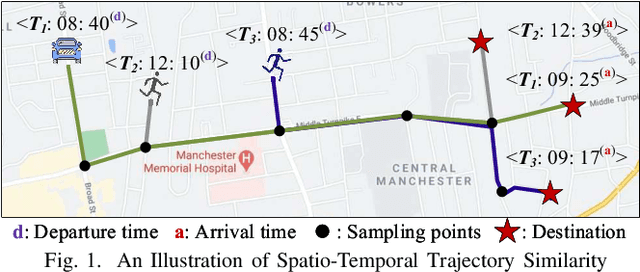
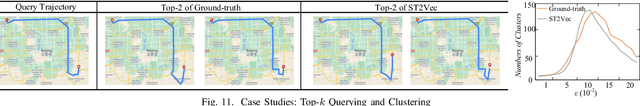
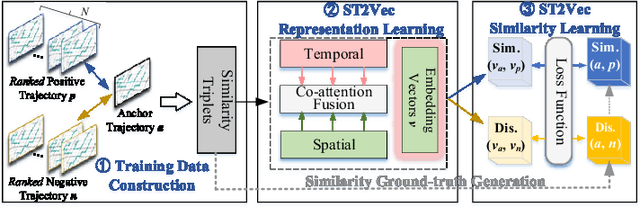
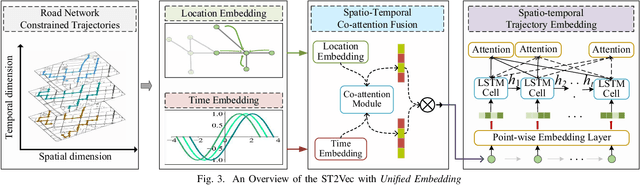
Abstract:People and vehicle trajectories embody important information of transportation infrastructures, and trajectory similarity computation is functionality in many real-world applications involving trajectory data analysis. Recently, deep-learning based trajectory similarity techniques hold the potential to offer improved efficiency and adaptability over traditional similarity techniques. Nevertheless, the existing trajectory similarity learning proposals emphasize spatial similarity over temporal similarity, making them suboptimal for time-aware analyses. To this end, we propose ST2Vec, a trajectory-representation-learning based architecture that considers fine-grained spatial and temporal correlations between pairs of trajectories for spatio-temporal similarity learning in road networks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first deep-learning proposal for spatio-temporal trajectory similarity analytics. Specifically, ST2Vec encompasses three phases: (i) training data preparation that selects representative training samples; (ii) spatial and temporal modeling that encode spatial and temporal characteristics of trajectories, where a generic temporal modeling module (TMM) is designed; and (iii) spatio-temporal co-attention fusion (STCF), where a unified fusion (UF) approach is developed to help generating unified spatio-temporal trajectory embeddings that capture the spatio-temporal similarity relations between trajectories. Further, inspired by curriculum concept, ST2Vec employs the curriculum learning for model optimization to improve both convergence and effectiveness. An experimental study offers evidence that ST2Vec outperforms all state-of-the-art competitors substantially in terms of effectiveness, efficiency, and scalability, while showing low parameter sensitivity and good model robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge