Yi-Cheng Chen
Miutsu: NTU's TaskBot for the Alexa Prize
May 16, 2022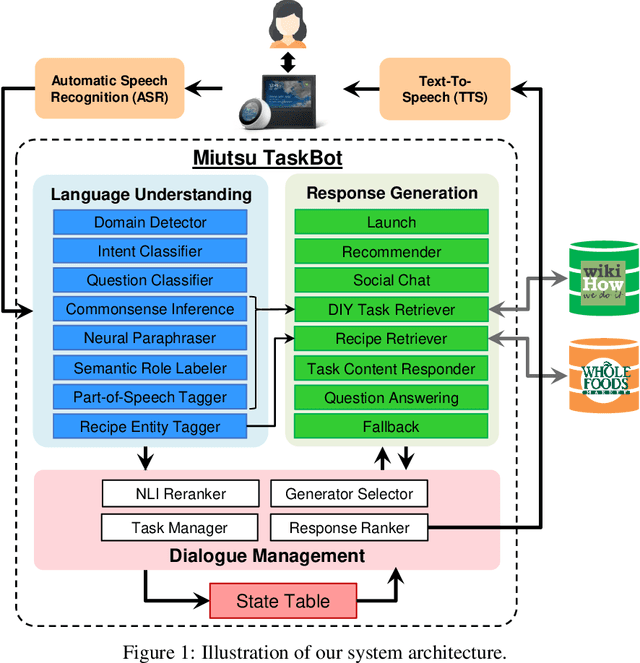
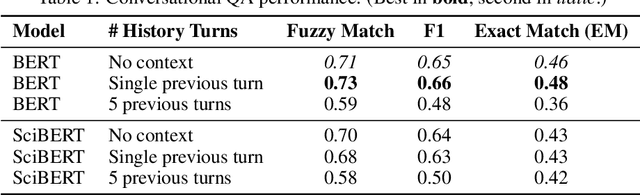
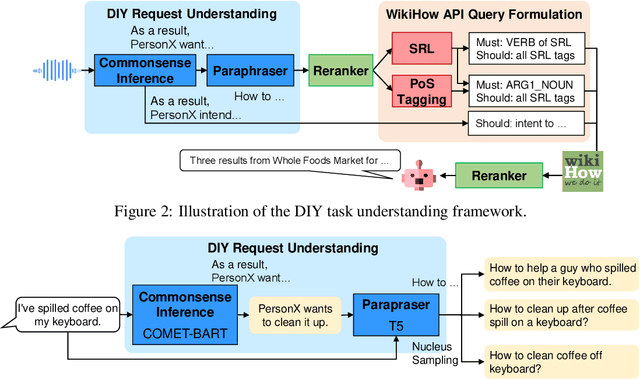
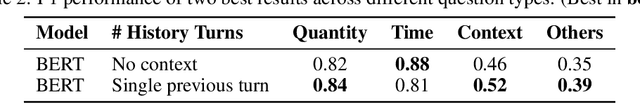
Abstract:This paper introduces Miutsu, National Taiwan University's Alexa Prize TaskBot, which is designed to assist users in completing tasks requiring multiple steps and decisions in two different domains -- home improvement and cooking. We overview our system design and architectural goals, and detail the proposed core elements, including question answering, task retrieval, social chatting, and various conversational modules. A dialogue flow is proposed to provide a robust and engaging conversation when handling complex tasks. We discuss the faced challenges during the competition and potential future work.
Accurate and Generalizable Quantitative Scoring of Liver Steatosis from Ultrasound Images via Scalable Deep Learning
Oct 12, 2021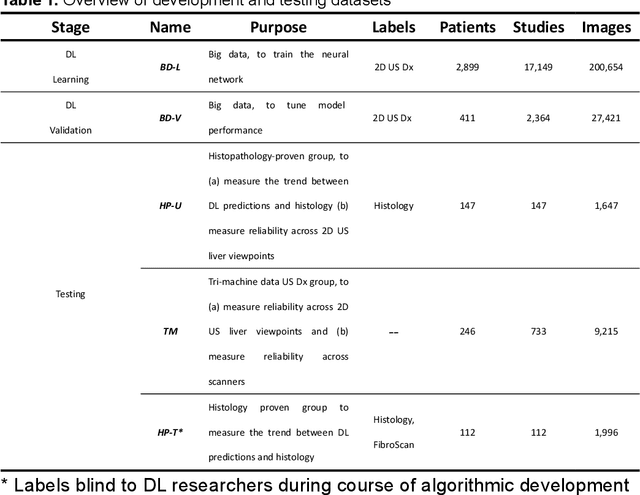


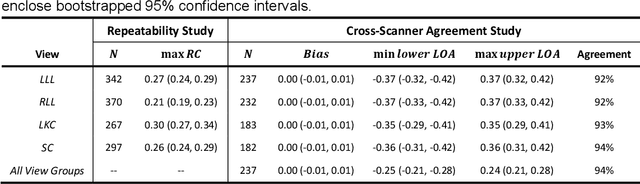
Abstract:Background & Aims: Hepatic steatosis is a major cause of chronic liver disease. 2D ultrasound is the most widely used non-invasive tool for screening and monitoring, but associated diagnoses are highly subjective. We developed a scalable deep learning (DL) algorithm for quantitative scoring of liver steatosis from 2D ultrasound images. Approach & Results: Using retrospectively collected multi-view ultrasound data from 3,310 patients, 19,513 studies, and 228,075 images, we trained a DL algorithm to diagnose steatosis stages (healthy, mild, moderate, or severe) from ultrasound diagnoses. Performance was validated on two multi-scanner unblinded and blinded (initially to DL developer) histology-proven cohorts (147 and 112 patients) with histopathology fatty cell percentage diagnoses, and a subset with FibroScan diagnoses. We also quantified reliability across scanners and viewpoints. Results were evaluated using Bland-Altman and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. The DL algorithm demonstrates repeatable measurements with a moderate number of images (3 for each viewpoint) and high agreement across 3 premium ultrasound scanners. High diagnostic performance was observed across all viewpoints: area under the curves of the ROC to classify >=mild, >=moderate, =severe steatosis grades were 0.85, 0.90, and 0.93, respectively. The DL algorithm outperformed or performed at least comparably to FibroScan with statistically significant improvements for all levels on the unblinded histology-proven cohort, and for =severe steatosis on the blinded histology-proven cohort. Conclusions: The DL algorithm provides a reliable quantitative steatosis assessment across view and scanners on two multi-scanner cohorts. Diagnostic performance was high with comparable or better performance than FibroScan.
A Time-dependent SIR model for COVID-19
Feb 28, 2020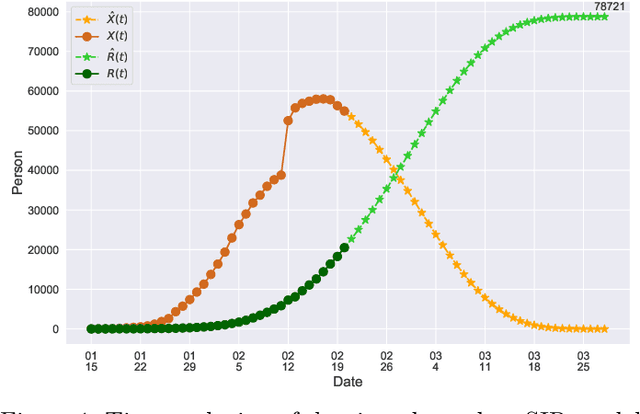
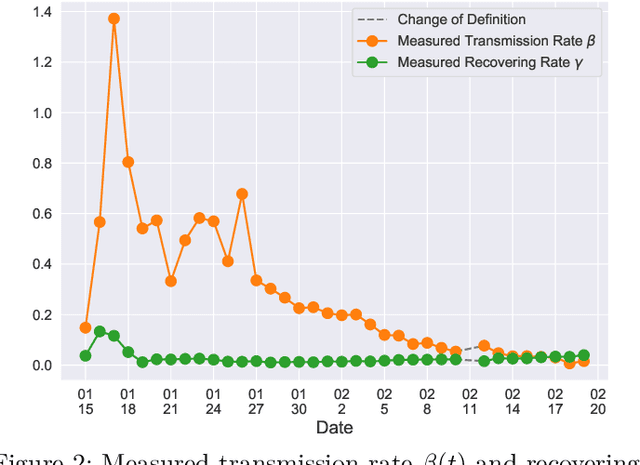

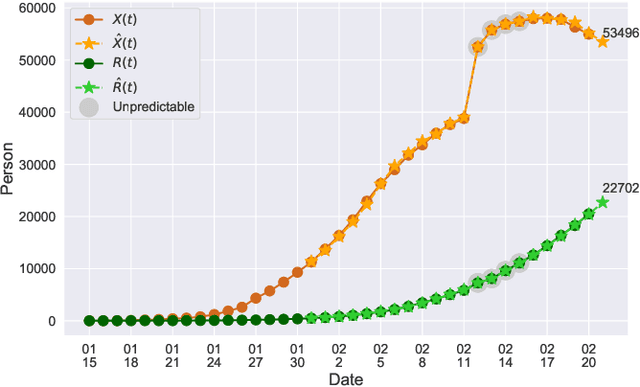
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a mathematical model for analyzing and predicting the number of confirmed cases of COVID-19. Our model is a time-dependent susceptible-infected-recovered (SIR) model that tracks two time series: (i) the transmission rate at time $t$ and (ii) the recovering rate at time $t$. Our time-dependent SIR method is better than the traditional static SIR model as it can adapt to the change of contagious disease control policies such as city lockdowns. Moreover, it is also more robust than the direct estimation of the number of confirmed cases, as a sudden change of the definition of the number of confirmed cases might result in a spike of the number of new cases. Using the data set provided by the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China (NHC) [2], we show that the one-day prediction errors for the numbers of confirmed cases are less than $3\%$ except the day when the definition of the number of confirmed cases is changed. Also, the turning point, defined as the day that the transmission rate is less than the recovering rate, is predicted to be Feb. 17, 2020. After that day, the basic reproduction number, known as the $R_0(t)$ value, is less than $1$ if the current contagious disease control policies are maintained in China. In that case, the total number of confirmed cases is predicted to be less than $80,000$ cases in China under our deterministic model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge