Ziming Guo
Evaluating and Enhancing LLMs for Multi-turn Text-to-SQL with Multiple Question Types
Dec 21, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced text-to-SQL systems. However, most LLM-based methods often narrowly focus on SQL generation, neglecting the complexities of real-world conversational queries. This oversight can lead to unreliable responses, particularly for ambiguous questions that cannot be directly addressed with SQL. To bridge this gap, we propose MMSQL, a comprehensive test suite designed to evaluate the question classification and SQL generation capabilities of LLMs by simulating real-world scenarios with diverse question types and multi-turn Q\&A interactions. Using MMSQL, we assessed the performance of popular LLMs, including both open-source and closed-source models, and identified key factors impacting their performance in such scenarios. Moreover, we introduce an LLM-based multi-agent framework that employs specialized agents to identify question types and determine appropriate answering strategies. Our experiments demonstrate that this approach significantly enhances the model's ability to navigate the complexities of conversational dynamics, effectively handling the diverse and complex nature of user queries.
QDA-SQL: Questions Enhanced Dialogue Augmentation for Multi-Turn Text-to-SQL
Jun 15, 2024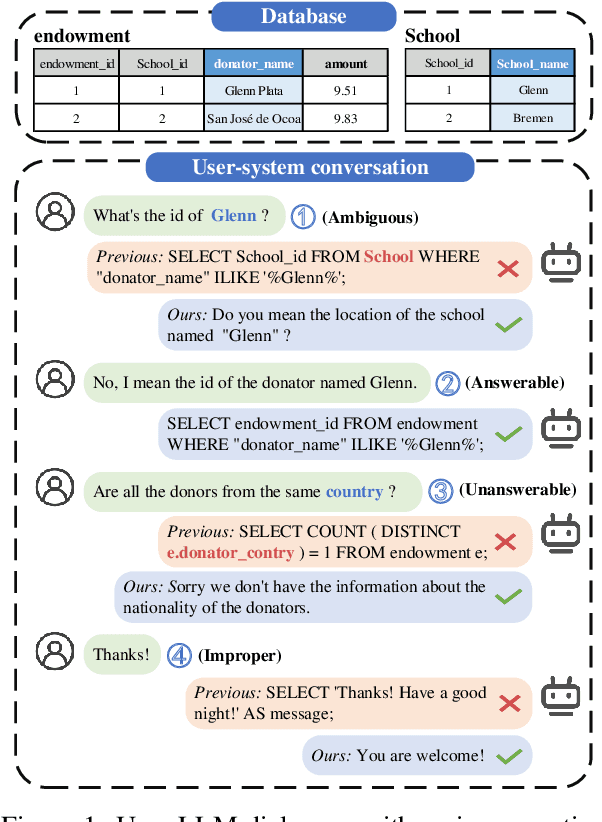
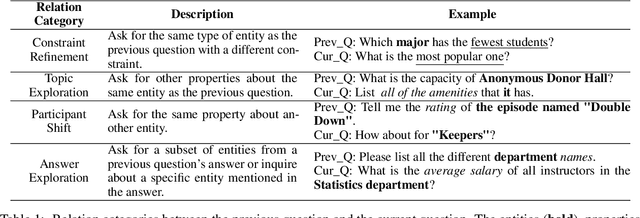
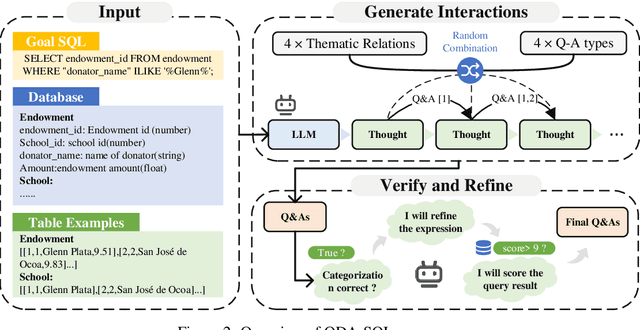
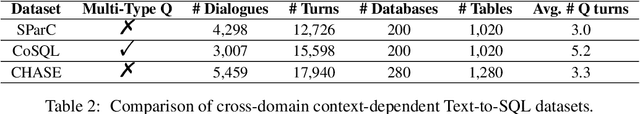
Abstract:Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) for specific domain tasks has achieved great success in Text-to-SQL tasks. However, these fine-tuned models often face challenges with multi-turn Text-to-SQL tasks caused by ambiguous or unanswerable questions. It is desired to enhance LLMs to handle multiple types of questions in multi-turn Text-to-SQL tasks. To address this, we propose a novel data augmentation method, called QDA-SQL, which generates multiple types of multi-turn Q\&A pairs by using LLMs. In QDA-SQL, we introduce a novel data augmentation method incorporating validation and correction mechanisms to handle complex multi-turn Text-to-SQL tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that QDA-SQL enables fine-tuned models to exhibit higher performance on SQL statement accuracy and enhances their ability to handle complex, unanswerable questions in multi-turn Text-to-SQL tasks. The generation script and test set are released at https://github.com/mcxiaoxiao/QDA-SQL.
CISum: Learning Cross-modality Interaction to Enhance Multimodal Semantic Coverage for Multimodal Summarization
Feb 20, 2023Abstract:Multimodal summarization (MS) aims to generate a summary from multimodal input. Previous works mainly focus on textual semantic coverage metrics such as ROUGE, which considers the visual content as supplemental data. Therefore, the summary is ineffective to cover the semantics of different modalities. This paper proposes a multi-task cross-modality learning framework (CISum) to improve multimodal semantic coverage by learning the cross-modality interaction in the multimodal article. To obtain the visual semantics, we translate images into visual descriptions based on the correlation with text content. Then, the visual description and text content are fused to generate the textual summary to capture the semantics of the multimodal content, and the most relevant image is selected as the visual summary. Furthermore, we design an automatic multimodal semantics coverage metric to evaluate the performance. Experimental results show that CISum outperforms baselines in multimodal semantics coverage metrics while maintaining the excellent performance of ROUGE and BLEU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge