Zhendong Yu
Precision Neural Network Quantization via Learnable Adaptive Modules
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Quantization Aware Training (QAT) is a neural network quantization technique that compresses model size and improves operational efficiency while effectively maintaining model performance. The paradigm of QAT is to introduce fake quantization operators during the training process, allowing the model to autonomously compensate for information loss caused by quantization. Making quantization parameters trainable can significantly improve the performance of QAT, but at the cost of compromising the flexibility during inference, especially when dealing with activation values with substantially different distributions. In this paper, we propose an effective learnable adaptive neural network quantization method, called Adaptive Step Size Quantization (ASQ), to resolve this conflict. Specifically, the proposed ASQ method first dynamically adjusts quantization scaling factors through a trained module capable of accommodating different activations. Then, to address the rigid resolution issue inherent in Power of Two (POT) quantization, we propose an efficient non-uniform quantization scheme. We utilize the Power Of Square root of Two (POST) as the basis for exponential quantization, effectively handling the bell-shaped distribution of neural network weights across various bit-widths while maintaining computational efficiency through a Look-Up Table method (LUT). Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed ASQ method is superior to the state-of-the-art QAT approaches. Notably that the ASQ is even competitive compared to full precision baselines, with its 4-bit quantized ResNet34 model improving accuracy by 1.2\% on ImageNet.
Nonequilbrium physics of generative diffusion models
May 20, 2024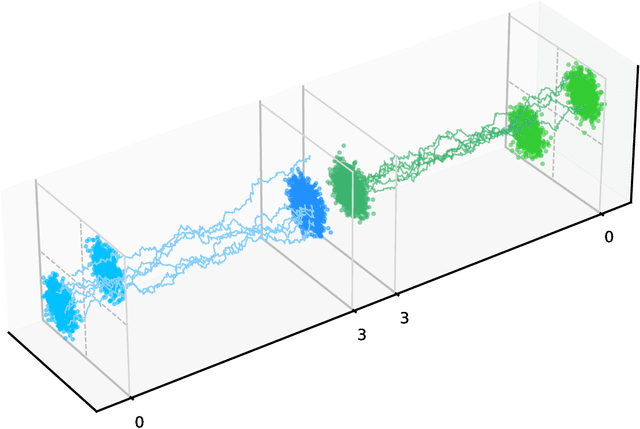
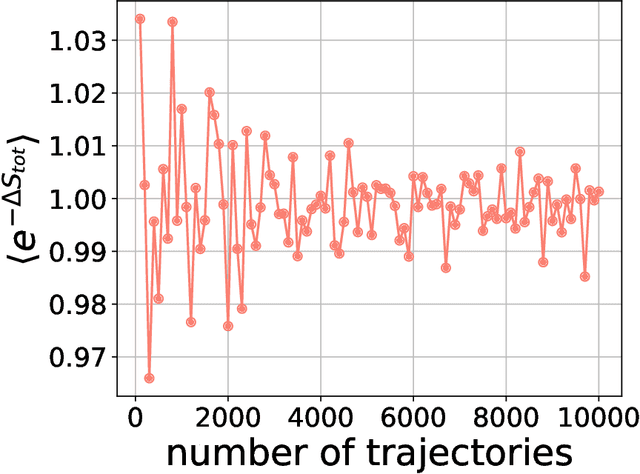
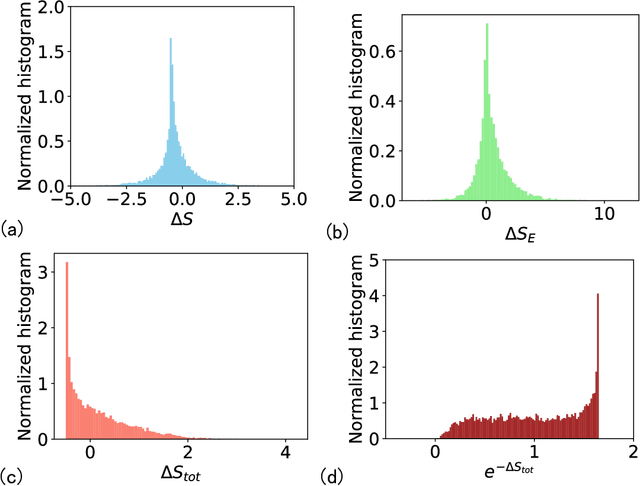
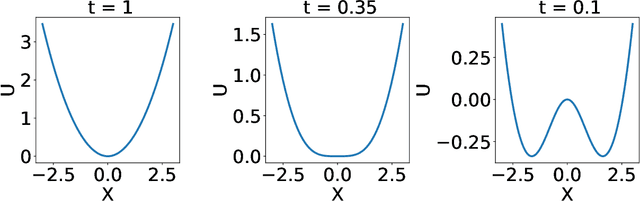
Abstract:Generative diffusion models apply the concept of Langevin dynamics in physics to machine leaning, attracting a lot of interest from industrial application, but a complete picture about inherent mechanisms is still lacking. In this paper, we provide a transparent physics analysis of the diffusion models, deriving the fluctuation theorem, entropy production, Franz-Parisi potential to understand the intrinsic phase transitions discovered recently. Our analysis is rooted in non-equlibrium physics and concepts from equilibrium physics, i.e., treating both forward and backward dynamics as a Langevin dynamics, and treating the reverse diffusion generative process as a statistical inference, where the time-dependent state variables serve as quenched disorder studied in spin glass theory. This unified principle is expected to guide machine learning practitioners to design better algorithms and theoretical physicists to link the machine learning to non-equilibrium thermodynamics.
Adversarial Code Learning for Image Generation
Jan 30, 2020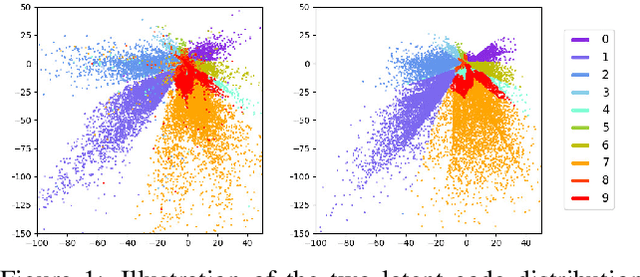
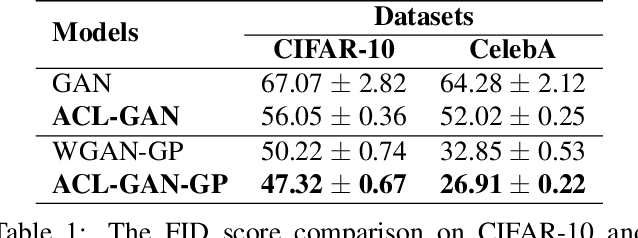
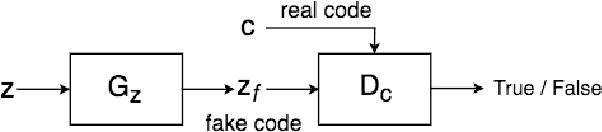
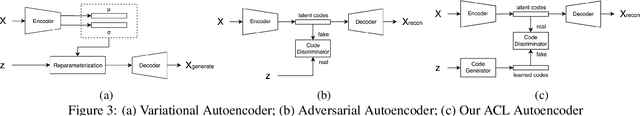
Abstract:We introduce the "adversarial code learning" (ACL) module that improves overall image generation performance to several types of deep models. Instead of performing a posterior distribution modeling in the pixel spaces of generators, ACLs aim to jointly learn a latent code with another image encoder/inference net, with a prior noise as its input. We conduct the learning in an adversarial learning process, which bears a close resemblance to the original GAN but again shifts the learning from image spaces to prior and latent code spaces. ACL is a portable module that brings up much more flexibility and possibilities in generative model designs. First, it allows flexibility to convert non-generative models like Autoencoders and standard classification models to decent generative models. Second, it enhances existing GANs' performance by generating meaningful codes and images from any part of the prior. We have incorporated our ACL module with the aforementioned frameworks and have performed experiments on synthetic, MNIST, CIFAR-10, and CelebA datasets. Our models have achieved significant improvements which demonstrated the generality for image generation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge