Yulia Gryaditskaya
SpaceTimePilot: Generative Rendering of Dynamic Scenes Across Space and Time
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:We present SpaceTimePilot, a video diffusion model that disentangles space and time for controllable generative rendering. Given a monocular video, SpaceTimePilot can independently alter the camera viewpoint and the motion sequence within the generative process, re-rendering the scene for continuous and arbitrary exploration across space and time. To achieve this, we introduce an effective animation time-embedding mechanism in the diffusion process, allowing explicit control of the output video's motion sequence with respect to that of the source video. As no datasets provide paired videos of the same dynamic scene with continuous temporal variations, we propose a simple yet effective temporal-warping training scheme that repurposes existing multi-view datasets to mimic temporal differences. This strategy effectively supervises the model to learn temporal control and achieve robust space-time disentanglement. To further enhance the precision of dual control, we introduce two additional components: an improved camera-conditioning mechanism that allows altering the camera from the first frame, and CamxTime, the first synthetic space-and-time full-coverage rendering dataset that provides fully free space-time video trajectories within a scene. Joint training on the temporal-warping scheme and the CamxTime dataset yields more precise temporal control. We evaluate SpaceTimePilot on both real-world and synthetic data, demonstrating clear space-time disentanglement and strong results compared to prior work. Project page: https://zheninghuang.github.io/Space-Time-Pilot/ Code: https://github.com/ZheningHuang/spacetimepilot
GroundUp: Rapid Sketch-Based 3D City Massing
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:We propose GroundUp, the first sketch-based ideation tool for 3D city massing of urban areas. We focus on early-stage urban design, where sketching is a common tool and the design starts from balancing building volumes (masses) and open spaces. With Human-Centered AI in mind, we aim to help architects quickly revise their ideas by easily switching between 2D sketches and 3D models, allowing for smoother iteration and sharing of ideas. Inspired by feedback from architects and existing workflows, our system takes as a first input a user sketch of multiple buildings in a top-down view. The user then draws a perspective sketch of the envisioned site. Our method is designed to exploit the complementarity of information in the two sketches and allows users to quickly preview and adjust the inferred 3D shapes. Our model has two main components. First, we propose a novel sketch-to-depth prediction network for perspective sketches that exploits top-down sketch shapes. Second, we use depth cues derived from the perspective sketch as a condition to our diffusion model, which ultimately completes the geometry in a top-down view. Thus, our final 3D geometry is represented as a heightfield, allowing users to construct the city `from the ground up'.
Open Vocabulary Semantic Scene Sketch Understanding
Dec 18, 2023



Abstract:We study the underexplored but fundamental vision problem of machine understanding of abstract freehand scene sketches. We introduce a sketch encoder that results in semantically-aware feature space, which we evaluate by testing its performance on a semantic sketch segmentation task. To train our model we rely only on the availability of bitmap sketches with their brief captions and do not require any pixel-level annotations. To obtain generalization to a large set of sketches and categories, we build on a vision transformer encoder pretrained with the CLIP model. We freeze the text encoder and perform visual-prompt tuning of the visual encoder branch while introducing a set of critical modifications. Firstly, we augment the classical key-query (k-q) self-attention blocks with value-value (v-v) self-attention blocks. Central to our model is a two-level hierarchical network design that enables efficient semantic disentanglement: The first level ensures holistic scene sketch encoding, and the second level focuses on individual categories. We, then, in the second level of the hierarchy, introduce a cross-attention between textual and visual branches. Our method outperforms zero-shot CLIP pixel accuracy of segmentation results by 37 points, reaching an accuracy of $85.5\%$ on the FS-COCO sketch dataset. Finally, we conduct a user study that allows us to identify further improvements needed over our method to reconcile machine and human understanding of scene sketches.
3D VR Sketch Guided 3D Shape Prototyping and Exploration
Jun 23, 2023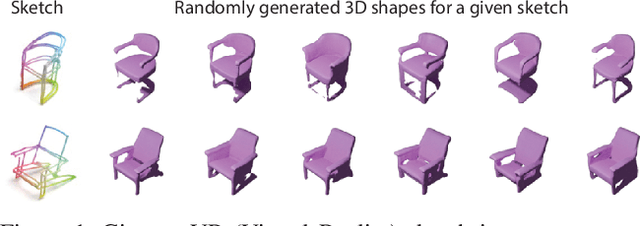
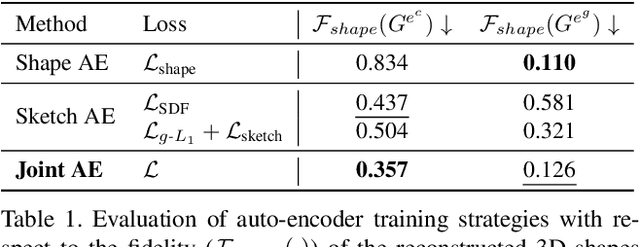
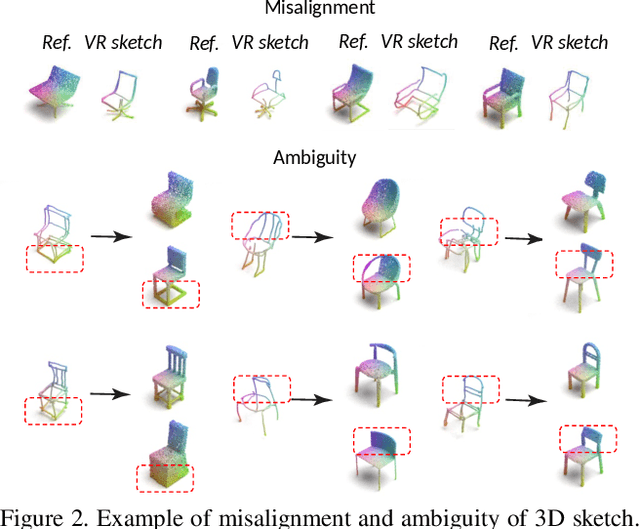
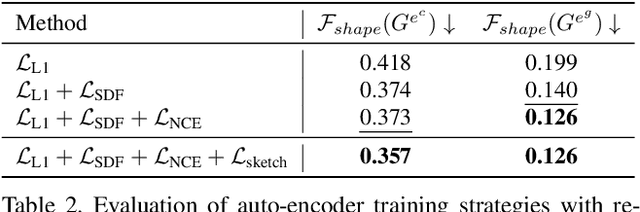
Abstract:3D shape modeling is labor-intensive and time-consuming and requires years of expertise. Recently, 2D sketches and text inputs were considered as conditional modalities to 3D shape generation networks to facilitate 3D shape modeling. However, text does not contain enough fine-grained information and is more suitable to describe a category or appearance rather than geometry, while 2D sketches are ambiguous, and depicting complex 3D shapes in 2D again requires extensive practice. Instead, we explore virtual reality sketches that are drawn directly in 3D. We assume that the sketches are created by novices, without any art training, and aim to reconstruct physically-plausible 3D shapes. Since such sketches are potentially ambiguous, we tackle the problem of the generation of multiple 3D shapes that follow the input sketch structure. Limited in the size of the training data, we carefully design our method, training the model step-by-step and leveraging multi-modal 3D shape representation. To guarantee the plausibility of generated 3D shapes we leverage the normalizing flow that models the distribution of the latent space of 3D shapes. To encourage the fidelity of the generated 3D models to an input sketch, we propose a dedicated loss that we deploy at different stages of the training process. We plan to make our code publicly available.
Zero-Shot 3D Shape Sketch View Similarity and Retrieval
Jun 14, 2023Abstract:We conduct a detailed study of the ability of pretrained on pretext tasks ViT and ResNet feature layers to quantify the similarity between pairs of 2D sketch views of individual 3D shapes. We assess the performance in terms of the models' abilities to retrieve similar views and ground-truth 3D shapes. Going beyond naive zero-shot performance study, we investigate alternative fine-tuning strategies on one or several shape classes, and their generalization to other shape classes. Leveraging progress in NPR (Non-Photo Realistic) rendering, we generate synthetic sketch views in several styles which we use to fine-tune pretrained foundation models using contrastive learning. We study how the scale of an object in a sketch affects the similarity of features at different network layers. We observe that depending on the scale, different feature layers can be more indicative of shape similarities in sketch views. However, we find that similar object scales result in the best performance of ViT and ResNet. In summary, we show that careful selection of a fine-tuning strategy allows us to obtain consistent improvement in zero-shot shape retrieval accuracy. We believe that our work will have a significant impact on research in the sketch domain, providing insights and guidance on how to adopt large pretrained models as perceptual losses.
SketchXAI: A First Look at Explainability for Human Sketches
Apr 23, 2023Abstract:This paper, for the very first time, introduces human sketches to the landscape of XAI (Explainable Artificial Intelligence). We argue that sketch as a ``human-centred'' data form, represents a natural interface to study explainability. We focus on cultivating sketch-specific explainability designs. This starts by identifying strokes as a unique building block that offers a degree of flexibility in object construction and manipulation impossible in photos. Following this, we design a simple explainability-friendly sketch encoder that accommodates the intrinsic properties of strokes: shape, location, and order. We then move on to define the first ever XAI task for sketch, that of stroke location inversion SLI. Just as we have heat maps for photos, and correlation matrices for text, SLI offers an explainability angle to sketch in terms of asking a network how well it can recover stroke locations of an unseen sketch. We offer qualitative results for readers to interpret as snapshots of the SLI process in the paper, and as GIFs on the project page. A minor but interesting note is that thanks to its sketch-specific design, our sketch encoder also yields the best sketch recognition accuracy to date while having the smallest number of parameters. The code is available at \url{https://sketchxai.github.io}.
Towards 3D VR-Sketch to 3D Shape Retrieval
Sep 20, 2022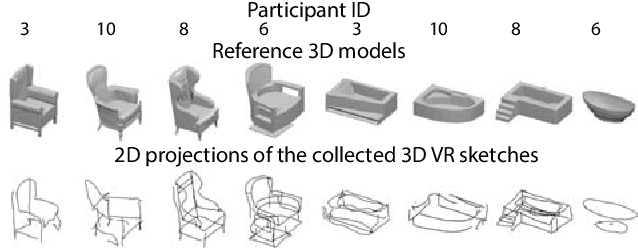
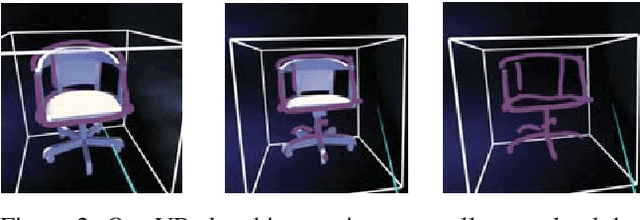
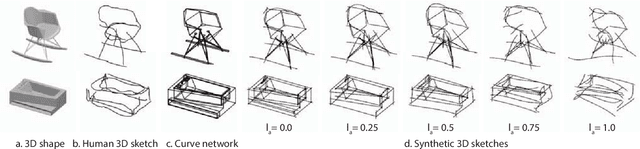
Abstract:Growing free online 3D shapes collections dictated research on 3D retrieval. Active debate has however been had on (i) what the best input modality is to trigger retrieval, and (ii) the ultimate usage scenario for such retrieval. In this paper, we offer a different perspective towards answering these questions -- we study the use of 3D sketches as an input modality and advocate a VR-scenario where retrieval is conducted. Thus, the ultimate vision is that users can freely retrieve a 3D model by air-doodling in a VR environment. As a first stab at this new 3D VR-sketch to 3D shape retrieval problem, we make four contributions. First, we code a VR utility to collect 3D VR-sketches and conduct retrieval. Second, we collect the first set of $167$ 3D VR-sketches on two shape categories from ModelNet. Third, we propose a novel approach to generate a synthetic dataset of human-like 3D sketches of different abstract levels to train deep networks. At last, we compare the common multi-view and volumetric approaches: We show that, in contrast to 3D shape to 3D shape retrieval, volumetric point-based approaches exhibit superior performance on 3D sketch to 3D shape retrieval due to the sparse and abstract nature of 3D VR-sketches. We believe these contributions will collectively serve as enablers for future attempts at this problem. The VR interface, code and datasets are available at https://tinyurl.com/3DSketch3DV.
Fine-Grained VR Sketching: Dataset and Insights
Sep 20, 2022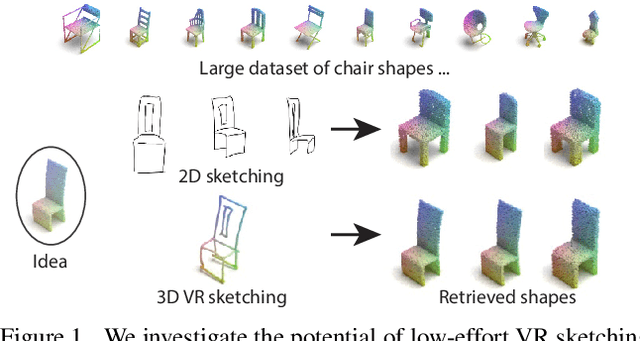
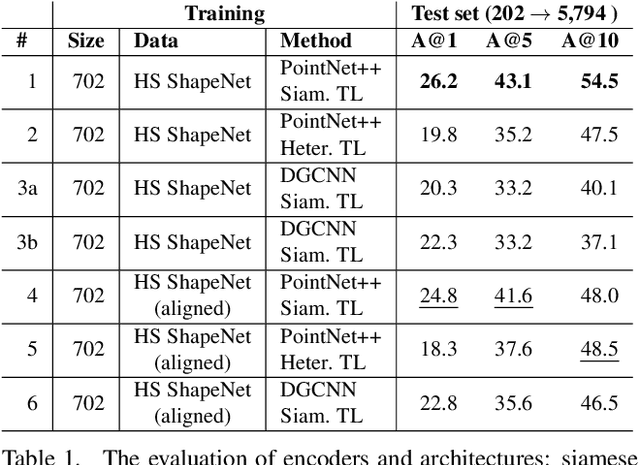
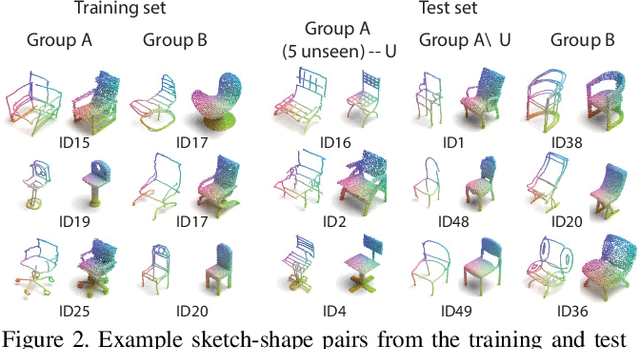
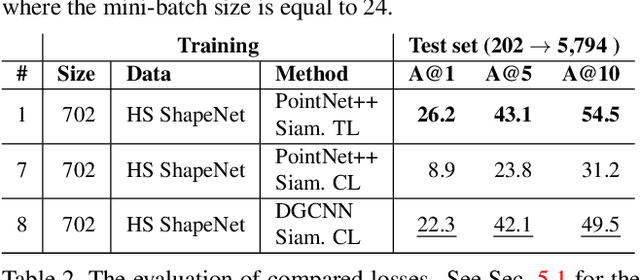
Abstract:We present the first fine-grained dataset of 1,497 3D VR sketch and 3D shape pairs of a chair category with large shapes diversity. Our dataset supports the recent trend in the sketch community on fine-grained data analysis, and extends it to an actively developing 3D domain. We argue for the most convenient sketching scenario where the sketch consists of sparse lines and does not require any sketching skills, prior training or time-consuming accurate drawing. We then, for the first time, study the scenario of fine-grained 3D VR sketch to 3D shape retrieval, as a novel VR sketching application and a proving ground to drive out generic insights to inform future research. By experimenting with carefully selected combinations of design factors on this new problem, we draw important conclusions to help follow-on work. We hope our dataset will enable other novel applications, especially those that require a fine-grained angle such as fine-grained 3D shape reconstruction. The dataset is available at tinyurl.com/VRSketch3DV21.
Structure-Aware 3D VR Sketch to 3D Shape Retrieval
Sep 19, 2022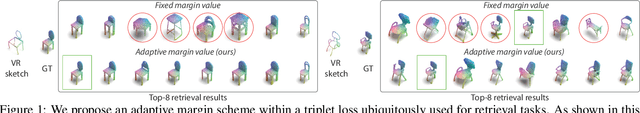

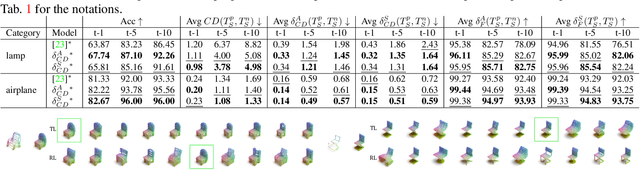
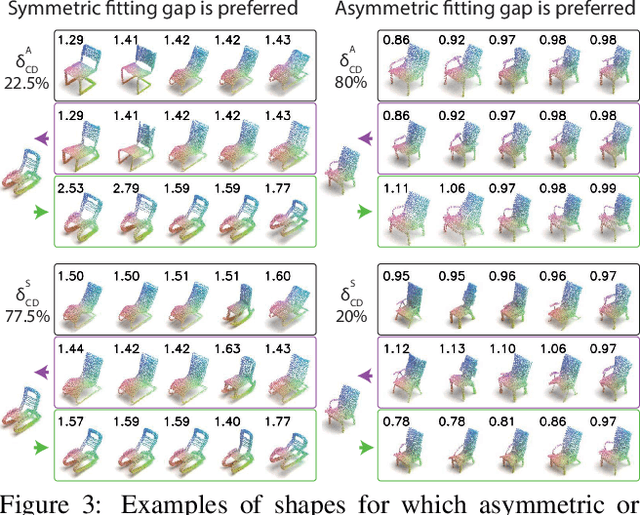
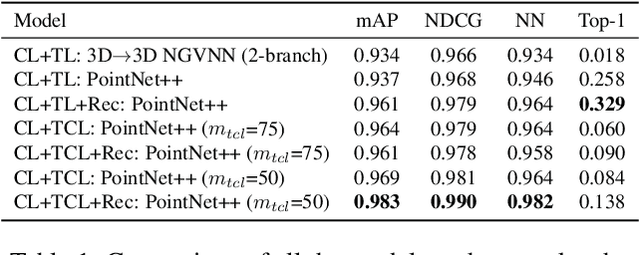
Abstract:We study the practical task of fine-grained 3D-VR-sketch-based 3D shape retrieval. This task is of particular interest as 2D sketches were shown to be effective queries for 2D images. However, due to the domain gap, it remains hard to achieve strong performance in 3D shape retrieval from 2D sketches. Recent work demonstrated the advantage of 3D VR sketching on this task. In our work, we focus on the challenge caused by inherent inaccuracies in 3D VR sketches. We observe that retrieval results obtained with a triplet loss with a fixed margin value, commonly used for retrieval tasks, contain many irrelevant shapes and often just one or few with a similar structure to the query. To mitigate this problem, we for the first time draw a connection between adaptive margin values and shape similarities. In particular, we propose to use a triplet loss with an adaptive margin value driven by a "fitting gap", which is the similarity of two shapes under structure-preserving deformations. We also conduct a user study which confirms that this fitting gap is indeed a suitable criterion to evaluate the structural similarity of shapes. Furthermore, we introduce a dataset of 202 VR sketches for 202 3D shapes drawn from memory rather than from observation. The code and data are available at https://github.com/Rowl1ng/Structure-Aware-VR-Sketch-Shape-Retrieval.
FS-COCO: Towards Understanding of Freehand Sketches of Common Objects in Context
Mar 15, 2022

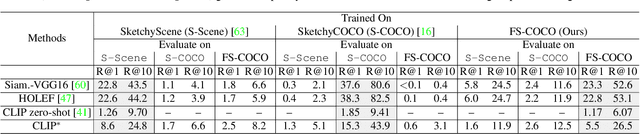
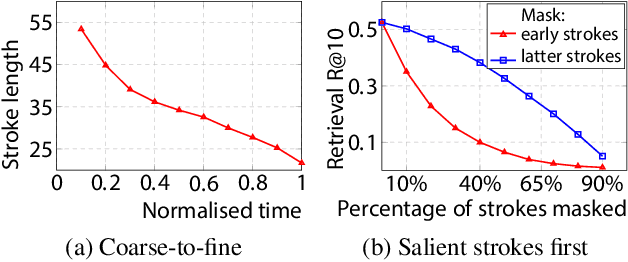
Abstract:We advance sketch research to scenes with the first dataset of freehand scene sketches, FS-COCO. With practical applications in mind, we collect sketches that convey well scene content but can be sketched within a few minutes by a person with any sketching skills. Our dataset comprises 10,000 freehand scene vector sketches with per point space-time information by 100 non-expert individuals, offering both object- and scene-level abstraction. Each sketch is augmented with its text description. Using our dataset, we study for the first time the problem of the fine-grained image retrieval from freehand scene sketches and sketch captions. We draw insights on (i) Scene salience encoded in sketches with strokes temporal order; (ii) The retrieval performance accuracy from scene sketches against image captions; (iii) Complementarity of information in sketches and image captions, as well as the potential benefit of combining the two modalities. In addition, we propose new solutions enabled by our dataset (i) We adopt meta-learning to show how the retrieval model can be fine-tuned to a new user style given just a small set of sketches, (ii) We extend a popular vector sketch LSTM-based encoder to handle sketches with larger complexity than was supported by previous work. Namely, we propose a hierarchical sketch decoder, which we leverage at a sketch-specific "pretext" task. Our dataset enables for the first time research on freehand scene sketch understanding and its practical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge