Zhengyu Diao
EmoTalk3D: High-Fidelity Free-View Synthesis of Emotional 3D Talking Head
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:We present a novel approach for synthesizing 3D talking heads with controllable emotion, featuring enhanced lip synchronization and rendering quality. Despite significant progress in the field, prior methods still suffer from multi-view consistency and a lack of emotional expressiveness. To address these issues, we collect EmoTalk3D dataset with calibrated multi-view videos, emotional annotations, and per-frame 3D geometry. By training on the EmoTalk3D dataset, we propose a \textit{`Speech-to-Geometry-to-Appearance'} mapping framework that first predicts faithful 3D geometry sequence from the audio features, then the appearance of a 3D talking head represented by 4D Gaussians is synthesized from the predicted geometry. The appearance is further disentangled into canonical and dynamic Gaussians, learned from multi-view videos, and fused to render free-view talking head animation. Moreover, our model enables controllable emotion in the generated talking heads and can be rendered in wide-range views. Our method exhibits improved rendering quality and stability in lip motion generation while capturing dynamic facial details such as wrinkles and subtle expressions. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in generating high-fidelity and emotion-controllable 3D talking heads. The code and EmoTalk3D dataset are released at https://nju-3dv.github.io/projects/EmoTalk3D.
Detailed Facial Geometry Recovery from Multi-view Images by Learning an Implicit Function
Jan 04, 2022
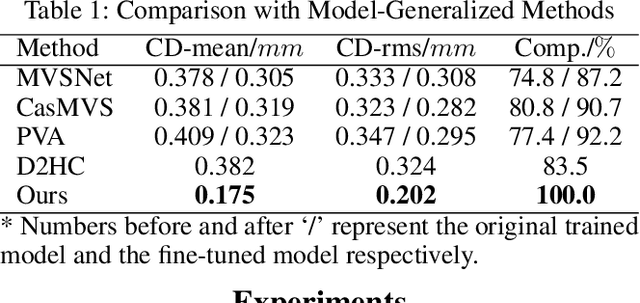

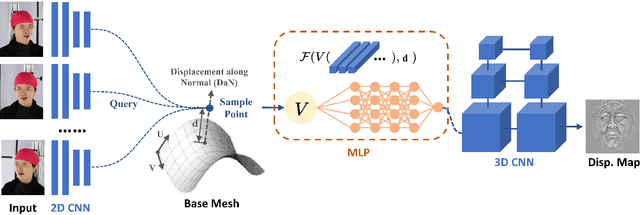
Abstract:Recovering detailed facial geometry from a set of calibrated multi-view images is valuable for its wide range of applications. Traditional multi-view stereo (MVS) methods adopt optimization methods to regularize the matching cost. Recently, learning-based methods integrate all these into an end-to-end neural network and show superiority of efficiency. In this paper, we propose a novel architecture to recover extremely detailed 3D faces in roughly 10 seconds. Unlike previous learning-based methods that regularize the cost volume via 3D CNN, we propose to learn an implicit function for regressing the matching cost. By fitting a 3D morphable model from multi-view images, the features of multiple images are extracted and aggregated in the mesh-attached UV space, which makes the implicit function more effective in recovering detailed facial shape. Our method outperforms SOTA learning-based MVS in accuracy by a large margin on the FaceScape dataset. The code and data will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge