Zhenqin Wu
MoleculeNet: A Benchmark for Molecular Machine Learning
Oct 26, 2018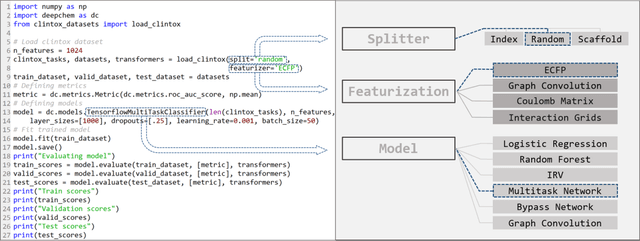
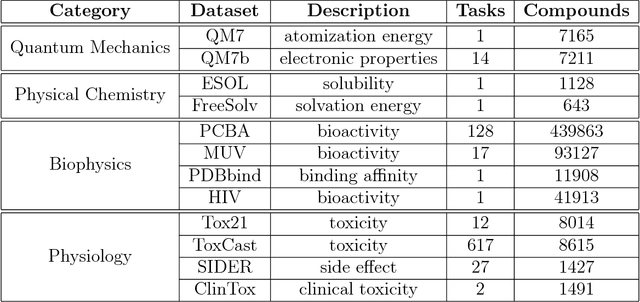
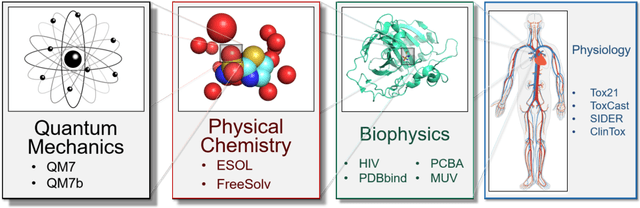
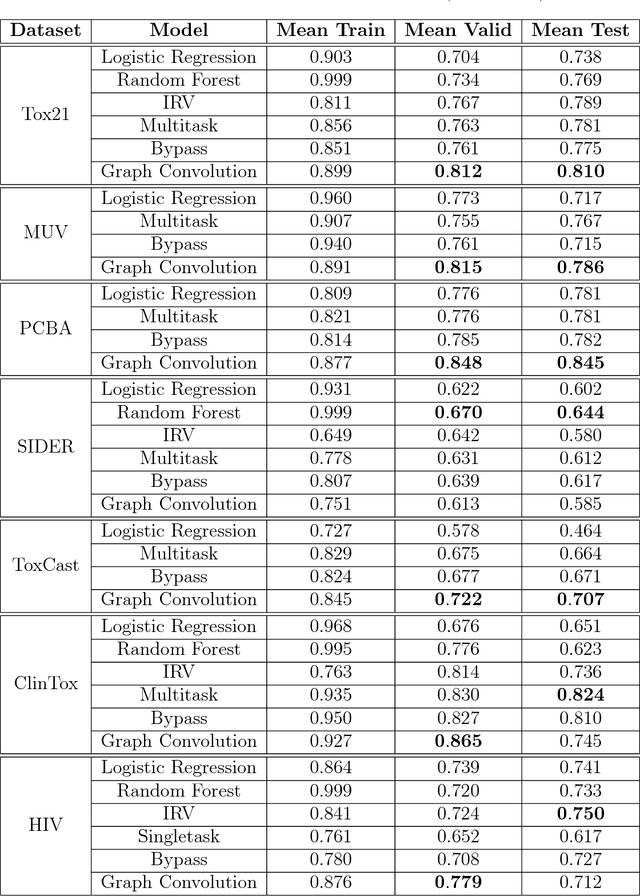
Abstract:Molecular machine learning has been maturing rapidly over the last few years. Improved methods and the presence of larger datasets have enabled machine learning algorithms to make increasingly accurate predictions about molecular properties. However, algorithmic progress has been limited due to the lack of a standard benchmark to compare the efficacy of proposed methods; most new algorithms are benchmarked on different datasets making it challenging to gauge the quality of proposed methods. This work introduces MoleculeNet, a large scale benchmark for molecular machine learning. MoleculeNet curates multiple public datasets, establishes metrics for evaluation, and offers high quality open-source implementations of multiple previously proposed molecular featurization and learning algorithms (released as part of the DeepChem open source library). MoleculeNet benchmarks demonstrate that learnable representations are powerful tools for molecular machine learning and broadly offer the best performance. However, this result comes with caveats. Learnable representations still struggle to deal with complex tasks under data scarcity and highly imbalanced classification. For quantum mechanical and biophysical datasets, the use of physics-aware featurizations can be more important than choice of particular learning algorithm.
PotentialNet for Molecular Property Prediction
Oct 22, 2018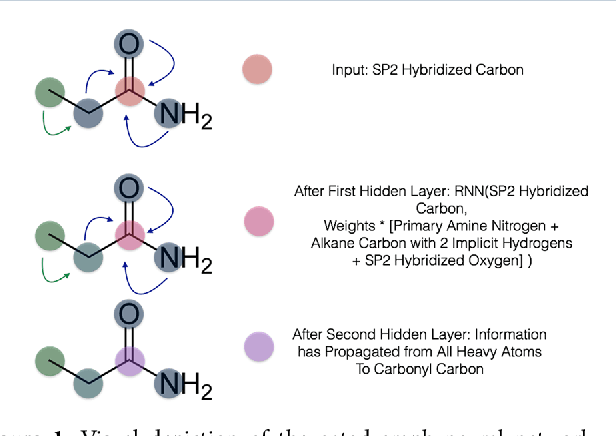
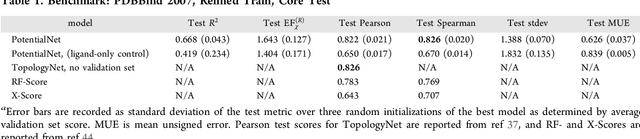
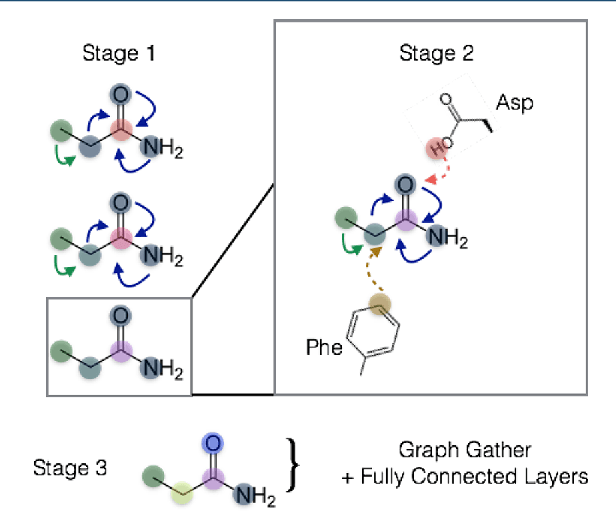
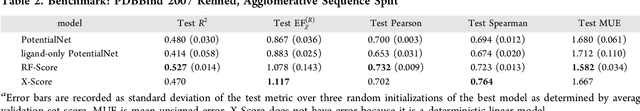
Abstract:The arc of drug discovery entails a multiparameter optimization problem spanning vast length scales. They key parameters range from solubility (angstroms) to protein-ligand binding (nanometers) to in vivo toxicity (meters). Through feature learning---instead of feature engineering---deep neural networks promise to outperform both traditional physics-based and knowledge-based machine learning models for predicting molecular properties pertinent to drug discovery. To this end, we present the PotentialNet family of graph convolutions. These models are specifically designed for and achieve state-of-the-art performance for protein-ligand binding affinity. We further validate these deep neural networks by setting new standards of performance in several ligand-based tasks. In parallel, we introduce a new metric, the Regression Enrichment Factor $EF_\chi^{(R)}$, to measure the early enrichment of computational models for chemical data. Finally, we introduce a cross-validation strategy based on structural homology clustering that can more accurately measure model generalizability, which crucially distinguishes the aims of machine learning for drug discovery from standard machine learning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge