Yunkui Pang
SinoSynth: A Physics-based Domain Randomization Approach for Generalizable CBCT Image Enhancement
Sep 27, 2024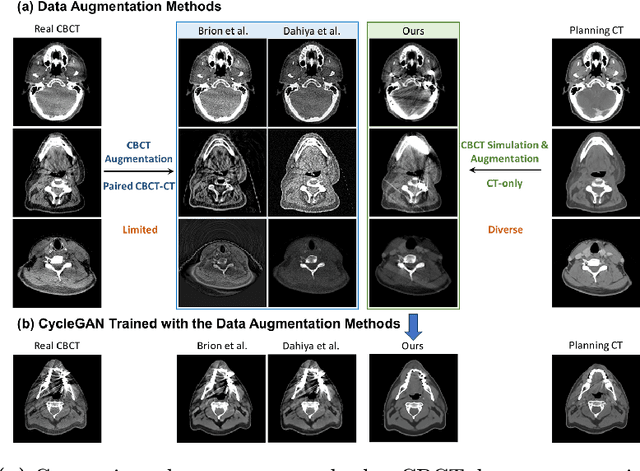
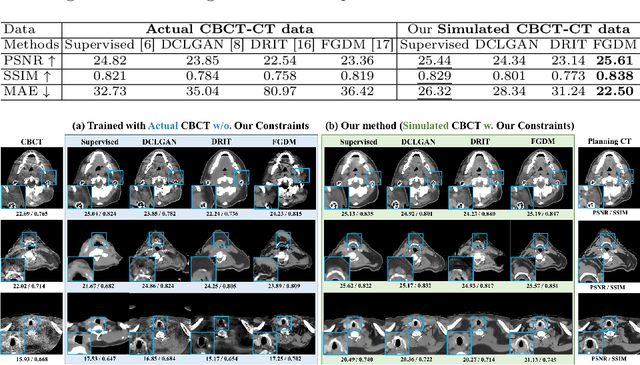
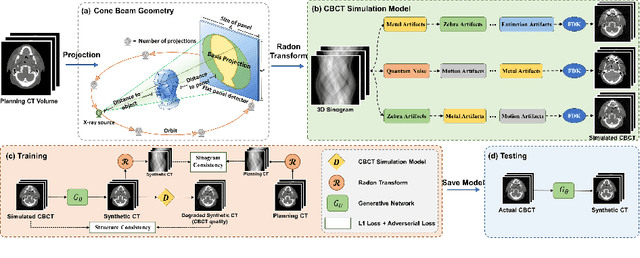
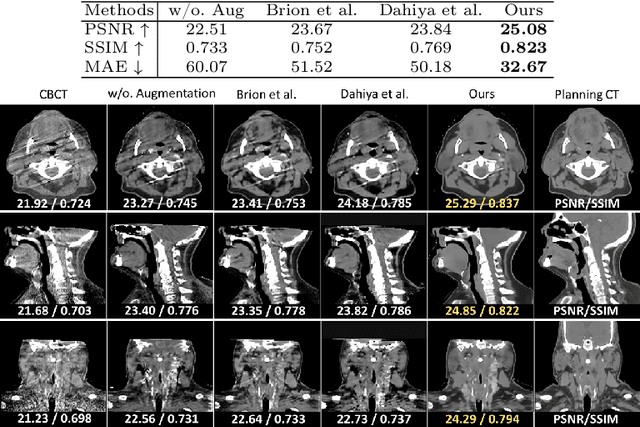
Abstract:Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) finds diverse applications in medicine. Ensuring high image quality in CBCT scans is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment delivery. Yet, the susceptibility of CBCT images to noise and artifacts undermines both their usefulness and reliability. Existing methods typically address CBCT artifacts through image-to-image translation approaches. These methods, however, are limited by the artifact types present in the training data, which may not cover the complete spectrum of CBCT degradations stemming from variations in imaging protocols. Gathering additional data to encompass all possible scenarios can often pose a challenge. To address this, we present SinoSynth, a physics-based degradation model that simulates various CBCT-specific artifacts to generate a diverse set of synthetic CBCT images from high-quality CT images without requiring pre-aligned data. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that several different generative networks trained on our synthesized data achieve remarkable results on heterogeneous multi-institutional datasets, outperforming even the same networks trained on actual data. We further show that our degradation model conveniently provides an avenue to enforce anatomical constraints in conditional generative models, yielding high-quality and structure-preserving synthetic CT images.
Towards Architecture-Insensitive Untrained Network Priors for Accelerated MRI Reconstruction
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:Untrained neural networks pioneered by Deep Image Prior (DIP) have recently enabled MRI reconstruction without requiring fully-sampled measurements for training. Their success is widely attributed to the implicit regularization induced by suitable network architectures. However, the lack of understanding of such architectural priors results in superfluous design choices and sub-optimal outcomes. This work aims to simplify the architectural design decisions for DIP-MRI to facilitate its practical deployment. We observe that certain architectural components are more prone to causing overfitting regardless of the number of parameters, incurring severe reconstruction artifacts by hindering accurate extrapolation on the un-acquired measurements. We interpret this phenomenon from a frequency perspective and find that the architectural characteristics favoring low frequencies, i.e., deep and narrow with unlearnt upsampling, can lead to enhanced generalization and hence better reconstruction. Building on this insight, we propose two architecture-agnostic remedies: one to constrain the frequency range of the white-noise input and the other to penalize the Lipschitz constants of the network. We demonstrate that even with just one extra line of code on the input, the performance gap between the ill-designed models and the high-performing ones can be closed. These results signify that for the first time, architectural biases on untrained MRI reconstruction can be mitigated without architectural modifications.
The Devil is in the Upsampling: Architectural Decisions Made Simpler for Denoising with Deep Image Prior
Apr 22, 2023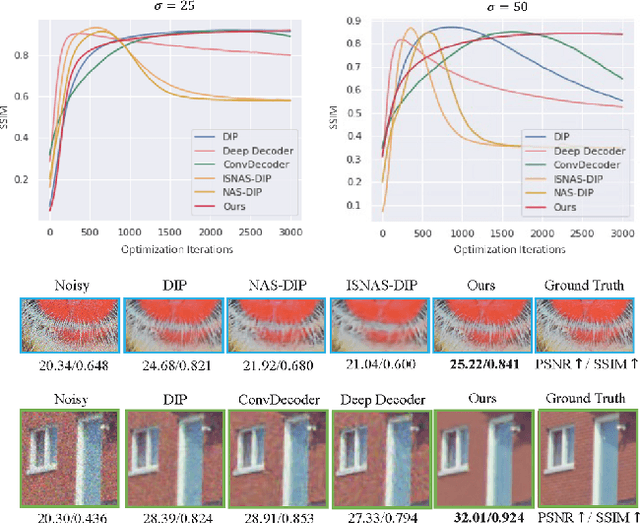
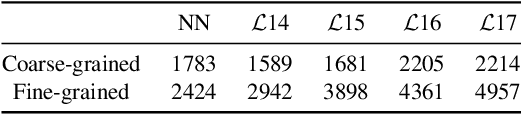
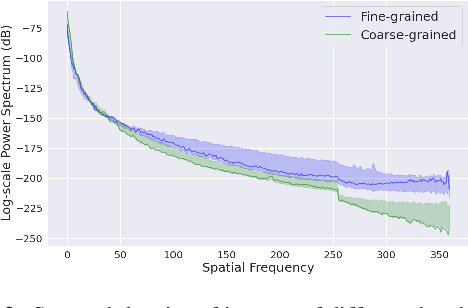
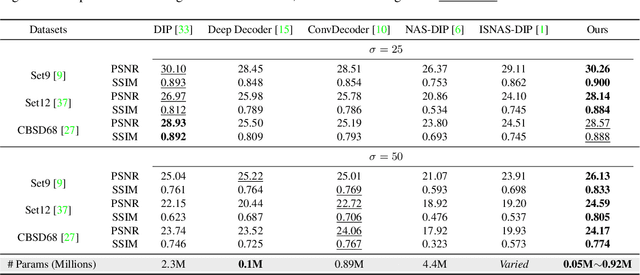
Abstract:Deep Image Prior (DIP) shows that some network architectures naturally bias towards smooth images and resist noises, a phenomenon known as spectral bias. Image denoising is an immediate application of this property. Although DIP has removed the requirement of large training sets, it still presents two practical challenges for denoising: architectural design and noise-fitting, which are often intertwined. Existing methods mostly handcraft or search for the architecture from a large design space, due to the lack of understanding on how the architectural choice corresponds to the image. In this study, we analyze from a frequency perspective to demonstrate that the unlearnt upsampling is the main driving force behind the denoising phenomenon in DIP. This finding then leads to strategies for estimating a suitable architecture for every image without a laborious search. Extensive experiments show that the estimated architectures denoise and preserve the textural details better than current methods with up to 95% fewer parameters. The under-parameterized nature also makes them especially robust to a higher level of noise.
Encouraging Disentangled and Convex Representation with Controllable Interpolation Regularization
Dec 06, 2021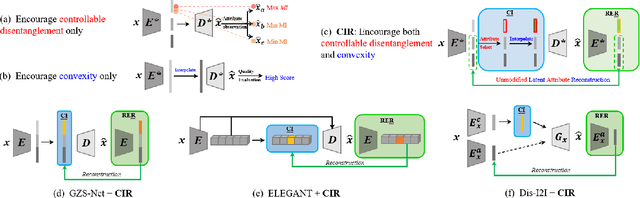
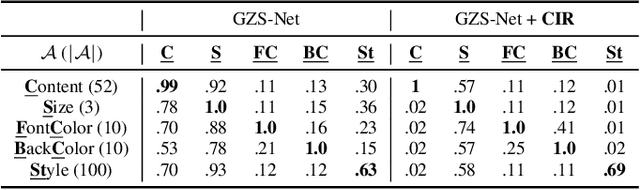
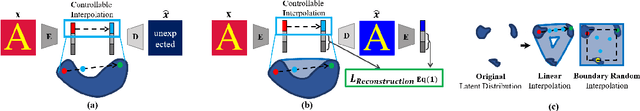
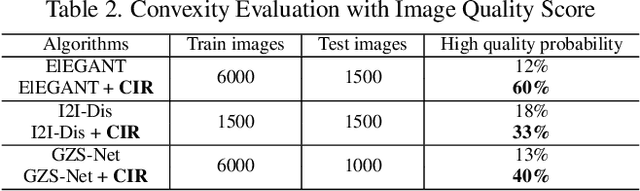
Abstract:We focus on controllable disentangled representation learning (C-Dis-RL), where users can control the partition of the disentangled latent space to factorize dataset attributes (concepts) for downstream tasks. Two general problems remain under-explored in current methods: (1) They lack comprehensive disentanglement constraints, especially missing the minimization of mutual information between different attributes across latent and observation domains. (2) They lack convexity constraints in disentangled latent space, which is important for meaningfully manipulating specific attributes for downstream tasks. To encourage both comprehensive C-Dis-RL and convexity simultaneously, we propose a simple yet efficient method: Controllable Interpolation Regularization (CIR), which creates a positive loop where the disentanglement and convexity can help each other. Specifically, we conduct controlled interpolation in latent space during training and 'reuse' the encoder to help form a 'perfect disentanglement' regularization. In that case, (a) disentanglement loss implicitly enlarges the potential 'understandable' distribution to encourage convexity; (b) convexity can in turn improve robust and precise disentanglement. CIR is a general module and we merge CIR with three different algorithms: ELEGANT, I2I-Dis, and GZS-Net to show the compatibility and effectiveness. Qualitative and quantitative experiments show improvement in C-Dis-RL and latent convexity by CIR. This further improves downstream tasks: controllable image synthesis, cross-modality image translation and zero-shot synthesis. More experiments demonstrate CIR can also improve other downstream tasks, such as new attribute value mining, data augmentation, and eliminating bias for fairness.
Sketch-Inspector: a Deep Mixture Model for High-Quality Sketch Generation of Cats
Nov 09, 2020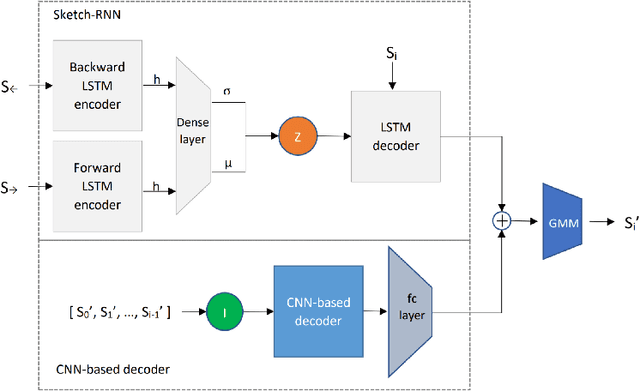
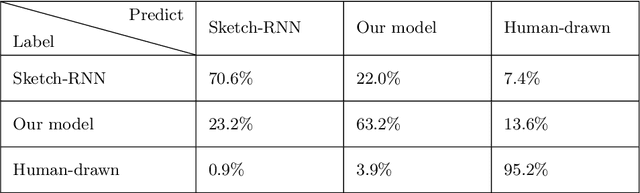
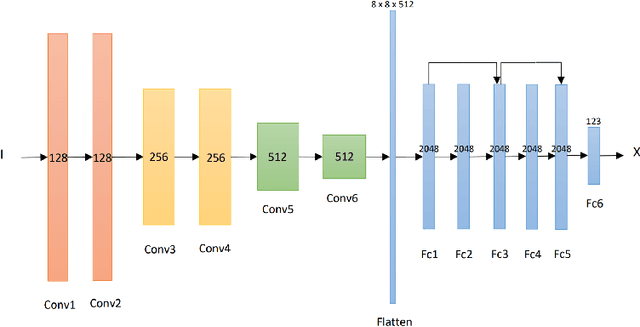
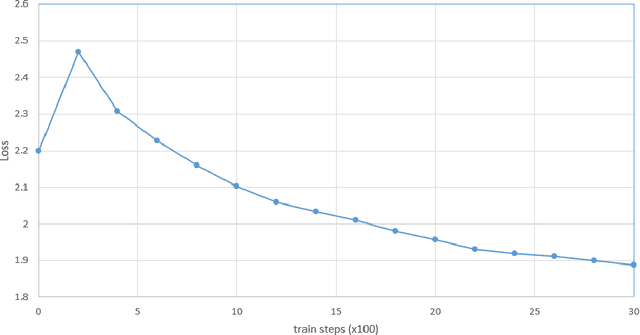
Abstract:With the involvement of artificial intelligence (AI), sketches can be automatically generated under certain topics. Even though breakthroughs have been made in previous studies in this area, a relatively high proportion of the generated figures are too abstract to recognize, which illustrates that AIs fail to learn the general pattern of the target object when drawing. This paper posits that supervising the process of stroke generation can lead to a more accurate sketch interpretation. Based on that, a sketch generating system with an assistant convolutional neural network (CNN) predictor to suggest the shape of the next stroke is presented in this paper. In addition, a CNN-based discriminator is introduced to judge the recognizability of the end product. Since the base-line model is ineffective at generating multi-class sketches, we restrict the model to produce one category. Because the image of a cat is easy to identify, we consider cat sketches selected from the QuickDraw data set. This paper compares the proposed model with the original Sketch-RNN on 75K human-drawn cat sketches. The result indicates that our model produces sketches with higher quality than human's sketches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge