Zhengjie Zhu
Towards A Generalizable Pathology Foundation Model via Unified Knowledge Distillation
Jul 26, 2024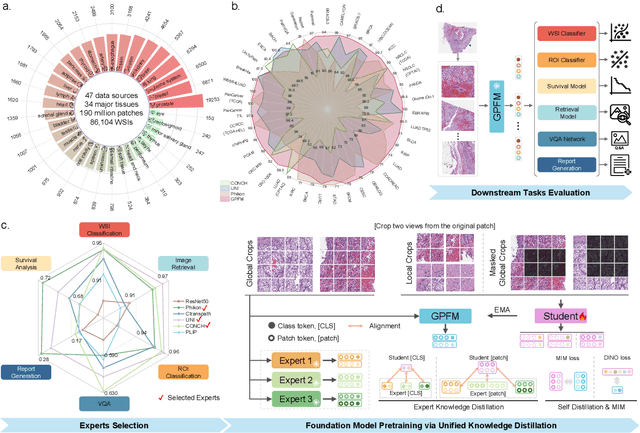

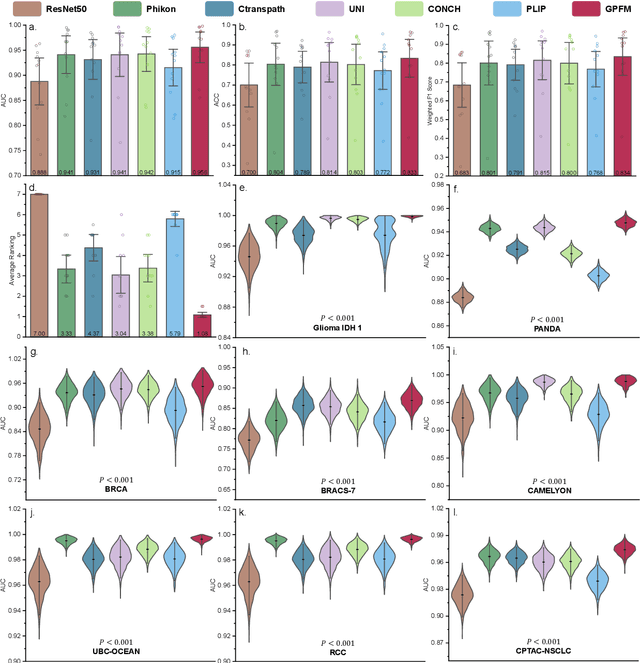
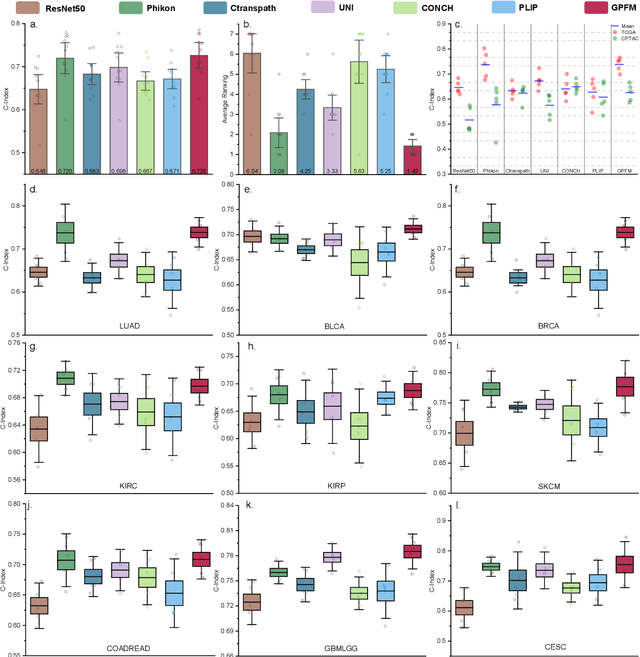
Abstract:Foundation models pretrained on large-scale datasets are revolutionizing the field of computational pathology (CPath). The generalization ability of foundation models is crucial for the success in various downstream clinical tasks. However, current foundation models have only been evaluated on a limited type and number of tasks, leaving their generalization ability and overall performance unclear. To address this gap, we established a most comprehensive benchmark to evaluate the performance of off-the-shelf foundation models across six distinct clinical task types, encompassing a total of 39 specific tasks. Our findings reveal that existing foundation models excel at certain task types but struggle to effectively handle the full breadth of clinical tasks. To improve the generalization of pathology foundation models, we propose a unified knowledge distillation framework consisting of both expert and self knowledge distillation, where the former allows the model to learn from the knowledge of multiple expert models, while the latter leverages self-distillation to enable image representation learning via local-global alignment. Based on this framework, a Generalizable Pathology Foundation Model (GPFM) is pretrained on a large-scale dataset consisting of 190 million images from around 86,000 public H\&E whole slides across 34 major tissue types. Evaluated on the established benchmark, GPFM achieves an impressive average rank of 1.36, with 29 tasks ranked 1st, while the the second-best model, UNI, attains an average rank of 2.96, with only 4 tasks ranked 1st. The superior generalization of GPFM demonstrates its exceptional modeling capabilities across a wide range of clinical tasks, positioning it as a new cornerstone for feature representation in CPath.
Prompt-Guided Adaptive Model Transformation for Whole Slide Image Classification
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) has emerged as a popular method for classifying histopathology whole slide images (WSIs). Existing approaches typically rely on frozen pre-trained models to extract instance features, neglecting the substantial domain shift between pre-training natural and histopathological images. To address this issue, we propose PAMT, a novel Prompt-guided Adaptive Model Transformation framework that enhances MIL classification performance by seamlessly adapting pre-trained models to the specific characteristics of histopathology data. To capture the intricate histopathology distribution, we introduce Representative Patch Sampling (RPS) and Prototypical Visual Prompt (PVP) to reform the input data, building a compact while informative representation. Furthermore, to narrow the domain gap, we introduce Adaptive Model Transformation (AMT) that integrates adapter blocks within the feature extraction pipeline, enabling the pre-trained models to learn domain-specific features. We rigorously evaluate our approach on two publicly available datasets, Camelyon16 and TCGA-NSCLC, showcasing substantial improvements across various MIL models. Our findings affirm the potential of PAMT to set a new benchmark in WSI classification, underscoring the value of a targeted reprogramming approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge