Yixuan Tan
Can LLMs Generate Reliable Test Case Generators? A Study on Competition-Level Programming Problems
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in code generation, capable of tackling complex tasks during inference. However, the extent to which LLMs can be utilized for code checking or debugging through test case generation remains largely unexplored. We investigate this problem from the perspective of competition-level programming (CP) programs and propose TCGBench, a Benchmark for (LLM generation of) Test Case Generators. This benchmark comprises two tasks, aimed at studying the capabilities of LLMs in (1) generating valid test case generators for a given CP problem, and further (2) generating targeted test case generators that expose bugs in human-written code. Experimental results indicate that while state-of-the-art LLMs can generate valid test case generators in most cases, most LLMs struggle to generate targeted test cases that reveal flaws in human code effectively. Especially, even advanced reasoning models (e.g., o3-mini) fall significantly short of human performance in the task of generating targeted generators. Furthermore, we construct a high-quality, manually curated dataset of instructions for generating targeted generators. Analysis demonstrates that the performance of LLMs can be enhanced with the aid of this dataset, by both prompting and fine-tuning.
DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-V3, a strong Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 671B total parameters with 37B activated for each token. To achieve efficient inference and cost-effective training, DeepSeek-V3 adopts Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) and DeepSeekMoE architectures, which were thoroughly validated in DeepSeek-V2. Furthermore, DeepSeek-V3 pioneers an auxiliary-loss-free strategy for load balancing and sets a multi-token prediction training objective for stronger performance. We pre-train DeepSeek-V3 on 14.8 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning stages to fully harness its capabilities. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that DeepSeek-V3 outperforms other open-source models and achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models. Despite its excellent performance, DeepSeek-V3 requires only 2.788M H800 GPU hours for its full training. In addition, its training process is remarkably stable. Throughout the entire training process, we did not experience any irrecoverable loss spikes or perform any rollbacks. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.
Improved convergence rate of kNN graph Laplacians
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:In graph-based data analysis, $k$-nearest neighbor ($k$NN) graphs are widely used due to their adaptivity to local data densities. Allowing weighted edges in the graph, the kernelized graph affinity provides a more general type of $k$NN graph where the $k$NN distance is used to set the kernel bandwidth adaptively. In this work, we consider a general class of $k$NN graph where the graph affinity is $W_{ij} = \epsilon^{-d/2} \; k_0 ( \| x_i - x_j \|^2 / \epsilon \phi( \widehat{\rho}(x_i), \widehat{\rho}(x_j) )^2 ) $, with $\widehat{\rho}(x)$ being the (rescaled) $k$NN distance at the point $x$, $\phi$ a symmetric bi-variate function, and $k_0$ a non-negative function on $[0,\infty)$. Under the manifold data setting, where $N$ i.i.d. samples $x_i$ are drawn from a density $p$ on a $d$-dimensional unknown manifold embedded in a high dimensional Euclidean space, we prove the point-wise convergence of the $k$NN graph Laplacian to the limiting manifold operator (depending on $p$) at the rate of $O(N^{-2/(d+6)}\,)$, up to a log factor, when $k_0$ and $\phi$ have $C^3$ regularity and satisfy other technical conditions. This fast rate is obtained when $\epsilon \sim N^{-2/(d+6)}\,$ and $k \sim N^{6/(d+6)}\,$, both at the optimal order to balance the theoretical bias and variance errors. When $k_0$ and $\phi$ have lower regularities, including when $k_0$ is a compactly supported function as in the standard $k$NN graph, the convergence rate degenerates to $O(N^{-1/(d+4)}\,)$. Our improved convergence rate is based on a refined analysis of the $k$NN estimator, which can be of independent interest. We validate our theory by numerical experiments on simulated data.
Fire-Flyer AI-HPC: A Cost-Effective Software-Hardware Co-Design for Deep Learning
Aug 26, 2024



Abstract:The rapid progress in Deep Learning (DL) and Large Language Models (LLMs) has exponentially increased demands of computational power and bandwidth. This, combined with the high costs of faster computing chips and interconnects, has significantly inflated High Performance Computing (HPC) construction costs. To address these challenges, we introduce the Fire-Flyer AI-HPC architecture, a synergistic hardware-software co-design framework and its best practices. For DL training, we deployed the Fire-Flyer 2 with 10,000 PCIe A100 GPUs, achieved performance approximating the DGX-A100 while reducing costs by half and energy consumption by 40%. We specifically engineered HFReduce to accelerate allreduce communication and implemented numerous measures to keep our Computation-Storage Integrated Network congestion-free. Through our software stack, including HaiScale, 3FS, and HAI-Platform, we achieved substantial scalability by overlapping computation and communication. Our system-oriented experience from DL training provides valuable insights to drive future advancements in AI-HPC.
Neural Differential Recurrent Neural Network with Adaptive Time Steps
Jun 02, 2023



Abstract:The neural Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) model has shown success in learning complex continuous-time processes from observations on discrete time stamps. In this work, we consider the modeling and forecasting of time series data that are non-stationary and may have sharp changes like spikes. We propose an RNN-based model, called RNN-ODE-Adap, that uses a neural ODE to represent the time development of the hidden states, and we adaptively select time steps based on the steepness of changes of the data over time so as to train the model more efficiently for the "spike-like" time series. Theoretically, RNN-ODE-Adap yields provably a consistent estimation of the intensity function for the Hawkes-type time series data. We also provide an approximation analysis of the RNN-ODE model showing the benefit of adaptive steps. The proposed model is demonstrated to achieve higher prediction accuracy with reduced computational cost on simulated dynamic system data and point process data and on a real electrocardiography dataset.
Direct Object Recognition Without Line-of-Sight Using Optical Coherence
Mar 18, 2019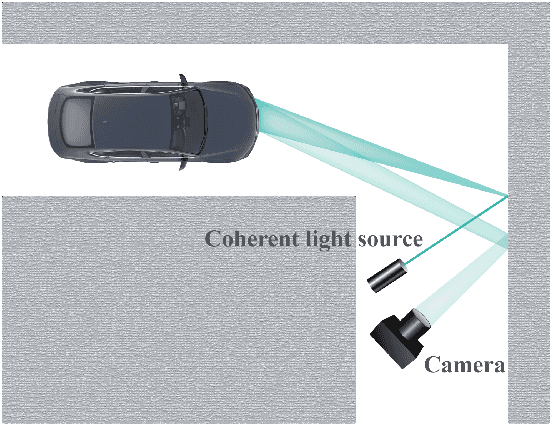
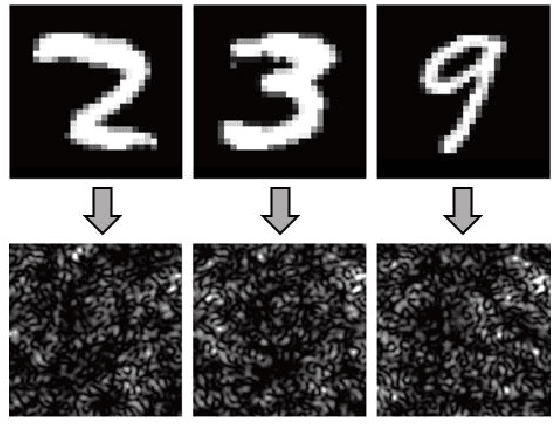


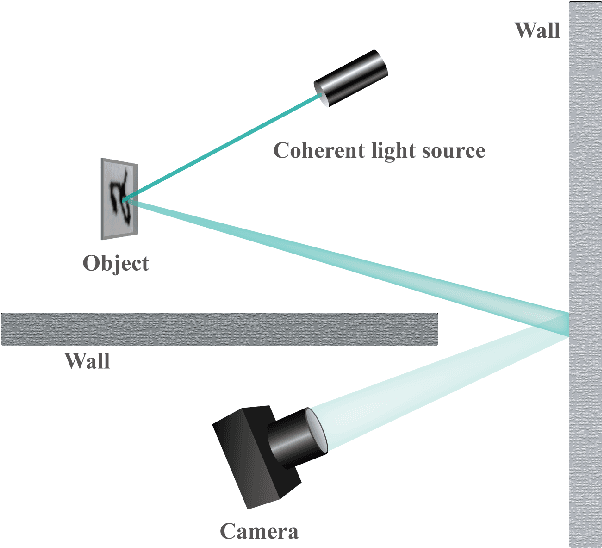
Abstract:Visual object recognition under situations in which the direct line-of-sight is blocked, such as when it is occluded around the corner, is of practical importance in a wide range of applications. With coherent illumination, the light scattered from diffusive walls forms speckle patterns that contain information of the hidden object. It is possible to realize non-line-of-sight (NLOS) recognition with these speckle patterns. We introduce a novel approach based on speckle pattern recognition with deep neural network, which is simpler and more robust than other NLOS recognition methods. Simulations and experiments are performed to verify the feasibility and performance of this approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge