Yasin Yazici
SemiCurv: Semi-Supervised Curvilinear Structure Segmentation
May 19, 2022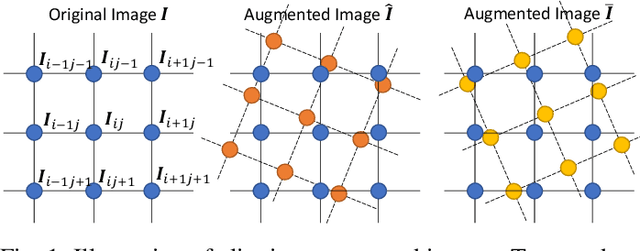
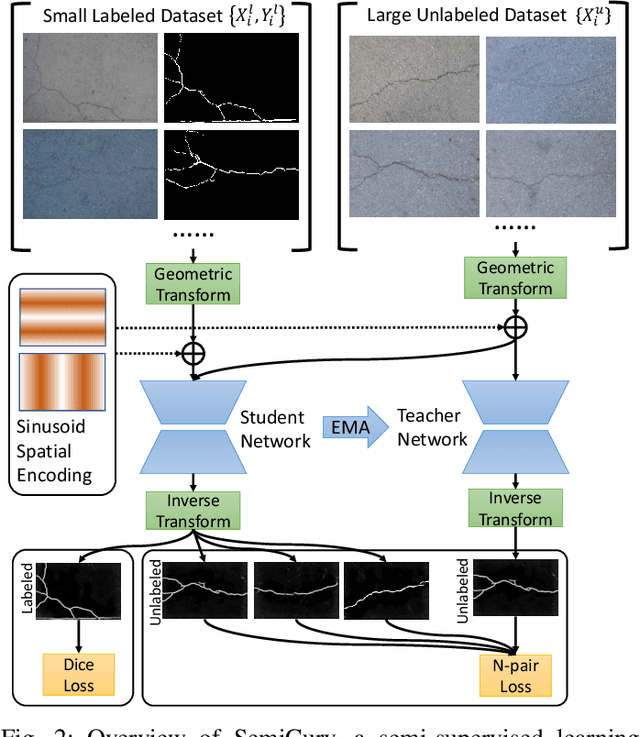
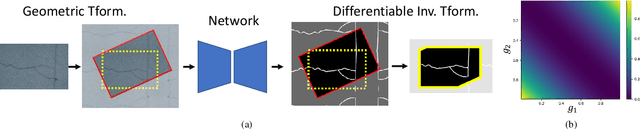
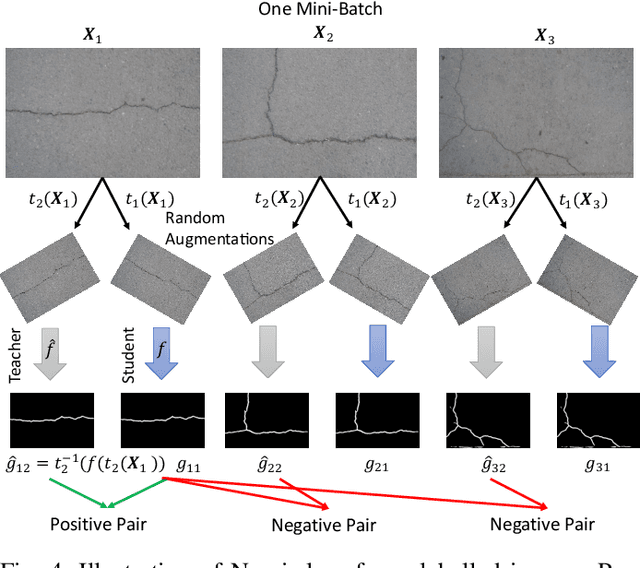
Abstract:Recent work on curvilinear structure segmentation has mostly focused on backbone network design and loss engineering. The challenge of collecting labelled data, an expensive and labor intensive process, has been overlooked. While labelled data is expensive to obtain, unlabelled data is often readily available. In this work, we propose SemiCurv, a semi-supervised learning (SSL) framework for curvilinear structure segmentation that is able to utilize such unlabelled data to reduce the labelling burden. Our framework addresses two key challenges in formulating curvilinear segmentation in a semi-supervised manner. First, to fully exploit the power of consistency based SSL, we introduce a geometric transformation as strong data augmentation and then align segmentation predictions via a differentiable inverse transformation to enable the computation of pixel-wise consistency. Second, the traditional mean square error (MSE) on unlabelled data is prone to collapsed predictions and this issue exacerbates with severe class imbalance (significantly more background pixels). We propose a N-pair consistency loss to avoid trivial predictions on unlabelled data. We evaluate SemiCurv on six curvilinear segmentation datasets, and find that with no more than 5% of the labelled data, it achieves close to 95% of the performance relative to its fully supervised counterpart.
Revisiting Pretraining for Semi-Supervised Learning in the Low-Label Regime
May 06, 2022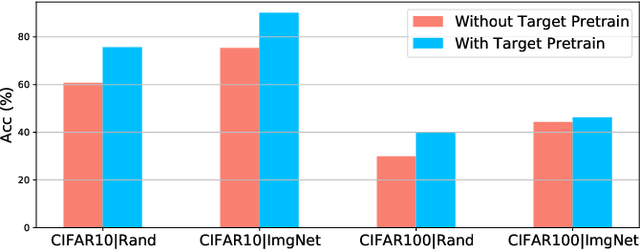
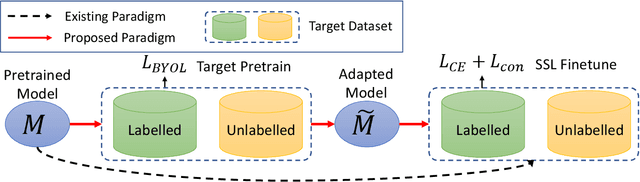
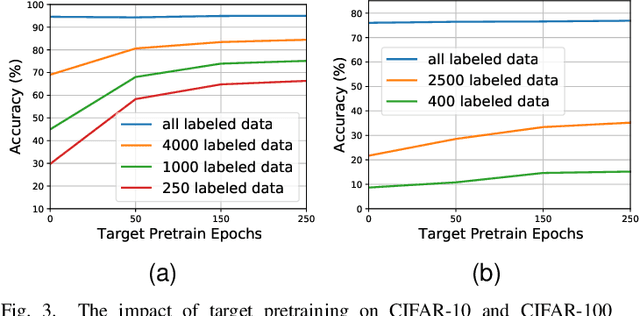
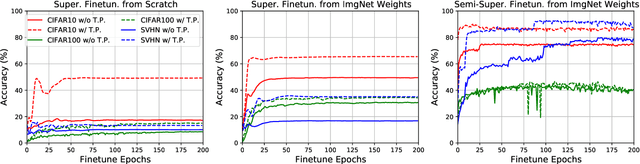
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) addresses the lack of labeled data by exploiting large unlabeled data through pseudolabeling. However, in the extremely low-label regime, pseudo labels could be incorrect, a.k.a. the confirmation bias, and the pseudo labels will in turn harm the network training. Recent studies combined finetuning (FT) from pretrained weights with SSL to mitigate the challenges and claimed superior results in the low-label regime. In this work, we first show that the better pretrained weights brought in by FT account for the state-of-the-art performance, and importantly that they are universally helpful to off-the-shelf semi-supervised learners. We further argue that direct finetuning from pretrained weights is suboptimal due to covariate shift and propose a contrastive target pretraining step to adapt model weights towards target dataset. We carried out extensive experiments on both classification and segmentation tasks by doing target pretraining then followed by semi-supervised finetuning. The promising results validate the efficacy of target pretraining for SSL, in particular in the low-label regime.
Empirical Analysis of Overfitting and Mode Drop in GAN Training
Jun 25, 2020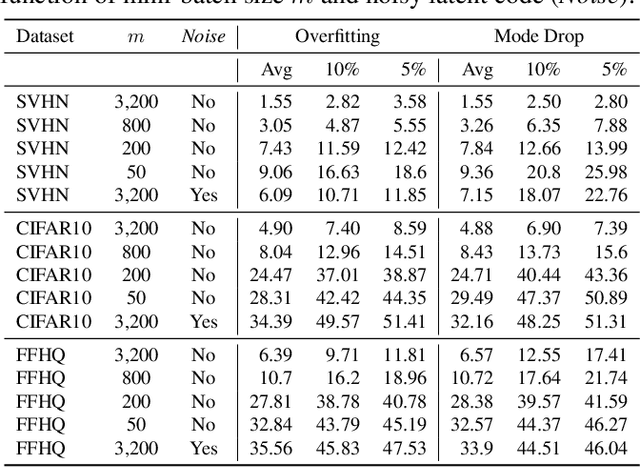

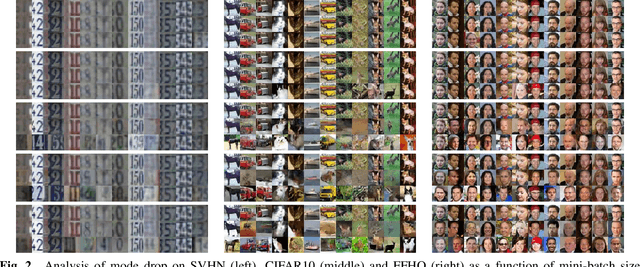
Abstract:We examine two key questions in GAN training, namely overfitting and mode drop, from an empirical perspective. We show that when stochasticity is removed from the training procedure, GANs can overfit and exhibit almost no mode drop. Our results shed light on important characteristics of the GAN training procedure. They also provide evidence against prevailing intuitions that GANs do not memorize the training set, and that mode dropping is mainly due to properties of the GAN objective rather than how it is optimized during training.
Classification Representations Can be Reused for Downstream Generations
Apr 16, 2020
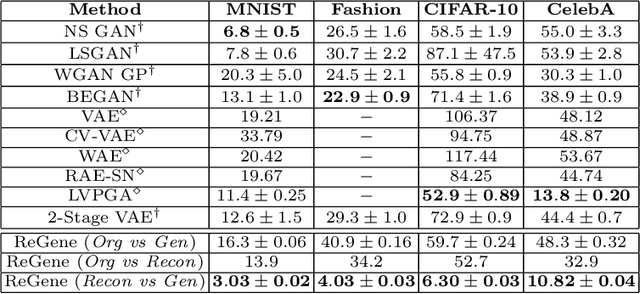
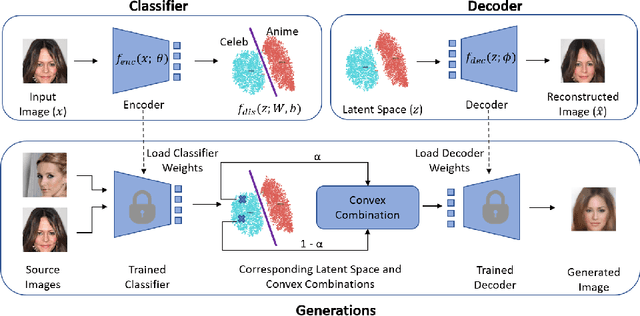
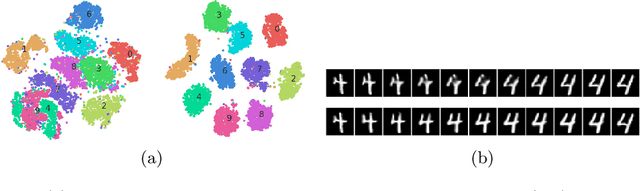
Abstract:Contrary to the convention of using supervision for class-conditioned $\it{generative}$ $\it{modeling}$, this work explores and demonstrates the feasibility of a learned supervised representation space trained on a discriminative classifier for the $\it{downstream}$ task of sample generation. Unlike generative modeling approaches that aim to $\it{model}$ the manifold distribution, we directly $\it{represent}$ the given data manifold in the classification space and leverage properties of latent space representations to generate new representations that are guaranteed to be in the same class. Interestingly, such representations allow for controlled sample generations for any given class from existing samples and do not require enforcing prior distribution. We show that these latent space representations can be smartly manipulated (using convex combinations of $n$ samples, $n\geq2$) to yield meaningful sample generations. Experiments on image datasets of varying resolutions demonstrate that downstream generations have higher classification accuracy than existing conditional generative models while being competitive in terms of FID.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge