Zhiyun Fan
SA-SOT: Speaker-Aware Serialized Output Training for Multi-Talker ASR
Mar 04, 2024
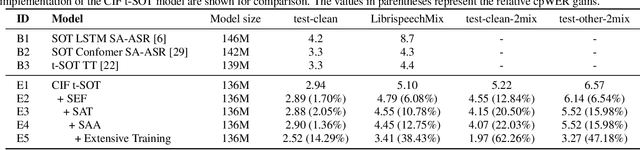
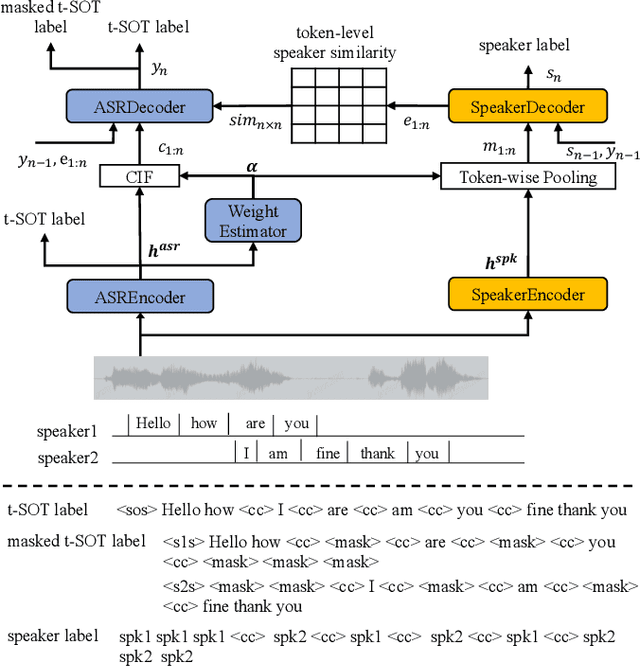
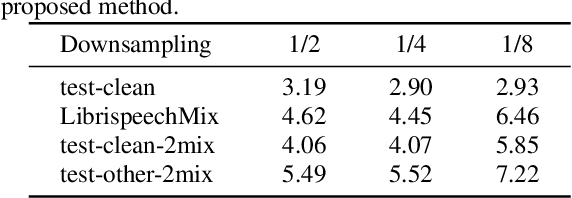
Abstract:Multi-talker automatic speech recognition plays a crucial role in scenarios involving multi-party interactions, such as meetings and conversations. Due to its inherent complexity, this task has been receiving increasing attention. Notably, the serialized output training (SOT) stands out among various approaches because of its simplistic architecture and exceptional performance. However, the frequent speaker changes in token-level SOT (t-SOT) present challenges for the autoregressive decoder in effectively utilizing context to predict output sequences. To address this issue, we introduce a masked t-SOT label, which serves as the cornerstone of an auxiliary training loss. Additionally, we utilize a speaker similarity matrix to refine the self-attention mechanism of the decoder. This strategic adjustment enhances contextual relationships within the same speaker's tokens while minimizing interactions between different speakers' tokens. We denote our method as speaker-aware SOT (SA-SOT). Experiments on the Librispeech datasets demonstrate that our SA-SOT obtains a relative cpWER reduction ranging from 12.75% to 22.03% on the multi-talker test sets. Furthermore, with more extensive training, our method achieves an impressive cpWER of 3.41%, establishing a new state-of-the-art result on the LibrispeechMix dataset.
Token-level Speaker Change Detection Using Speaker Difference and Speech Content via Continuous Integrate-and-fire
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:In multi-talker scenarios such as meetings and conversations, speech processing systems are usually required to segment the audio and then transcribe each segmentation. These two stages are addressed separately by speaker change detection (SCD) and automatic speech recognition (ASR). Most previous SCD systems rely solely on speaker information and ignore the importance of speech content. In this paper, we propose a novel SCD system that considers both cues of speaker difference and speech content. These two cues are converted into token-level representations by the continuous integrate-and-fire (CIF) mechanism and then combined for detecting speaker changes on the token acoustic boundaries. We evaluate the performance of our approach on a public real-recorded meeting dataset, AISHELL-4. The experiment results show that our method outperforms a competitive frame-level baseline system by 2.45% equal coverage-purity (ECP). In addition, we demonstrate the importance of speech content and speaker difference to the SCD task, and the advantages of conducting SCD on the token acoustic boundaries compared with conducting SCD frame by frame.
Sequence-level Speaker Change Detection with Difference-based Continuous Integrate-and-fire
Jun 27, 2022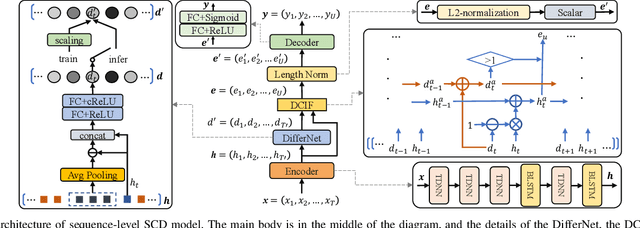
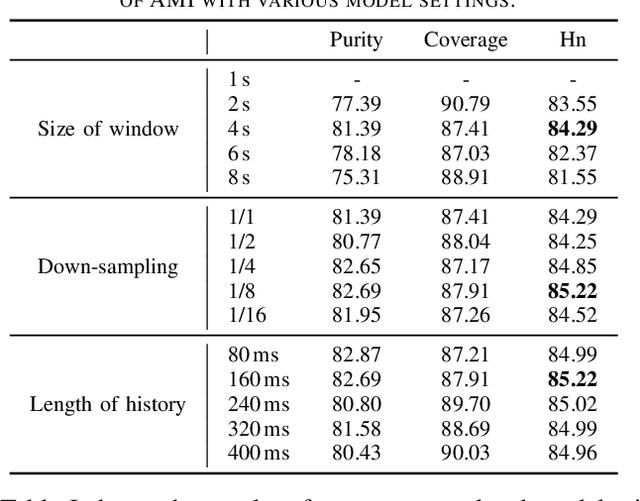
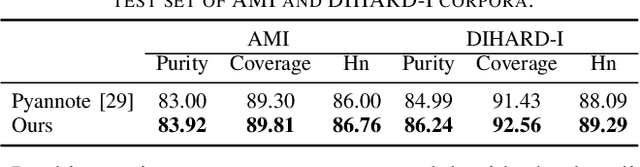
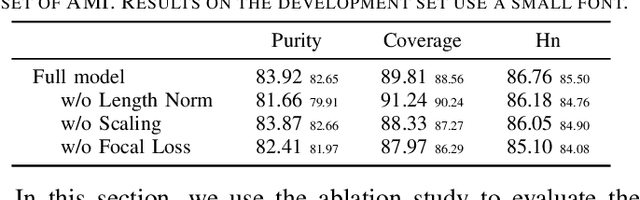
Abstract:Speaker change detection is an important task in multi-party interactions such as meetings and conversations. In this paper, we address the speaker change detection task from the perspective of sequence transduction. Specifically, we propose a novel encoder-decoder framework that directly converts the input feature sequence to the speaker identity sequence. The difference-based continuous integrate-and-fire mechanism is designed to support this framework. It detects speaker changes by integrating the speaker difference between the encoder outputs frame-by-frame and transfers encoder outputs to segment-level speaker embeddings according to the detected speaker changes. The whole framework is supervised by the speaker identity sequence, a weaker label than the precise speaker change points. The experiments on the AMI and DIHARD-I corpora show that our sequence-level method consistently outperforms a strong frame-level baseline that uses the precise speaker change labels.
Exploring wav2vec 2.0 on speaker verification and language identification
Jan 14, 2021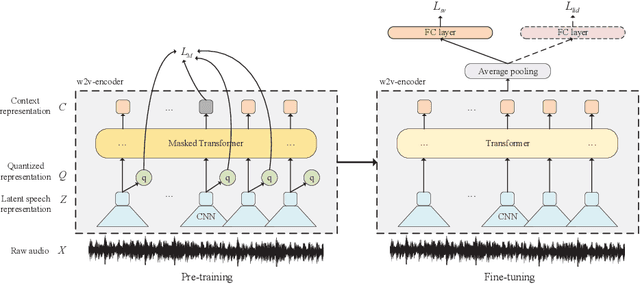
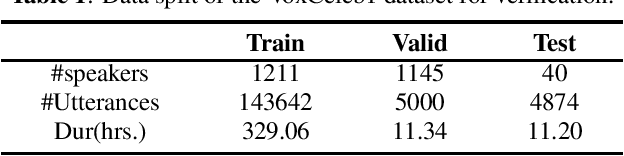

Abstract:Wav2vec 2.0 is a recently proposed self-supervised framework for speech representation learning. It follows a two-stage training process of pre-training and fine-tuning, and performs well in speech recognition tasks especially ultra-low resource cases. In this work, we attempt to extend self-supervised framework to speaker verification and language identification. First, we use some preliminary experiments to indicate that wav2vec 2.0 can capture the information about the speaker and language. Then we demonstrate the effectiveness of wav2vec 2.0 on the two tasks respectively. For speaker verification, we obtain a new state-of-the-art result, Equal Error Rate (EER) of 3.61% on the VoxCeleb1 dataset. For language identification, we obtain an EER of 12.02% on 1 second condition and an EER of 3.47% on full-length condition of the AP17-OLR dataset. Finally, we utilize one model to achieve the unified modeling by the multi-task learning for the two tasks.
Speaker-aware speech-transformer
Jan 02, 2020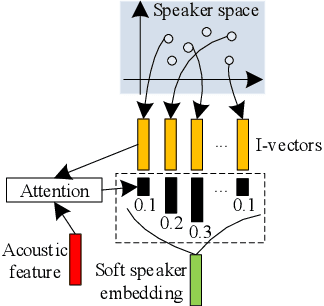
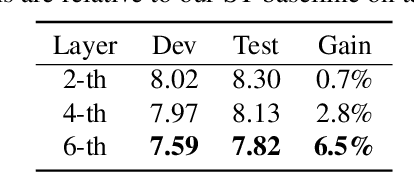
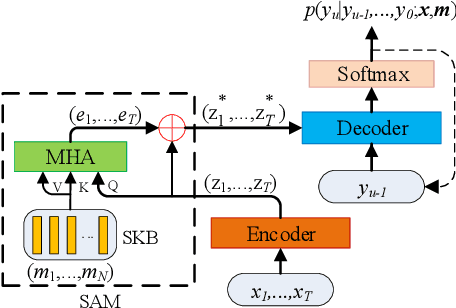
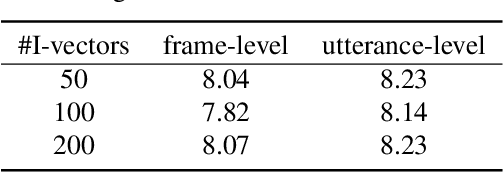
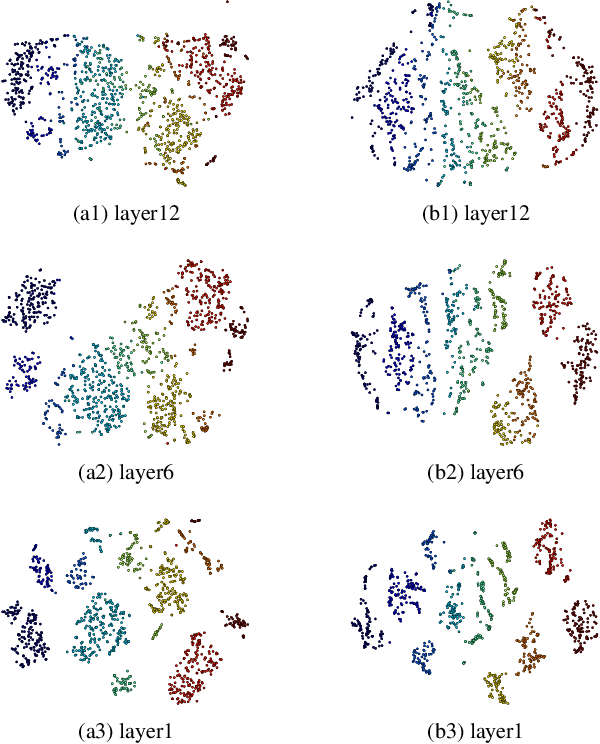
Abstract:Recently, end-to-end (E2E) models become a competitive alternative to the conventional hybrid automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. However, they still suffer from speaker mismatch in training and testing condition. In this paper, we use Speech-Transformer (ST) as the study platform to investigate speaker aware training of E2E models. We propose a model called Speaker-Aware Speech-Transformer (SAST), which is a standard ST equipped with a speaker attention module (SAM). The SAM has a static speaker knowledge block (SKB) that is made of i-vectors. At each time step, the encoder output attends to the i-vectors in the block, and generates a weighted combined speaker embedding vector, which helps the model to normalize the speaker variations. The SAST model trained in this way becomes independent of specific training speakers and thus generalizes better to unseen testing speakers. We investigate different factors of SAM. Experimental results on the AISHELL-1 task show that SAST achieves a relative 6.5% CER reduction (CERR) over the speaker-independent (SI) baseline. Moreover, we demonstrate that SAST still works quite well even if the i-vectors in SKB all come from a different data source other than the acoustic training set.
Unsupervised pre-traing for sequence to sequence speech recognition
Oct 28, 2019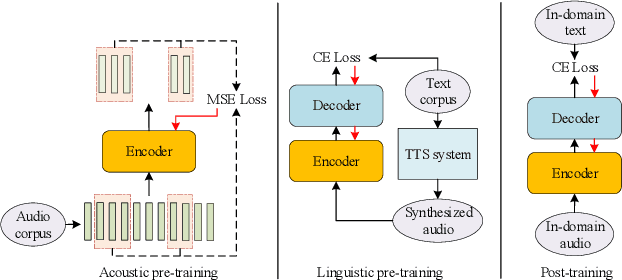

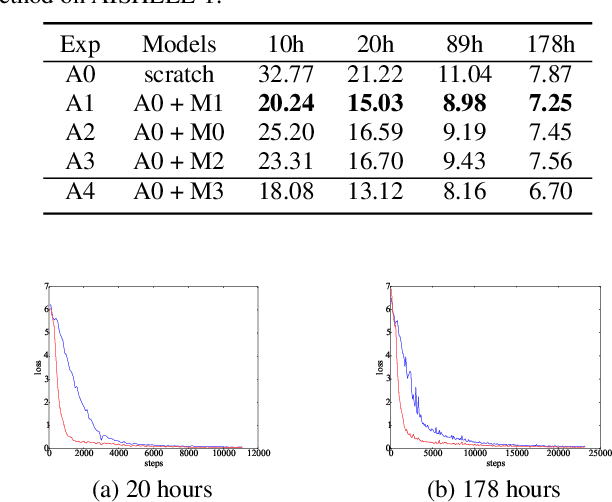
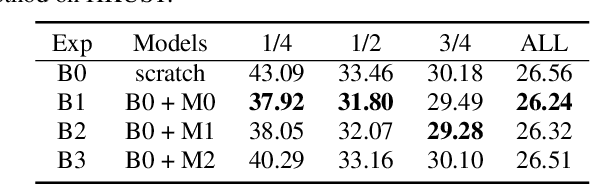
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel approach to pre-train encoder-decoder sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) model with unpaired speech and transcripts respectively. Our pre-training method is divided into two stages, named acoustic pre-trianing and linguistic pre-training. In the acoustic pre-training stage, we use a large amount of speech to pre-train the encoder by predicting masked speech feature chunks with its context. In the linguistic pre-training stage, we generate synthesized speech from a large number of transcripts using a single-speaker text to speech (TTS) system, and use the synthesized paired data to pre-train decoder. This two-stage pre-training method integrates rich acoustic and linguistic knowledge into seq2seq model, which will benefit downstream automatic speech recognition (ASR) tasks. The unsupervised pre-training is finished on AISHELL-2 dataset and we apply the pre-trained model to multiple paired data ratios of AISHELL-1 and HKUST. We obtain relative character error rate reduction (CERR) from 38.24% to 7.88% on AISHELL-1 and from 12.00% to 1.20% on HKUST. Besides, we apply our pretrained model to a cross-lingual case with CALLHOME dataset. For all six languages in CALLHOME dataset, our pre-training method makes model outperform baseline consistently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge