Yuan Xin
Jailbreaking Attacks vs. Content Safety Filters: How Far Are We in the LLM Safety Arms Race?
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed, ensuring their safe use is paramount. Jailbreaking, adversarial prompts that bypass model alignment to trigger harmful outputs, present significant risks, with existing studies reporting high success rates in evading common LLMs. However, previous evaluations have focused solely on the models, neglecting the full deployment pipeline, which typically incorporates additional safety mechanisms like content moderation filters. To address this gap, we present the first systematic evaluation of jailbreak attacks targeting LLM safety alignment, assessing their success across the full inference pipeline, including both input and output filtering stages. Our findings yield two key insights: first, nearly all evaluated jailbreak techniques can be detected by at least one safety filter, suggesting that prior assessments may have overestimated the practical success of these attacks; second, while safety filters are effective in detection, there remains room to better balance recall and precision to further optimize protection and user experience. We highlight critical gaps and call for further refinement of detection accuracy and usability in LLM safety systems.
Inside the Black Box: Detecting Data Leakage in Pre-trained Language Encoders
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:Despite being prevalent in the general field of Natural Language Processing (NLP), pre-trained language models inherently carry privacy and copyright concerns due to their nature of training on large-scale web-scraped data. In this paper, we pioneer a systematic exploration of such risks associated with pre-trained language encoders, specifically focusing on the membership leakage of pre-training data exposed through downstream models adapted from pre-trained language encoders-an aspect largely overlooked in existing literature. Our study encompasses comprehensive experiments across four types of pre-trained encoder architectures, three representative downstream tasks, and five benchmark datasets. Intriguingly, our evaluations reveal, for the first time, the existence of membership leakage even when only the black-box output of the downstream model is exposed, highlighting a privacy risk far greater than previously assumed. Alongside, we present in-depth analysis and insights toward guiding future researchers and practitioners in addressing the privacy considerations in developing pre-trained language models.
Provably Robust Cost-Sensitive Learning via Randomized Smoothing
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:We focus on learning adversarially robust classifiers under a cost-sensitive scenario, where the potential harm of different classwise adversarial transformations is encoded in a binary cost matrix. Existing methods are either empirical that cannot certify robustness or suffer from inherent scalability issues. In this work, we study whether randomized smoothing, a more scalable robustness certification framework, can be leveraged to certify cost-sensitive robustness. Built upon a notion of cost-sensitive certified radius, we show how to adapt the standard randomized smoothing certification pipeline to produce tight robustness guarantees for any cost matrix. In addition, with fine-grained certified radius optimization schemes specifically designed for different data subgroups, we propose an algorithm to train smoothed classifiers that are optimized for cost-sensitive robustness. Extensive experiments on image benchmarks and a real-world medical dataset demonstrate the superiority of our method in achieving significantly improved performance of certified cost-sensitive robustness while having a negligible impact on overall accuracy.
Multi-Prototype Networks for Unconstrained Set-based Face Recognition
Mar 23, 2019
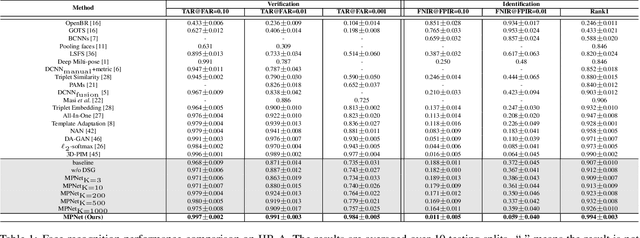
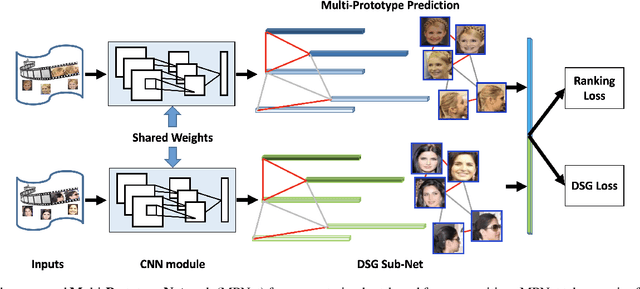
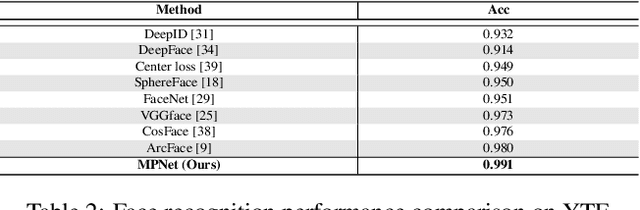
Abstract:In this paper, we study the challenging unconstrained set-based face recognition problem where each subject face is instantiated by a set of media (images and videos) instead of a single image. Naively aggregating information from all the media within a set would suffer from the large intra-set variance caused by heterogeneous factors (e.g., varying media modalities, poses and illuminations) and fail to learn discriminative face representations. A novel Multi-Prototype Network (MPNet) model is thus proposed to learn multiple prototype face representations adaptively from the media sets. Each learned prototype is representative for the subject face under certain condition in terms of pose, illumination and media modality. Instead of handcrafting the set partition for prototype learning, MPNet introduces a Dense SubGraph (DSG) learning sub-net that implicitly untangles inconsistent media and learns a number of representative prototypes. Qualitative and quantitative experiments clearly demonstrate superiority of the proposed model over state-of-the-arts.
Fast and Accurate Neural Word Segmentation for Chinese
Apr 24, 2017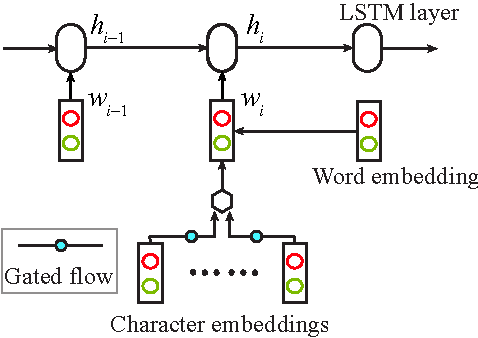
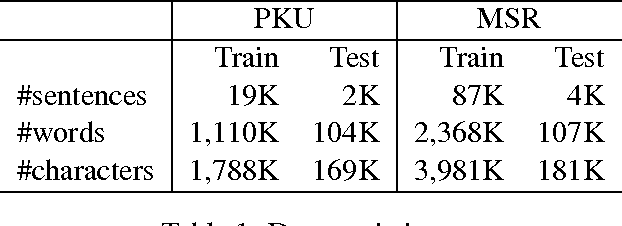
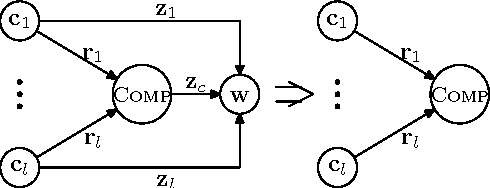

Abstract:Neural models with minimal feature engineering have achieved competitive performance against traditional methods for the task of Chinese word segmentation. However, both training and working procedures of the current neural models are computationally inefficient. This paper presents a greedy neural word segmenter with balanced word and character embedding inputs to alleviate the existing drawbacks. Our segmenter is truly end-to-end, capable of performing segmentation much faster and even more accurate than state-of-the-art neural models on Chinese benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge