Zhiqiang Wan
iBARLE: imBalance-Aware Room Layout Estimation
Aug 29, 2023



Abstract:Room layout estimation predicts layouts from a single panorama. It requires datasets with large-scale and diverse room shapes to train the models. However, there are significant imbalances in real-world datasets including the dimensions of layout complexity, camera locations, and variation in scene appearance. These issues considerably influence the model training performance. In this work, we propose the imBalance-Aware Room Layout Estimation (iBARLE) framework to address these issues. iBARLE consists of (1) Appearance Variation Generation (AVG) module, which promotes visual appearance domain generalization, (2) Complex Structure Mix-up (CSMix) module, which enhances generalizability w.r.t. room structure, and (3) a gradient-based layout objective function, which allows more effective accounting for occlusions in complex layouts. All modules are jointly trained and help each other to achieve the best performance. Experiments and ablation studies based on ZInD~\cite{cruz2021zillow} dataset illustrate that iBARLE has state-of-the-art performance compared with other layout estimation baselines.
U2RLE: Uncertainty-Guided 2-Stage Room Layout Estimation
Apr 17, 2023



Abstract:While the existing deep learning-based room layout estimation techniques demonstrate good overall accuracy, they are less effective for distant floor-wall boundary. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel uncertainty-guided approach for layout boundary estimation introducing new two-stage CNN architecture termed U2RLE. The initial stage predicts both floor-wall boundary and its uncertainty and is followed by the refinement of boundaries with high positional uncertainty using a different, distance-aware loss. Finally, outputs from the two stages are merged to produce the room layout. Experiments using ZInD and Structure3D datasets show that U2RLE improves over current state-of-the-art, being able to handle both near and far walls better. In particular, U2RLE outperforms current state-of-the-art techniques for the most distant walls.
PSMNet: Position-aware Stereo Merging Network for Room Layout Estimation
Mar 30, 2022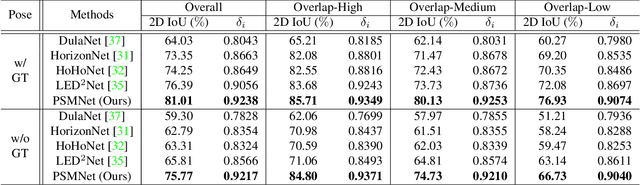
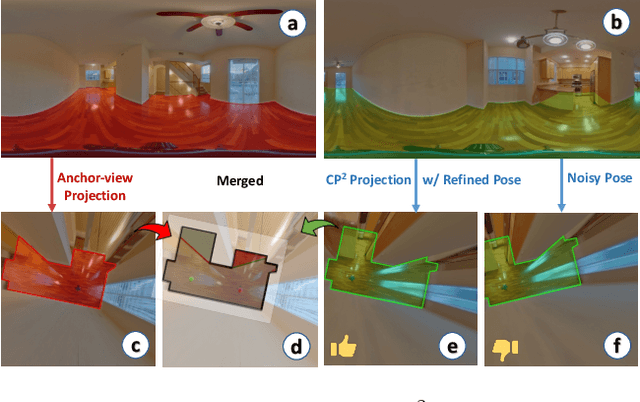
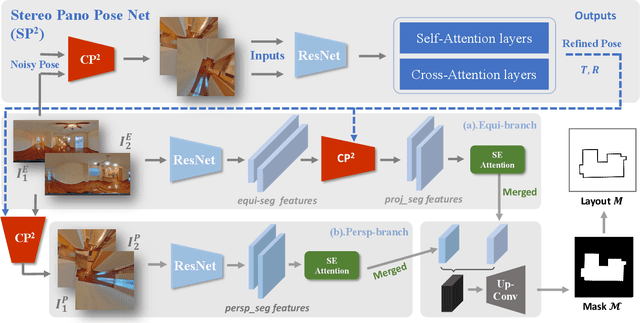
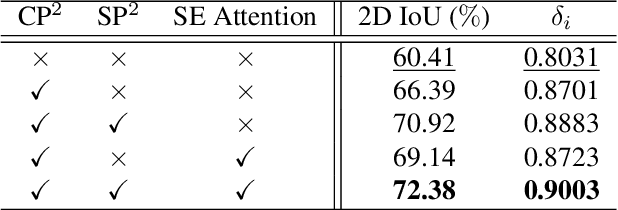

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new deep learning-based method for estimating room layout given a pair of 360 panoramas. Our system, called Position-aware Stereo Merging Network or PSMNet, is an end-to-end joint layout-pose estimator. PSMNet consists of a Stereo Pano Pose (SP2) transformer and a novel Cross-Perspective Projection (CP2) layer. The stereo-view SP2 transformer is used to implicitly infer correspondences between views, and can handle noisy poses. The pose-aware CP2 layer is designed to render features from the adjacent view to the anchor (reference) view, in order to perform view fusion and estimate the visible layout. Our experiments and analysis validate our method, which significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art layout estimators, especially for large and complex room spaces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge