Nils Barlaug
ShallowBlocker: Improving Set Similarity Joins for Blocking
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:Blocking is a crucial step in large-scale entity matching but often requires significant manual engineering from an expert for each new dataset. Recent work has show that deep learning is state-of-the-art and has great potential for achieving hands-off and accurate blocking compared to classical methods. However, in practice, such deep learning methods are often unstable, offers little interpretability, and require hyperparameter tuning and significant computational resources. In this paper, we propose a hands-off blocking method based on classical string similarity measures: ShallowBlocker. It uses a novel hybrid set similarity join combining absolute similarity, relative similarity, and local cardinality conditions with a new effective pre-candidate filter replacing size filter. We show that the method achieves state-of-the-art pair effectiveness on both unsupervised and supervised blocking in a scalable way.
Balancing Multi-Domain Corpora Learning for Open-Domain Response Generation
May 05, 2022
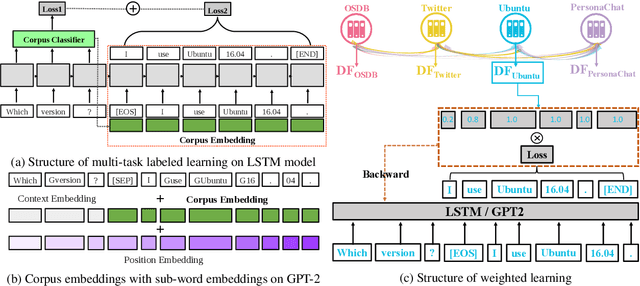
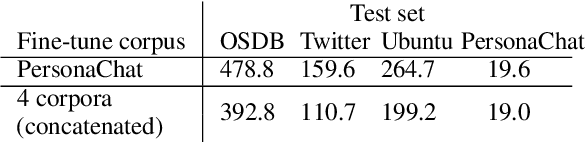
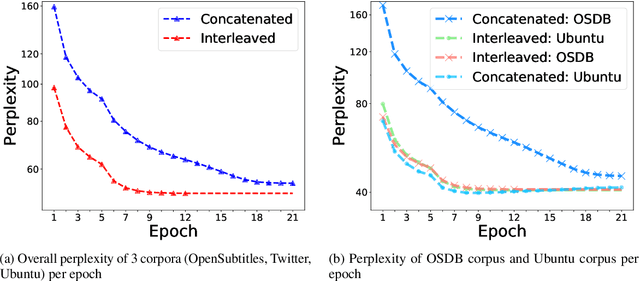
Abstract:Open-domain conversational systems are assumed to generate equally good responses on multiple domains. Previous work achieved good performance on the single corpus, but training and evaluating on multiple corpora from different domains are less studied. This paper explores methods of generating relevant responses for each of multiple multi-domain corpora. We first examine interleaved learning which intermingles multiple corpora as the baseline. We then investigate two multi-domain learning methods, labeled learning and multi-task labeled learning, which encode each corpus through a unique corpus embedding. Furthermore, we propose Domain-specific Frequency (DF), a novel word-level importance weight that measures the relative importance of a word for a specific corpus compared to other corpora. Based on DF, we propose weighted learning, a method that integrates DF to the loss function. We also adopt DF as a new evaluation metric. Extensive experiments show that our methods gain significant improvements on both automatic and human evaluation. We share our code and data for reproducibility
LEMON: Explainable Entity Matching
Oct 01, 2021

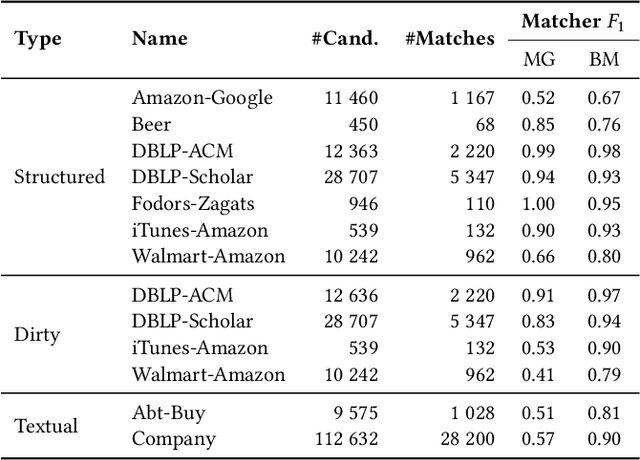
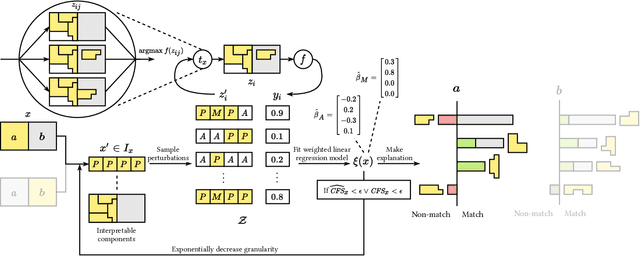
Abstract:State-of-the-art entity matching (EM) methods are hard to interpret, and there is significant value in bringing explainable AI to EM. Unfortunately, most popular explainability methods do not work well out of the box for EM and need adaptation. In this paper, we identify three challenges of applying local post hoc feature attribution methods to entity matching: cross-record interaction effects, non-match explanations, and variation in sensitivity. We propose our novel model-agnostic and schema-flexible method LEMON that addresses all three challenges by (i) producing dual explanations to avoid cross-record interaction effects, (ii) introducing the novel concept of attribution potential to explain how two records could have matched, and (iii) automatically choosing explanation granularity to match the sensitivity of the matcher and record pair in question. Experiments on public datasets demonstrate that the proposed method is more faithful to the matcher and does a better job of helping users understand the decision boundary of the matcher than previous work. Furthermore, user studies show that the rate at which human subjects can construct counterfactual examples after seeing an explanation from our proposed method increases from 54% to 64% for matches and from 15% to 49% for non-matches compared to explanations from a standard adaptation of LIME.
Neural Networks for Entity Matching
Oct 21, 2020
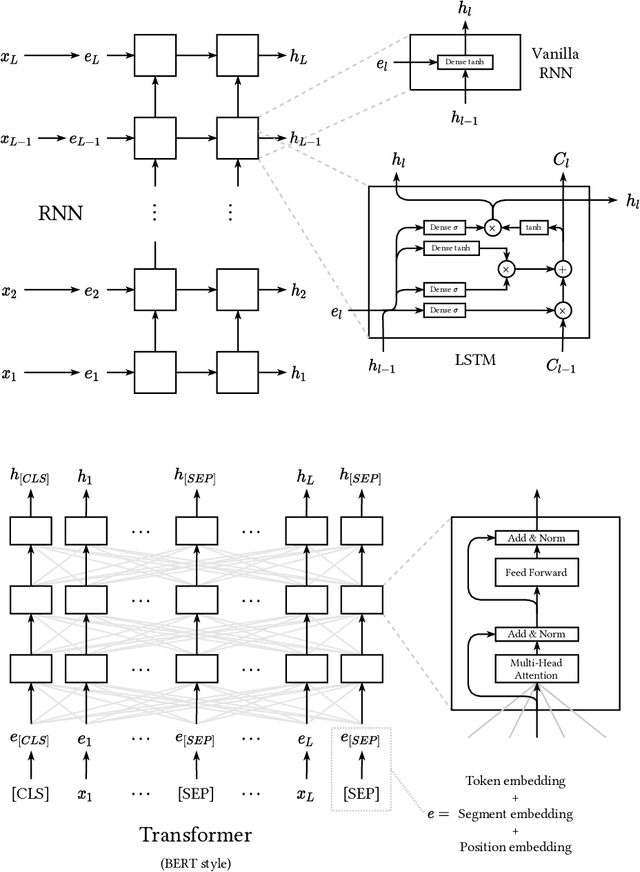
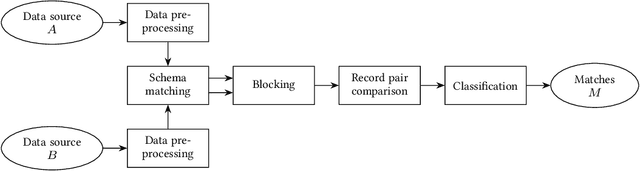
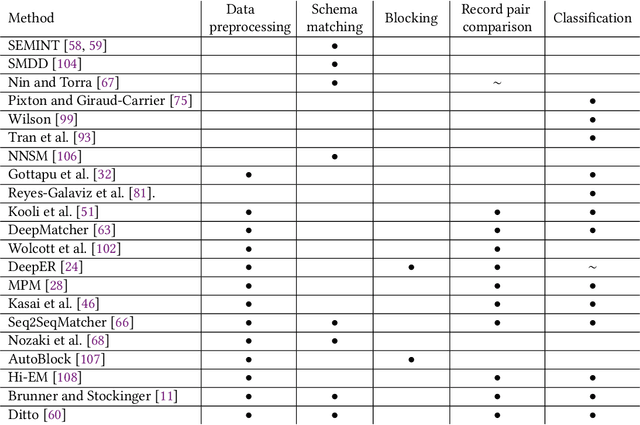
Abstract:Entity matching is the problem of identifying which records refer to the same real-world entity. It has been actively researched for decades, and a variety of different approaches have been developed. Even today, it remains a challenging problem, and there is still generous room for improvement. In recent years we have seen new methods based upon deep learning techniques for natural language processing emerge. In this survey, we present how neural networks have been used for entity matching. Specifically, we identify which steps of the entity matching process existing work have targeted using neural networks, and provide an overview of the different techniques used at each step. We also discuss contributions from deep learning in entity matching compared to traditional methods, and propose a taxonomy of deep neural networks for entity matching.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge