Yaoyiran Li
CALRec: Contrastive Alignment of Generative LLMs For Sequential Recommendation
May 03, 2024Abstract:Traditional recommender systems such as matrix factorization methods rely on learning a shared dense embedding space to represent both items and user preferences. Sequence models such as RNN, GRUs, and, recently, Transformers have also excelled in the task of sequential recommendation. This task requires understanding the sequential structure present in users' historical interactions to predict the next item they may like. Building upon the success of Large Language Models (LLMs) in a variety of tasks, researchers have recently explored using LLMs that are pretrained on vast corpora of text for sequential recommendation. To use LLMs in sequential recommendations, both the history of user interactions and the model's prediction of the next item are expressed in text form. We propose CALRec, a two-stage LLM finetuning framework that finetunes a pretrained LLM in a two-tower fashion using a mixture of two contrastive losses and a language modeling loss: the LLM is first finetuned on a data mixture from multiple domains followed by another round of target domain finetuning. Our model significantly outperforms many state-of-the-art baselines (+37% in Recall@1 and +24% in NDCG@10) and systematic ablation studies reveal that (i) both stages of finetuning are crucial, and, when combined, we achieve improved performance, and (ii) contrastive alignment is effective among the target domains explored in our experiments.
Self-Augmented In-Context Learning for Unsupervised Word Translation
Feb 15, 2024Abstract:Recent work has shown that, while large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong word translation or bilingual lexicon induction (BLI) capabilities in few-shot setups, they still cannot match the performance of 'traditional' mapping-based approaches in the unsupervised scenario where no seed translation pairs are available, especially for lower-resource languages. To address this challenge with LLMs, we propose self-augmented in-context learning (SAIL) for unsupervised BLI: starting from a zero-shot prompt, SAIL iteratively induces a set of high-confidence word translation pairs for in-context learning (ICL) from an LLM, which it then reapplies to the same LLM in the ICL fashion. Our method shows substantial gains over zero-shot prompting of LLMs on two established BLI benchmarks spanning a wide range of language pairs, also outperforming mapping-based baselines across the board. In addition to achieving state-of-the-art unsupervised BLI performance, we also conduct comprehensive analyses on SAIL and discuss its limitations.
On Bilingual Lexicon Induction with Large Language Models
Oct 21, 2023Abstract:Bilingual Lexicon Induction (BLI) is a core task in multilingual NLP that still, to a large extent, relies on calculating cross-lingual word representations. Inspired by the global paradigm shift in NLP towards Large Language Models (LLMs), we examine the potential of the latest generation of LLMs for the development of bilingual lexicons. We ask the following research question: Is it possible to prompt and fine-tune multilingual LLMs (mLLMs) for BLI, and how does this approach compare against and complement current BLI approaches? To this end, we systematically study 1) zero-shot prompting for unsupervised BLI and 2) few-shot in-context prompting with a set of seed translation pairs, both without any LLM fine-tuning, as well as 3) standard BLI-oriented fine-tuning of smaller LLMs. We experiment with 18 open-source text-to-text mLLMs of different sizes (from 0.3B to 13B parameters) on two standard BLI benchmarks covering a range of typologically diverse languages. Our work is the first to demonstrate strong BLI capabilities of text-to-text mLLMs. The results reveal that few-shot prompting with in-context examples from nearest neighbours achieves the best performance, establishing new state-of-the-art BLI scores for many language pairs. We also conduct a series of in-depth analyses and ablation studies, providing more insights on BLI with (m)LLMs, also along with their limitations.
Translation-Enhanced Multilingual Text-to-Image Generation
May 30, 2023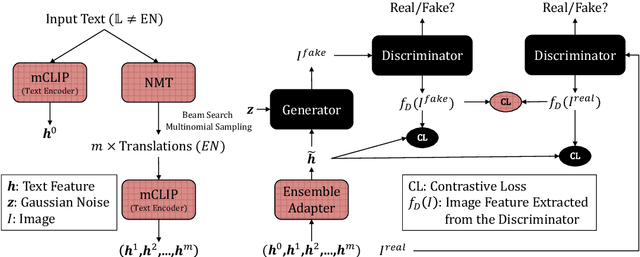
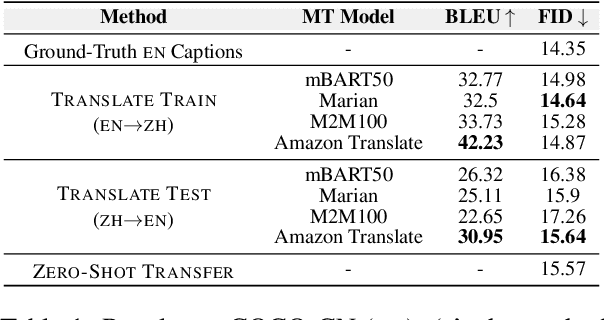
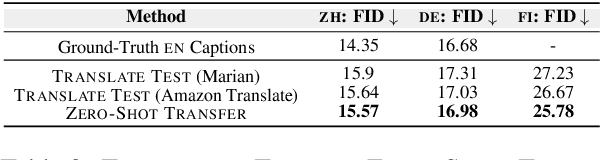

Abstract:Research on text-to-image generation (TTI) still predominantly focuses on the English language due to the lack of annotated image-caption data in other languages; in the long run, this might widen inequitable access to TTI technology. In this work, we thus investigate multilingual TTI (termed mTTI) and the current potential of neural machine translation (NMT) to bootstrap mTTI systems. We provide two key contributions. 1) Relying on a multilingual multi-modal encoder, we provide a systematic empirical study of standard methods used in cross-lingual NLP when applied to mTTI: Translate Train, Translate Test, and Zero-Shot Transfer. 2) We propose Ensemble Adapter (EnsAd), a novel parameter-efficient approach that learns to weigh and consolidate the multilingual text knowledge within the mTTI framework, mitigating the language gap and thus improving mTTI performance. Our evaluations on standard mTTI datasets COCO-CN, Multi30K Task2, and LAION-5B demonstrate the potential of translation-enhanced mTTI systems and also validate the benefits of the proposed EnsAd which derives consistent gains across all datasets. Further investigations on model variants, ablation studies, and qualitative analyses provide additional insights on the inner workings of the proposed mTTI approaches.
Improving Bilingual Lexicon Induction with Cross-Encoder Reranking
Oct 30, 2022



Abstract:Bilingual lexicon induction (BLI) with limited bilingual supervision is a crucial yet challenging task in multilingual NLP. Current state-of-the-art BLI methods rely on the induction of cross-lingual word embeddings (CLWEs) to capture cross-lingual word similarities; such CLWEs are obtained 1) via traditional static models (e.g., VecMap), or 2) by extracting type-level CLWEs from multilingual pretrained language models (mPLMs), or 3) through combining the former two options. In this work, we propose a novel semi-supervised post-hoc reranking method termed BLICEr (BLI with Cross-Encoder Reranking), applicable to any precalculated CLWE space, which improves their BLI capability. The key idea is to 'extract' cross-lingual lexical knowledge from mPLMs, and then combine it with the original CLWEs. This crucial step is done via 1) creating a word similarity dataset, comprising positive word pairs (i.e., true translations) and hard negative pairs induced from the original CLWE space, and then 2) fine-tuning an mPLM (e.g., mBERT or XLM-R) in a cross-encoder manner to predict the similarity scores. At inference, we 3) combine the similarity score from the original CLWE space with the score from the BLI-tuned cross-encoder. BLICEr establishes new state-of-the-art results on two standard BLI benchmarks spanning a wide spectrum of diverse languages: it substantially outperforms a series of strong baselines across the board. We also validate the robustness of BLICEr with different CLWEs.
Improving Word Translation via Two-Stage Contrastive Learning
Mar 26, 2022



Abstract:Word translation or bilingual lexicon induction (BLI) is a key cross-lingual task, aiming to bridge the lexical gap between different languages. In this work, we propose a robust and effective two-stage contrastive learning framework for the BLI task. At Stage C1, we propose to refine standard cross-lingual linear maps between static word embeddings (WEs) via a contrastive learning objective; we also show how to integrate it into the self-learning procedure for even more refined cross-lingual maps. In Stage C2, we conduct BLI-oriented contrastive fine-tuning of mBERT, unlocking its word translation capability. We also show that static WEs induced from the `C2-tuned' mBERT complement static WEs from Stage C1. Comprehensive experiments on standard BLI datasets for diverse languages and different experimental setups demonstrate substantial gains achieved by our framework. While the BLI method from Stage C1 already yields substantial gains over all state-of-the-art BLI methods in our comparison, even stronger improvements are met with the full two-stage framework: e.g., we report gains for 112/112 BLI setups, spanning 28 language pairs.
Emergent Communication Pretraining for Few-Shot Machine Translation
Nov 02, 2020



Abstract:While state-of-the-art models that rely upon massively multilingual pretrained encoders achieve sample efficiency in downstream applications, they still require abundant amounts of unlabelled text. Nevertheless, most of the world's languages lack such resources. Hence, we investigate a more radical form of unsupervised knowledge transfer in the absence of linguistic data. In particular, for the first time we pretrain neural networks via emergent communication from referential games. Our key assumption is that grounding communication on images---as a crude approximation of real-world environments---inductively biases the model towards learning natural languages. On the one hand, we show that this substantially benefits machine translation in few-shot settings. On the other hand, this also provides an extrinsic evaluation protocol to probe the properties of emergent languages ex vitro. Intuitively, the closer they are to natural languages, the higher the gains from pretraining on them should be. For instance, in this work we measure the influence of communication success and maximum sequence length on downstream performances. Finally, we introduce a customised adapter layer and annealing strategies for the regulariser of maximum-a-posteriori inference during fine-tuning. These turn out to be crucial to facilitate knowledge transfer and prevent catastrophic forgetting. Compared to a recurrent baseline, our method yields gains of $59.0\%$$\sim$$147.6\%$ in BLEU score with only $500$ NMT training instances and $65.1\%$$\sim$$196.7\%$ with $1,000$ NMT training instances across four language pairs. These proof-of-concept results reveal the potential of emergent communication pretraining for both natural language processing tasks in resource-poor settings and extrinsic evaluation of artificial languages.
Two-Headed Monster And Crossed Co-Attention Networks
Nov 10, 2019



Abstract:This paper presents some preliminary investigations of a new co-attention mechanism in neural transduction models. We propose a paradigm, termed Two-Headed Monster (THM), which consists of two symmetric encoder modules and one decoder module connected with co-attention. As a specific and concrete implementation of THM, Crossed Co-Attention Networks (CCNs) are designed based on the Transformer model. We demonstrate CCNs on WMT 2014 EN-DE and WMT 2016 EN-FI translation tasks and our model outperforms the strong Transformer baseline by 0.51 (big) and 0.74 (base) BLEU points on EN-DE and by 0.17 (big) and 0.47 (base) BLEU points on EN-FI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge