Yongjin Kwon
GaussExplorer: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Embodied Exploration and Reasoning
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:We present GaussExplorer, a framework for embodied exploration and reasoning built on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). While prior approaches to language-embedded 3DGS have made meaningful progress in aligning simple text queries with Gaussian embeddings, they are generally optimized for relatively simple queries and struggle to interpret more complex, compositional language queries. Alternative studies based on object-centric RGB-D structured memories provide spatial grounding but are constrained by pre-fixed viewpoints. To address these issues, GaussExplorer introduces Vision-Language Models (VLMs) on top of 3DGS to enable question-driven exploration and reasoning within 3D scenes. We first identify pre-captured images that are most correlated with the query question, and subsequently adjust them into novel viewpoints to more accurately capture visual information for better reasoning by VLMs. Experiments show that ours outperforms existing methods on several benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of integrating VLM-based reasoning with 3DGS for embodied tasks.
ENInst: Enhancing Weakly-supervised Low-shot Instance Segmentation
Feb 20, 2023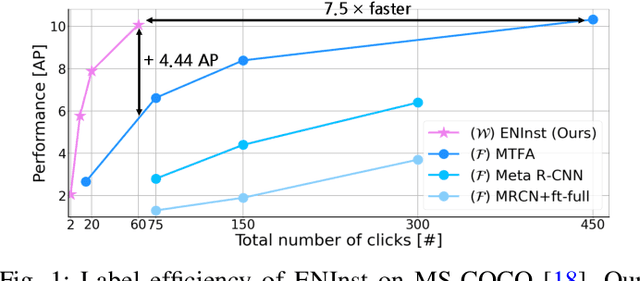
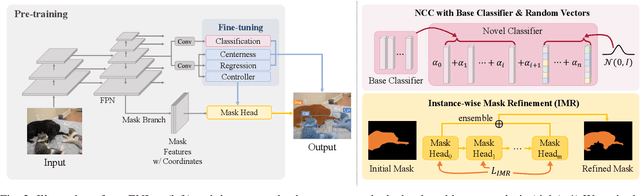
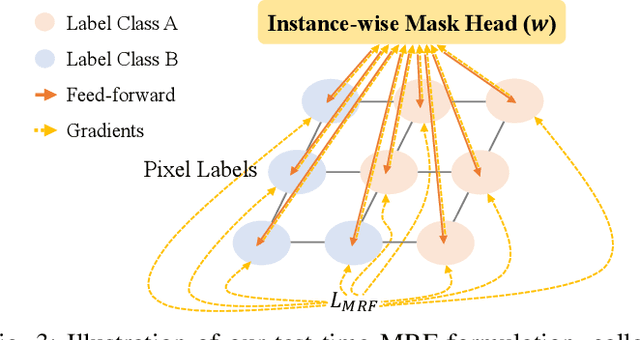

Abstract:We address a weakly-supervised low-shot instance segmentation, an annotation-efficient training method to deal with novel classes effectively. Since it is an under-explored problem, we first investigate the difficulty of the problem and identify the performance bottleneck by conducting systematic analyses of model components and individual sub-tasks with a simple baseline model. Based on the analyses, we propose ENInst with sub-task enhancement methods: instance-wise mask refinement for enhancing pixel localization quality and novel classifier composition for improving classification accuracy. Our proposed method lifts the overall performance by enhancing the performance of each sub-task. We demonstrate that our ENInst is 7.5 times more efficient in achieving comparable performance to the existing fully-supervised few-shot models and even outperforms them at times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge