Yongbin Qin
A Reasoning Paradigm for Named Entity Recognition
Nov 15, 2025



Abstract:Generative LLMs typically improve Named Entity Recognition (NER) performance through instruction tuning. They excel at generating entities by semantic pattern matching but lack an explicit, verifiable reasoning mechanism. This "cognitive shortcutting" leads to suboptimal performance and brittle generalization, especially in zero-shot and lowresource scenarios where reasoning from limited contextual cues is crucial. To address this issue, a reasoning framework is proposed for NER, which shifts the extraction paradigm from implicit pattern matching to explicit reasoning. This framework consists of three stages: Chain of Thought (CoT) generation, CoT tuning, and reasoning enhancement. First, a dataset annotated with NER-oriented CoTs is generated, which contain task-relevant reasoning chains. Then, they are used to tune the NER model to generate coherent rationales before deriving the final answer. Finally, a reasoning enhancement stage is implemented to optimize the reasoning process using a comprehensive reward signal. This stage ensures explicit and verifiable extractions. Experiments show that ReasoningNER demonstrates impressive cognitive ability in the NER task, achieving competitive performance. In zero-shot settings, it achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, outperforming GPT-4 by 12.3 percentage points on the F1 score. Analytical results also demonstrate its great potential to advance research in reasoningoriented information extraction. Our codes are available at https://github.com/HuiResearch/ReasoningIE.
MoCha-Stereo: Motif Channel Attention Network for Stereo Matching
Apr 11, 2024Abstract:Learning-based stereo matching techniques have made significant progress. However, existing methods inevitably lose geometrical structure information during the feature channel generation process, resulting in edge detail mismatches. In this paper, the Motif Cha}nnel Attention Stereo Matching Network (MoCha-Stereo) is designed to address this problem. We provide the Motif Channel Correlation Volume (MCCV) to determine more accurate edge matching costs. MCCV is achieved by projecting motif channels, which capture common geometric structures in feature channels, onto feature maps and cost volumes. In addition, edge variations in %potential feature channels of the reconstruction error map also affect details matching, we propose the Reconstruction Error Motif Penalty (REMP) module to further refine the full-resolution disparity estimation. REMP integrates the frequency information of typical channel features from the reconstruction error. MoCha-Stereo ranks 1st on the KITTI-2015 and KITTI-2012 Reflective leaderboards. Our structure also shows excellent performance in Multi-View Stereo. Code is avaliable at https://github.com/ZYangChen/MoCha-Stereo.
* Accepted to CVPR 2024
A Two Dimensional Feature Engineering Method for Relation Extraction
Apr 07, 2024Abstract:Transforming a sentence into a two-dimensional (2D) representation (e.g., the table filling) has the ability to unfold a semantic plane, where an element of the plane is a word-pair representation of a sentence which may denote a possible relation representation composed of two named entities. The 2D representation is effective in resolving overlapped relation instances. However, in related works, the representation is directly transformed from a raw input. It is weak to utilize prior knowledge, which is important to support the relation extraction task. In this paper, we propose a two-dimensional feature engineering method in the 2D sentence representation for relation extraction. Our proposed method is evaluated on three public datasets (ACE05 Chinese, ACE05 English, and SanWen) and achieves the state-of-the-art performance. The results indicate that two-dimensional feature engineering can take advantage of a two-dimensional sentence representation and make full use of prior knowledge in traditional feature engineering. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Wang-ck123/A-Two-Dimensional-Feature-Engineering-Method-for-Entity-Relation-Extraction
A Bi-consolidating Model for Joint Relational Triple Extraction
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:Current methods to extract relational triples directly make a prediction based on a possible entity pair in a raw sentence without depending on entity recognition. The task suffers from a serious semantic overlapping problem, in which several relation triples may share one or two entities in a sentence. It is weak to learn discriminative semantic features relevant to a relation triple. In this paper, based on a two-dimensional sentence representation, a bi-consolidating model is proposed to address this problem by simultaneously reinforcing the local and global semantic features relevant to a relation triple. This model consists of a local consolidation component and a global consolidation component. The first component uses a pixel difference convolution to enhance semantic information of a possible triple representation from adjacent regions and mitigate noise in neighbouring neighbours. The second component strengthens the triple representation based a channel attention and a spatial attention, which has the advantage to learn remote semantic dependencies in a sentence. They are helpful to improve the performance of both entity identification and relation type classification in relation triple extraction. After evaluated on several publish datasets, it achieves competitive performance. Analytical experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our model for relational triple extraction and give motivation for other natural language processing tasks.
DFGET: Displacement-Field Assisted Graph Energy Transmitter for Gland Instance Segmentation
Dec 11, 2023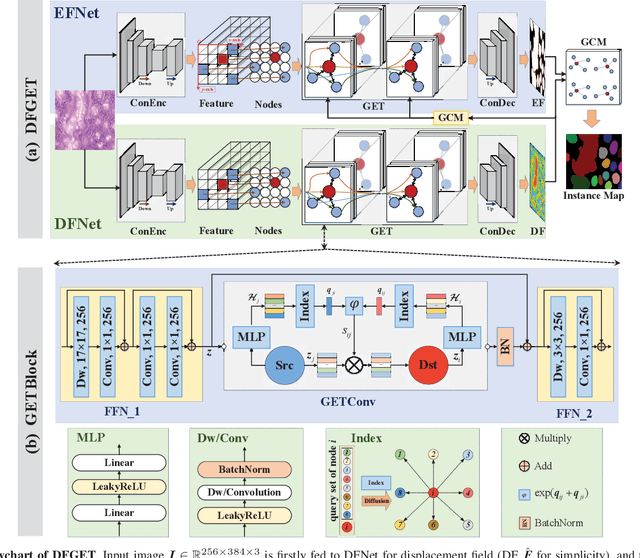
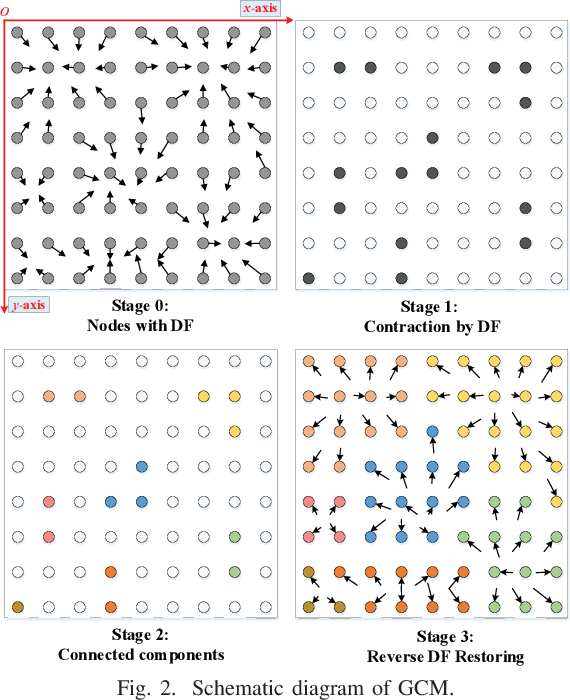
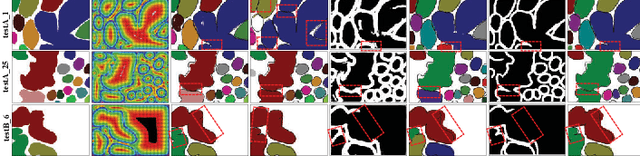
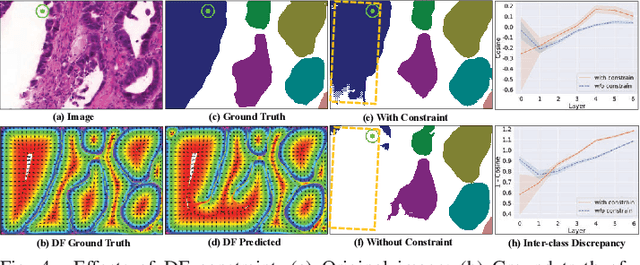
Abstract:Gland instance segmentation is an essential but challenging task in the diagnosis and treatment of adenocarcinoma. The existing models usually achieve gland instance segmentation through multi-task learning and boundary loss constraint. However, how to deal with the problems of gland adhesion and inaccurate boundary in segmenting the complex samples remains a challenge. In this work, we propose a displacement-field assisted graph energy transmitter (DFGET) framework to solve these problems. Specifically, a novel message passing manner based on anisotropic diffusion is developed to update the node features, which can distinguish the isomorphic graphs and improve the expressivity of graph nodes for complex samples. Using such graph framework, the gland semantic segmentation map and the displacement field (DF) of the graph nodes are estimated with two graph network branches. With the constraint of DF, a graph cluster module based on diffusion theory is presented to improve the intra-class feature consistency and inter-class feature discrepancy, as well as to separate the adherent glands from the semantic segmentation maps. Extensive comparison and ablation experiments on the GlaS dataset demonstrate the superiority of DFGET and effectiveness of the proposed anisotropic message passing manner and clustering method. Compared to the best comparative model, DFGET increases the object-Dice and object-F1 score by 2.5% and 3.4% respectively, while decreases the object-HD by 32.4%, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Annotation of Chinese Predicate Heads and Relevant Elements
Apr 01, 2021


Abstract:A predicate head is a verbal expression that plays a role as the structural center of a sentence. Identifying predicate heads is critical to understanding a sentence. It plays the leading role in organizing the relevant syntactic elements in a sentence, including subject elements, adverbial elements, etc. For some languages, such as English, word morphologies are valuable for identifying predicate heads. However, Chinese offers no morphological information to indicate words` grammatical roles. A Chinese sentence often contains several verbal expressions; identifying the expression that plays the role of the predicate head is not an easy task. Furthermore, Chinese sentences are inattentive to structure and provide no delimitation between words. Therefore, identifying Chinese predicate heads involves significant challenges. In Chinese information extraction, little work has been performed in predicate head recognition. No generally accepted evaluation dataset supports work in this important area. This paper presents the first attempt to develop an annotation guideline for Chinese predicate heads and their relevant syntactic elements. This annotation guideline emphasizes the role of the predicate as the structural center of a sentence. The design of relevant syntactic element annotation also follows this principle. Many considerations are proposed to achieve this goal, e.g., patterns of predicate heads, a flattened annotation structure, and a simpler syntactic unit type. Based on the proposed annotation guideline, more than 1,500 documents were manually annotated. The corpus will be available online for public access. With this guideline and annotated corpus, our goal is to broadly impact and advance the research in the area of Chinese information extraction and to provide the research community with a critical resource that has been lacking for a long time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge