Ruixue Tang
A Bi-consolidating Model for Joint Relational Triple Extraction
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:Current methods to extract relational triples directly make a prediction based on a possible entity pair in a raw sentence without depending on entity recognition. The task suffers from a serious semantic overlapping problem, in which several relation triples may share one or two entities in a sentence. It is weak to learn discriminative semantic features relevant to a relation triple. In this paper, based on a two-dimensional sentence representation, a bi-consolidating model is proposed to address this problem by simultaneously reinforcing the local and global semantic features relevant to a relation triple. This model consists of a local consolidation component and a global consolidation component. The first component uses a pixel difference convolution to enhance semantic information of a possible triple representation from adjacent regions and mitigate noise in neighbouring neighbours. The second component strengthens the triple representation based a channel attention and a spatial attention, which has the advantage to learn remote semantic dependencies in a sentence. They are helpful to improve the performance of both entity identification and relation type classification in relation triple extraction. After evaluated on several publish datasets, it achieves competitive performance. Analytical experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our model for relational triple extraction and give motivation for other natural language processing tasks.
Interpretable Neural Computation for Real-World Compositional Visual Question Answering
Oct 10, 2020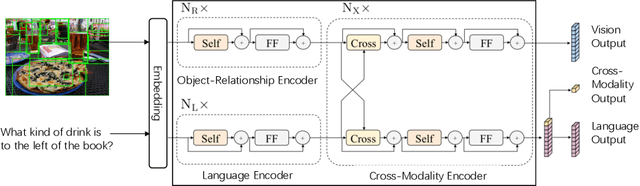



Abstract:There are two main lines of research on visual question answering (VQA): compositional model with explicit multi-hop reasoning, and monolithic network with implicit reasoning in the latent feature space. The former excels in interpretability and compositionality but fails on real-world images, while the latter usually achieves better performance due to model flexibility and parameter efficiency. We aim to combine the two to build an interpretable framework for real-world compositional VQA. In our framework, images and questions are disentangled into scene graphs and programs, and a symbolic program executor runs on them with full transparency to select the attention regions, which are then iteratively passed to a visual-linguistic pre-trained encoder to predict answers. Experiments conducted on the GQA benchmark demonstrate that our framework outperforms the compositional prior arts and achieves competitive accuracy among monolithic ones. With respect to the validity, plausibility and distribution metrics, our framework surpasses others by a considerable margin.
Semantic Equivalent Adversarial Data Augmentation for Visual Question Answering
Jul 19, 2020



Abstract:Visual Question Answering (VQA) has achieved great success thanks to the fast development of deep neural networks (DNN). On the other hand, the data augmentation, as one of the major tricks for DNN, has been widely used in many computer vision tasks. However, there are few works studying the data augmentation problem for VQA and none of the existing image based augmentation schemes (such as rotation and flipping) can be directly applied to VQA due to its semantic structure -- an $\langle image, question, answer\rangle$ triplet needs to be maintained correctly. For example, a direction related Question-Answer (QA) pair may not be true if the associated image is rotated or flipped. In this paper, instead of directly manipulating images and questions, we use generated adversarial examples for both images and questions as the augmented data. The augmented examples do not change the visual properties presented in the image as well as the \textbf{semantic} meaning of the question, the correctness of the $\langle image, question, answer\rangle$ is thus still maintained. We then use adversarial learning to train a classic VQA model (BUTD) with our augmented data. We find that we not only improve the overall performance on VQAv2, but also can withstand adversarial attack effectively, compared to the baseline model. The source code is available at https://github.com/zaynmi/seada-vqa.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge