Kim Jun-Seong
GaussExplorer: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Embodied Exploration and Reasoning
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:We present GaussExplorer, a framework for embodied exploration and reasoning built on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). While prior approaches to language-embedded 3DGS have made meaningful progress in aligning simple text queries with Gaussian embeddings, they are generally optimized for relatively simple queries and struggle to interpret more complex, compositional language queries. Alternative studies based on object-centric RGB-D structured memories provide spatial grounding but are constrained by pre-fixed viewpoints. To address these issues, GaussExplorer introduces Vision-Language Models (VLMs) on top of 3DGS to enable question-driven exploration and reasoning within 3D scenes. We first identify pre-captured images that are most correlated with the query question, and subsequently adjust them into novel viewpoints to more accurately capture visual information for better reasoning by VLMs. Experiments show that ours outperforms existing methods on several benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of integrating VLM-based reasoning with 3DGS for embodied tasks.
SA-ResGS: Self-Augmented Residual 3D Gaussian Splatting for Next Best View Selection
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:We propose Self-Augmented Residual 3D Gaussian Splatting (SA-ResGS), a novel framework to stabilize uncertainty quantification and enhancing uncertainty-aware supervision in next-best-view (NBV) selection for active scene reconstruction. SA-ResGS improves both the reliability of uncertainty estimates and their effectiveness for supervision by generating Self-Augmented point clouds (SA-Points) via triangulation between a training view and a rasterized extrapolated view, enabling efficient scene coverage estimation. While improving scene coverage through physically guided view selection, SA-ResGS also addresses the challenge of under-supervised Gaussians, exacerbated by sparse and wide-baseline views, by introducing the first residual learning strategy tailored for 3D Gaussian Splatting. This targeted supervision enhances gradient flow in high-uncertainty Gaussians by combining uncertainty-driven filtering with dropout- and hard-negative-mining-inspired sampling. Our contributions are threefold: (1) a physically grounded view selection strategy that promotes efficient and uniform scene coverage; (2) an uncertainty-aware residual supervision scheme that amplifies learning signals for weakly contributing Gaussians, improving training stability and uncertainty estimation across scenes with diverse camera distributions; (3) an implicit unbiasing of uncertainty quantification as a consequence of constrained view selection and residual supervision, which together mitigate conflicting effects of wide-baseline exploration and sparse-view ambiguity in NBV planning. Experiments on active view selection demonstrate that SA-ResGS outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in both reconstruction quality and view selection robustness.
Dr. Splat: Directly Referring 3D Gaussian Splatting via Direct Language Embedding Registration
Feb 23, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Dr. Splat, a novel approach for open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding leveraging 3D Gaussian Splatting. Unlike existing language-embedded 3DGS methods, which rely on a rendering process, our method directly associates language-aligned CLIP embeddings with 3D Gaussians for holistic 3D scene understanding. The key of our method is a language feature registration technique where CLIP embeddings are assigned to the dominant Gaussians intersected by each pixel-ray. Moreover, we integrate Product Quantization (PQ) trained on general large-scale image data to compactly represent embeddings without per-scene optimization. Experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing approaches in 3D perception benchmarks, such as open-vocabulary 3D semantic segmentation, 3D object localization, and 3D object selection tasks. For video results, please visit : https://drsplat.github.io/
SoundBrush: Sound as a Brush for Visual Scene Editing
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:We propose SoundBrush, a model that uses sound as a brush to edit and manipulate visual scenes. We extend the generative capabilities of the Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) to incorporate audio information for editing visual scenes. Inspired by existing image-editing works, we frame this task as a supervised learning problem and leverage various off-the-shelf models to construct a sound-paired visual scene dataset for training. This richly generated dataset enables SoundBrush to learn to map audio features into the textual space of the LDM, allowing for visual scene editing guided by diverse in-the-wild sound. Unlike existing methods, SoundBrush can accurately manipulate the overall scenery or even insert sounding objects to best match the audio inputs while preserving the original content. Furthermore, by integrating with novel view synthesis techniques, our framework can be extended to edit 3D scenes, facilitating sound-driven 3D scene manipulation. Demos are available at https://soundbrush.github.io/.
Revisiting Learning-based Video Motion Magnification for Real-time Processing
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Video motion magnification is a technique to capture and amplify subtle motion in a video that is invisible to the naked eye. The deep learning-based prior work successfully demonstrates the modelling of the motion magnification problem with outstanding quality compared to conventional signal processing-based ones. However, it still lags behind real-time performance, which prevents it from being extended to various online applications. In this paper, we investigate an efficient deep learning-based motion magnification model that runs in real time for full-HD resolution videos. Due to the specified network design of the prior art, i.e. inhomogeneous architecture, the direct application of existing neural architecture search methods is complicated. Instead of automatic search, we carefully investigate the architecture module by module for its role and importance in the motion magnification task. Two key findings are 1) Reducing the spatial resolution of the latent motion representation in the decoder provides a good trade-off between computational efficiency and task quality, and 2) surprisingly, only a single linear layer and a single branch in the encoder are sufficient for the motion magnification task. Based on these findings, we introduce a real-time deep learning-based motion magnification model with4.2X fewer FLOPs and is 2.7X faster than the prior art while maintaining comparable quality.
Learning-based Axial Motion Magnification
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:Video motion magnification amplifies invisible small motions to be perceptible, which provides humans with spatially dense and holistic understanding about small motions from the scene of interest. This is based on the premise that magnifying small motions enhances the legibility of the motion. In the real world, however, vibrating objects often possess complex systems, having complex natural frequencies, modes, and directions. Existing motion magnification often fails to improve the legibility since the intricate motions still retain complex characteristics even when magnified, which distracts us from analyzing them. In this work, we focus on improving the legibility by proposing a new concept, axial motion magnification, which magnifies decomposed motions along the user-specified direction. Axial motion magnification can be applied to various applications where motions of specific axes are critical, by providing simplified and easily readable motion information. We propose a novel learning-based axial motion magnification method with the Motion Separation Module that enables to disentangle and magnify the motion representation along axes of interest. Further, we build a new synthetic training dataset for the axial motion magnification task. Our proposed method improves the legibility of resulting motions along certain axes, while adding additional user controllability. Our method can be directly adopted to the generic motion magnification and achieves favorable performance against competing methods. Our project page is available at https://axial-momag.github.io/axial-momag/.
HDR-Plenoxels: Self-Calibrating High Dynamic Range Radiance Fields
Aug 14, 2022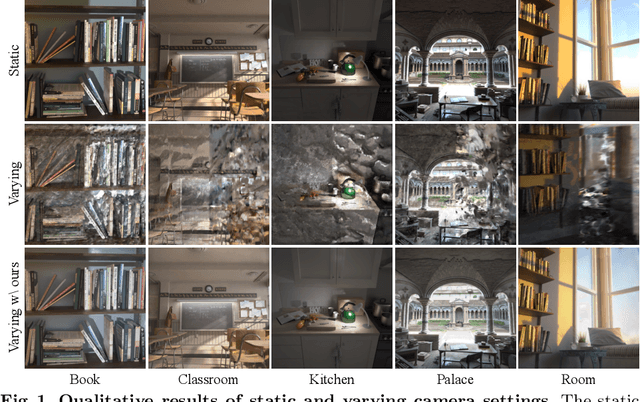
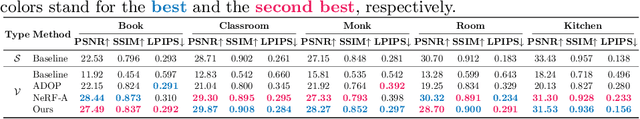
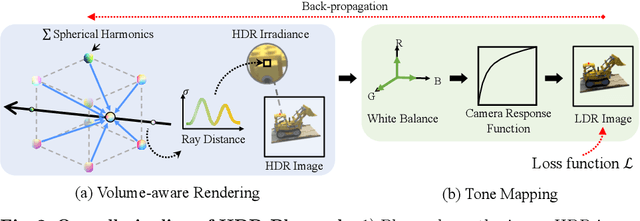
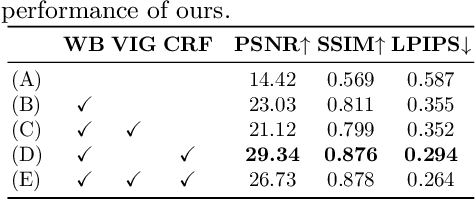
Abstract:We propose high dynamic range radiance (HDR) fields, HDR-Plenoxels, that learn a plenoptic function of 3D HDR radiance fields, geometry information, and varying camera settings inherent in 2D low dynamic range (LDR) images. Our voxel-based volume rendering pipeline reconstructs HDR radiance fields with only multi-view LDR images taken from varying camera settings in an end-to-end manner and has a fast convergence speed. To deal with various cameras in real-world scenarios, we introduce a tone mapping module that models the digital in-camera imaging pipeline (ISP) and disentangles radiometric settings. Our tone mapping module allows us to render by controlling the radiometric settings of each novel view. Finally, we build a multi-view dataset with varying camera conditions, which fits our problem setting. Our experiments show that HDR-Plenoxels can express detail and high-quality HDR novel views from only LDR images with various cameras.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge