Yiyi Wang
PianoBART: Symbolic Piano Music Generation and Understanding with Large-Scale Pre-Training
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:Learning musical structures and composition patterns is necessary for both music generation and understanding, but current methods do not make uniform use of learned features to generate and comprehend music simultaneously. In this paper, we propose PianoBART, a pre-trained model that uses BART for both symbolic piano music generation and understanding. We devise a multi-level object selection strategy for different pre-training tasks of PianoBART, which can prevent information leakage or loss and enhance learning ability. The musical semantics captured in pre-training are fine-tuned for music generation and understanding tasks. Experiments demonstrate that PianoBART efficiently learns musical patterns and achieves outstanding performance in generating high-quality coherent pieces and comprehending music. Our code and supplementary material are available at https://github.com/RS2002/PianoBart.
ProMISe: Promptable Medical Image Segmentation using SAM
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:With the proposal of the Segment Anything Model (SAM), fine-tuning SAM for medical image segmentation (MIS) has become popular. However, due to the large size of the SAM model and the significant domain gap between natural and medical images, fine-tuning-based strategies are costly with potential risk of instability, feature damage and catastrophic forgetting. Furthermore, some methods of transferring SAM to a domain-specific MIS through fine-tuning strategies disable the model's prompting capability, severely limiting its utilization scenarios. In this paper, we propose an Auto-Prompting Module (APM), which provides SAM-based foundation model with Euclidean adaptive prompts in the target domain. Our experiments demonstrate that such adaptive prompts significantly improve SAM's non-fine-tuned performance in MIS. In addition, we propose a novel non-invasive method called Incremental Pattern Shifting (IPS) to adapt SAM to specific medical domains. Experimental results show that the IPS enables SAM to achieve state-of-the-art or competitive performance in MIS without the need for fine-tuning. By coupling these two methods, we propose ProMISe, an end-to-end non-fine-tuned framework for Promptable Medical Image Segmentation. Our experiments demonstrate that both using our methods individually or in combination achieves satisfactory performance in low-cost pattern shifting, with all of SAM's parameters frozen.
AbLit: A Resource for Analyzing and Generating Abridged Versions of English Literature
Feb 13, 2023
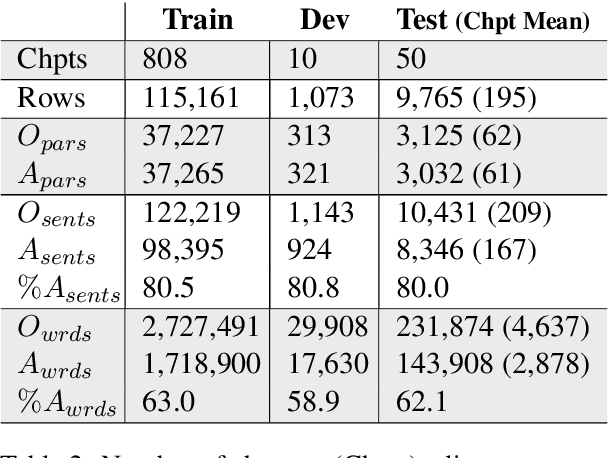
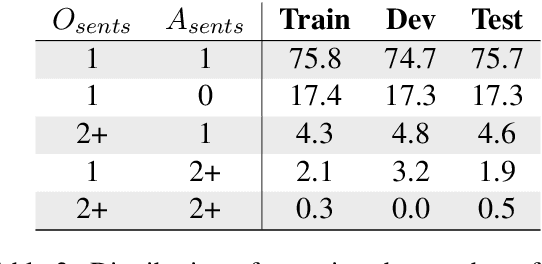
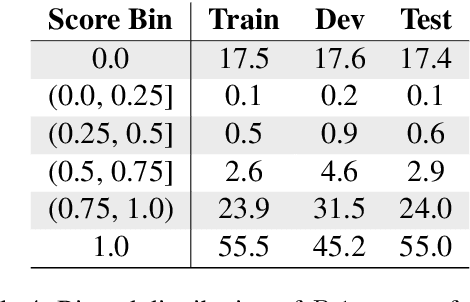
Abstract:Creating an abridged version of a text involves shortening it while maintaining its linguistic qualities. In this paper, we examine this task from an NLP perspective for the first time. We present a new resource, AbLit, which is derived from abridged versions of English literature books. The dataset captures passage-level alignments between the original and abridged texts. We characterize the linguistic relations of these alignments, and create automated models to predict these relations as well as to generate abridgements for new texts. Our findings establish abridgement as a challenging task, motivating future resources and research. The dataset is available at github.com/roemmele/AbLit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge