Yujie Xing
Unifying and Enhancing Graph Transformers via a Hierarchical Mask Framework
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:Graph Transformers (GTs) have emerged as a powerful paradigm for graph representation learning due to their ability to model diverse node interactions. However, existing GTs often rely on intricate architectural designs tailored to specific interactions, limiting their flexibility. To address this, we propose a unified hierarchical mask framework that reveals an underlying equivalence between model architecture and attention mask construction. This framework enables a consistent modeling paradigm by capturing diverse interactions through carefully designed attention masks. Theoretical analysis under this framework demonstrates that the probability of correct classification positively correlates with the receptive field size and label consistency, leading to a fundamental design principle: an effective attention mask should ensure both a sufficiently large receptive field and a high level of label consistency. While no single existing mask satisfies this principle across all scenarios, our analysis reveals that hierarchical masks offer complementary strengths, motivating their effective integration. Then, we introduce M3Dphormer, a Mixture-of-Experts-based Graph Transformer with Multi-Level Masking and Dual Attention Computation. M3Dphormer incorporates three theoretically grounded hierarchical masks and employs a bi-level expert routing mechanism to adaptively integrate multi-level interaction information. To ensure scalability, we further introduce a dual attention computation scheme that dynamically switches between dense and sparse modes based on local mask sparsity. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that M3Dphormer achieves state-of-the-art performance, validating the effectiveness of our unified framework and model design.
Query-Based and Unnoticeable Graph Injection Attack from Neighborhood Perspective
Feb 04, 2025

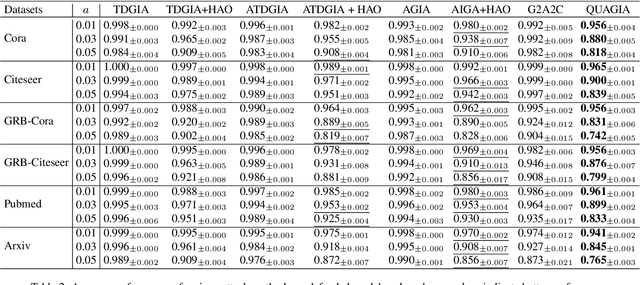

Abstract:The robustness of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) has become an increasingly important topic due to their expanding range of applications. Various attack methods have been proposed to explore the vulnerabilities of GNNs, ranging from Graph Modification Attacks (GMA) to the more practical and flexible Graph Injection Attacks (GIA). However, existing methods face two key challenges: (i) their reliance on surrogate models, which often leads to reduced attack effectiveness due to structural differences and prior biases, and (ii) existing GIA methods often sacrifice attack success rates in undefended settings to bypass certain defense models, thereby limiting their overall effectiveness. To overcome these limitations, we propose QUGIA, a Query-based and Unnoticeable Graph Injection Attack. QUGIA injects nodes by first selecting edges based on victim node connections and then generating node features using a Bayesian framework. This ensures that the injected nodes are similar to the original graph nodes, implicitly preserving homophily and making the attack more unnoticeable. Unlike previous methods, QUGIA does not rely on surrogate models, thereby avoiding performance degradation and achieving better generalization. Extensive experiments on six real-world datasets with diverse characteristics demonstrate that QUGIA achieves unnoticeable attacks and outperforms state-of-the-art attackers. The code will be released upon acceptance.
Boosting Graph Robustness Against Backdoor Attacks: An Over-Similarity Perspective
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved notable success in tasks such as social and transportation networks. However, recent studies have highlighted the vulnerability of GNNs to backdoor attacks, raising significant concerns about their reliability in real-world applications. Despite initial efforts to defend against specific graph backdoor attacks, existing defense methods face two main challenges: either the inability to establish a clear distinction between triggers and clean nodes, resulting in the removal of many clean nodes, or the failure to eliminate the impact of triggers, making it challenging to restore the target nodes to their pre-attack state. Through empirical analysis of various existing graph backdoor attacks, we observe that the triggers generated by these methods exhibit over-similarity in both features and structure. Based on this observation, we propose a novel graph backdoor defense method SimGuard. We first utilizes a similarity-based metric to detect triggers and then employs contrastive learning to train a backdoor detector that generates embeddings capable of separating triggers from clean nodes, thereby improving detection efficiency. Extensive experiments conducted on real-world datasets demonstrate that our proposed method effectively defends against various graph backdoor attacks while preserving performance on clean nodes. The code will be released upon acceptance.
Less is More: on the Over-Globalizing Problem in Graph Transformers
May 02, 2024Abstract:Graph Transformer, due to its global attention mechanism, has emerged as a new tool in dealing with graph-structured data. It is well recognized that the global attention mechanism considers a wider receptive field in a fully connected graph, leading many to believe that useful information can be extracted from all the nodes. In this paper, we challenge this belief: does the globalizing property always benefit Graph Transformers? We reveal the over-globalizing problem in Graph Transformer by presenting both empirical evidence and theoretical analysis, i.e., the current attention mechanism overly focuses on those distant nodes, while the near nodes, which actually contain most of the useful information, are relatively weakened. Then we propose a novel Bi-Level Global Graph Transformer with Collaborative Training (CoBFormer), including the inter-cluster and intra-cluster Transformers, to prevent the over-globalizing problem while keeping the ability to extract valuable information from distant nodes. Moreover, the collaborative training is proposed to improve the model's generalization ability with a theoretical guarantee. Extensive experiments on various graphs well validate the effectiveness of our proposed CoBFormer.
Graph Fairness Learning under Distribution Shifts
Jan 30, 2024



Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have achieved remarkable performance on graph-structured data. However, GNNs may inherit prejudice from the training data and make discriminatory predictions based on sensitive attributes, such as gender and race. Recently, there has been an increasing interest in ensuring fairness on GNNs, but all of them are under the assumption that the training and testing data are under the same distribution, i.e., training data and testing data are from the same graph. Will graph fairness performance decrease under distribution shifts? How does distribution shifts affect graph fairness learning? All these open questions are largely unexplored from a theoretical perspective. To answer these questions, we first theoretically identify the factors that determine bias on a graph. Subsequently, we explore the factors influencing fairness on testing graphs, with a noteworthy factor being the representation distances of certain groups between the training and testing graph. Motivated by our theoretical analysis, we propose our framework FatraGNN. Specifically, to guarantee fairness performance on unknown testing graphs, we propose a graph generator to produce numerous graphs with significant bias and under different distributions. Then we minimize the representation distances for each certain group between the training graph and generated graphs. This empowers our model to achieve high classification and fairness performance even on generated graphs with significant bias, thereby effectively handling unknown testing graphs. Experiments on real-world and semi-synthetic datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our model in terms of both accuracy and fairness.
Evaluating and Improving Context Attention Distribution on Multi-Turn Response Generation using Self-Contained Distractions
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Despite the rapid progress of open-domain generation-based conversational agents, most deployed systems treat dialogue contexts as single-turns, while systems dealing with multi-turn contexts are less studied. There is a lack of a reliable metric for evaluating multi-turn modelling, as well as an effective solution for improving it. In this paper, we focus on an essential component of multi-turn generation-based conversational agents: context attention distribution, i.e. how systems distribute their attention on dialogue's context. For evaluation of this component, We introduce a novel attention-mechanism-based metric: DAS ratio. To improve performance on this component, we propose an optimization strategy that employs self-contained distractions. Our experiments on the Ubuntu chatlogs dataset show that models with comparable perplexity can be distinguished by their ability on context attention distribution. Our proposed optimization strategy improves both non-hierarchical and hierarchical models on the proposed metric by about 10% from baselines.
Balancing Multi-Domain Corpora Learning for Open-Domain Response Generation
May 05, 2022
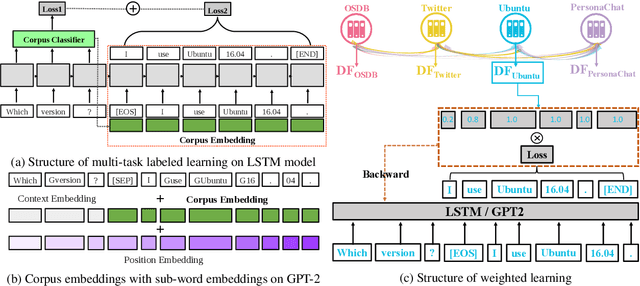
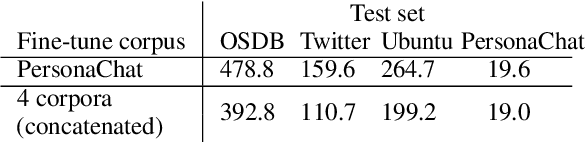
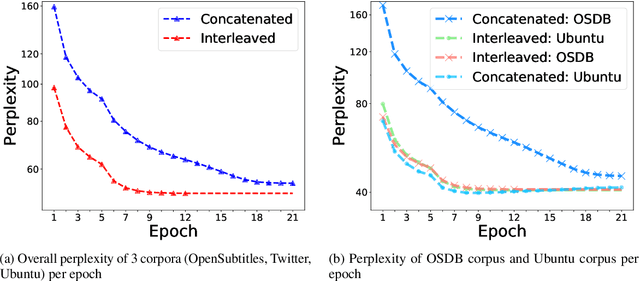
Abstract:Open-domain conversational systems are assumed to generate equally good responses on multiple domains. Previous work achieved good performance on the single corpus, but training and evaluating on multiple corpora from different domains are less studied. This paper explores methods of generating relevant responses for each of multiple multi-domain corpora. We first examine interleaved learning which intermingles multiple corpora as the baseline. We then investigate two multi-domain learning methods, labeled learning and multi-task labeled learning, which encode each corpus through a unique corpus embedding. Furthermore, we propose Domain-specific Frequency (DF), a novel word-level importance weight that measures the relative importance of a word for a specific corpus compared to other corpora. Based on DF, we propose weighted learning, a method that integrates DF to the loss function. We also adopt DF as a new evaluation metric. Extensive experiments show that our methods gain significant improvements on both automatic and human evaluation. We share our code and data for reproducibility
Automatic Evaluation of Neural Personality-based Chatbots
Sep 30, 2018


Abstract:Stylistic variation is critical to render the utterances generated by conversational agents natural and engaging. In this paper, we focus on sequence-to-sequence models for open-domain dialogue response generation and propose a new method to evaluate the extent to which such models are able to generate responses that reflect different personality traits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge