Yiliang Xu
EFFOcc: A Minimal Baseline for EFficient Fusion-based 3D Occupancy Network
Jun 11, 2024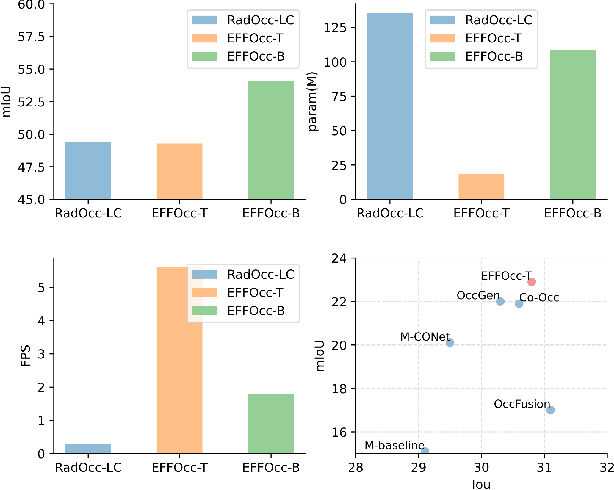
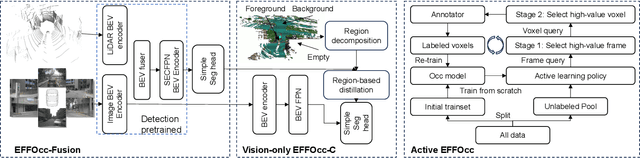
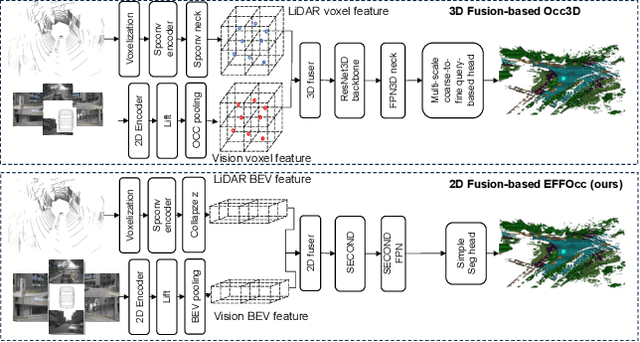

Abstract:3D occupancy prediction (Occ) is a rapidly rising challenging perception task in the field of autonomous driving which represents the driving scene as uniformly partitioned 3D voxel grids with semantics. Compared to 3D object detection, grid perception has great advantage of better recognizing irregularly shaped, unknown category, or partially occluded general objects. However, existing 3D occupancy networks (occnets) are both computationally heavy and label-hungry. In terms of model complexity, occnets are commonly composed of heavy Conv3D modules or transformers on the voxel level. In terms of label annotations requirements, occnets are supervised with large-scale expensive dense voxel labels. Model and data inefficiency, caused by excessive network parameters and label annotations requirement, severely hinder the onboard deployment of occnets. This paper proposes an efficient 3d occupancy network (EFFOcc), that targets the minimal network complexity and label requirement while achieving state-of-the-art accuracy. EFFOcc only uses simple 2D operators, and improves Occ accuracy to the state-of-the-art on multiple large-scale benchmarks: Occ3D-nuScenes, Occ3D-Waymo, and OpenOccupancy-nuScenes. On Occ3D-nuScenes benchmark, EFFOcc has only 18.4M parameters, and achieves 50.46 in terms of mean IoU (mIoU), to our knowledge, it is the occnet with minimal parameters compared with related occnets. Moreover, we propose a two-stage active learning strategy to reduce the requirements of labelled data. Active EFFOcc trained with 6\% labelled voxels achieves 47.19 mIoU, which is 95.7% fully supervised performance. The proposed EFFOcc also supports improved vision-only occupancy prediction with the aid of region-decomposed distillation. Code and demo videos will be available at https://github.com/synsin0/EFFOcc.
QuadFormer: Quadruple Transformer for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Power Line Segmentation of Aerial Images
Nov 29, 2022Abstract:Accurate segmentation of power lines in aerial images is essential to ensure the flight safety of aerial vehicles. Acquiring high-quality ground truth annotations for training a deep learning model is a laborious process. Therefore, developing algorithms that can leverage knowledge from labelled synthetic data to unlabelled real images is highly demanded. This process is studied in Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA). Recent approaches to self-training have achieved remarkable performance in UDA for semantic segmentation, which trains a model with pseudo labels on the target domain. However, the pseudo labels are noisy due to a discrepancy in the two data distributions. We identify that context dependency is important for bridging this domain gap. Motivated by this, we propose QuadFormer, a novel framework designed for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. The hierarchical quadruple transformer combines cross-attention and self-attention mechanisms to adapt transferable context. Based on cross-attentive and self-attentive feature representations, we introduce a pseudo label correction scheme to online denoise the pseudo labels and reduce the domain gap. Additionally, we present two datasets - ARPLSyn and ARPLReal to further advance research in unsupervised domain adaptive powerline segmentation. Finally, experimental results indicate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance for the domain adaptive power line segmentation on ARPLSyn$\rightarrow$TTTPLA and ARPLSyn$\rightarrow$ARPLReal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge