Yaoyi Chen
Operator Forces For Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics
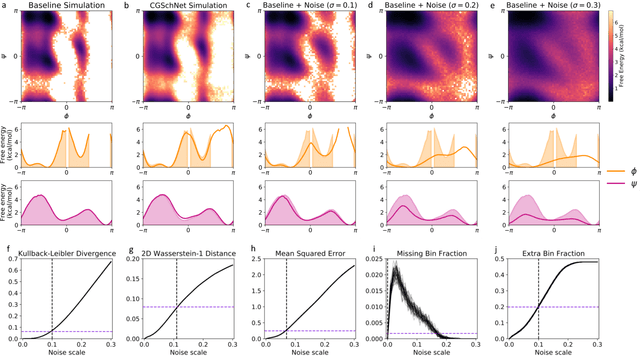
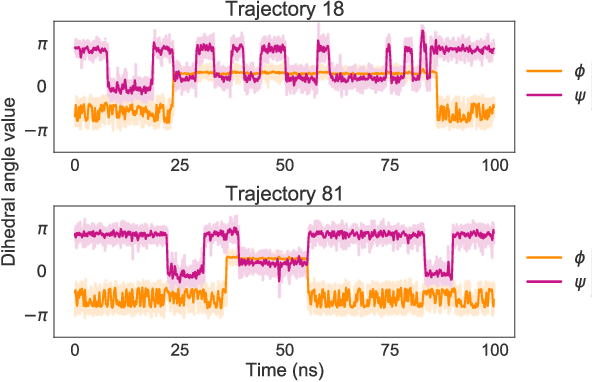
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Coarse-grained (CG) molecular dynamics simulations extend the length and time scale of atomistic simulations by replacing groups of correlated atoms with CG beads. Machine-learned coarse-graining (MLCG) has recently emerged as a promising approach to construct highly accurate force fields for CG molecular dynamics. However, the calibration of MLCG force fields typically hinges on force matching, which demands extensive reference atomistic trajectories with corresponding force labels. In practice, atomistic forces are often not recorded, making traditional force matching infeasible on pre-existing datasets. Recently, noise-based kernels have been introduced to adapt force matching to the low-data regime, including situations in which reference atomistic forces are not present. While this approach produces force fields which recapitulate slow collective motion, it introduces significant local distortions due to the corrupting effects of the noise-based kernel. In this work, we introduce more general kernels based on normalizing flows that substantially reduce these local distortions while preserving global conformational accuracy. We demonstrate our method on small proteins, showing that flow-based kernels can generate high-quality CG forces solely from configurational samples.
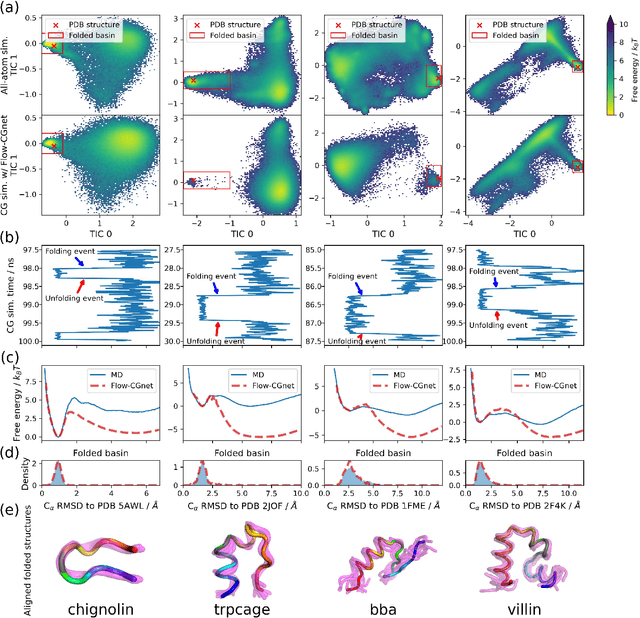
Navigating protein landscapes with a machine-learned transferable coarse-grained model
Oct 27, 2023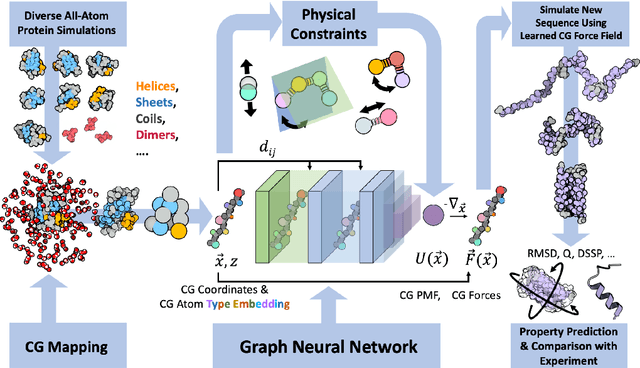
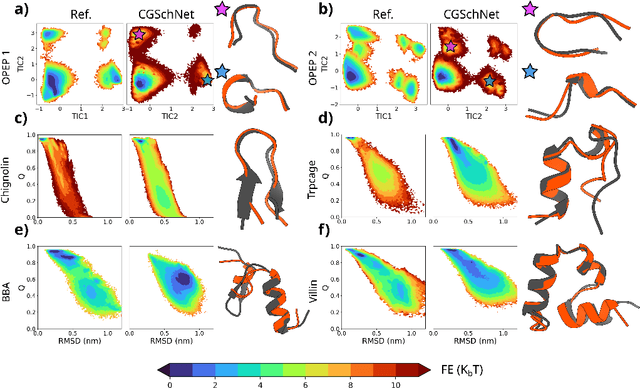

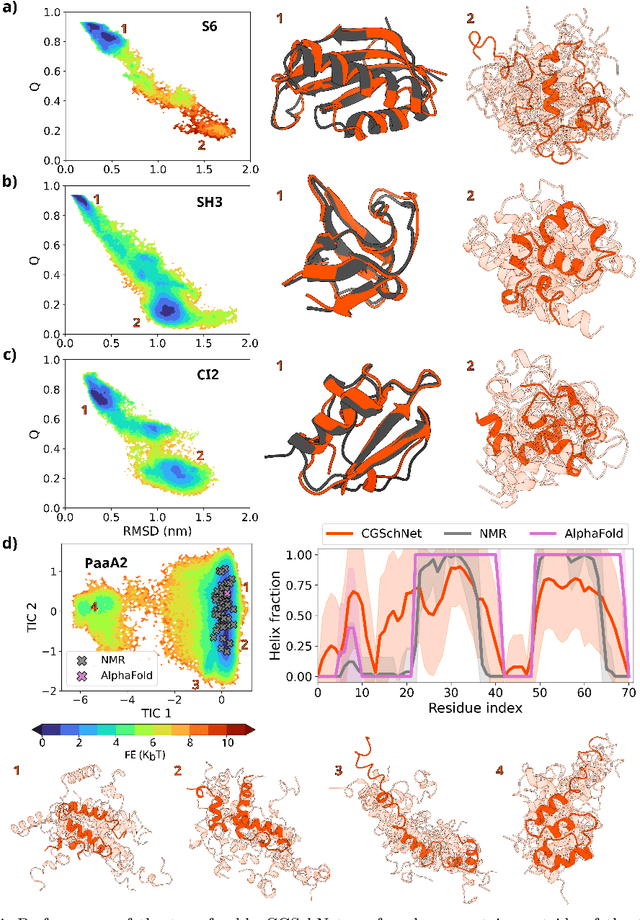
Abstract:The most popular and universally predictive protein simulation models employ all-atom molecular dynamics (MD), but they come at extreme computational cost. The development of a universal, computationally efficient coarse-grained (CG) model with similar prediction performance has been a long-standing challenge. By combining recent deep learning methods with a large and diverse training set of all-atom protein simulations, we here develop a bottom-up CG force field with chemical transferability, which can be used for extrapolative molecular dynamics on new sequences not used during model parametrization. We demonstrate that the model successfully predicts folded structures, intermediates, metastable folded and unfolded basins, and the fluctuations of intrinsically disordered proteins while it is several orders of magnitude faster than an all-atom model. This showcases the feasibility of a universal and computationally efficient machine-learned CG model for proteins.
Statistically Optimal Force Aggregation for Coarse-Graining Molecular Dynamics
Feb 14, 2023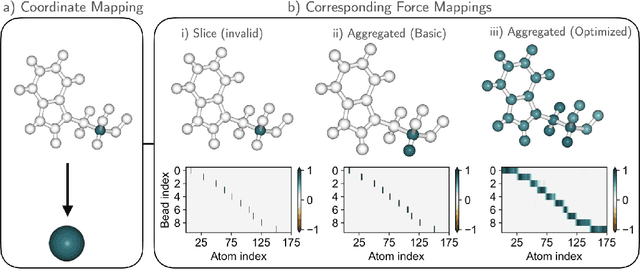
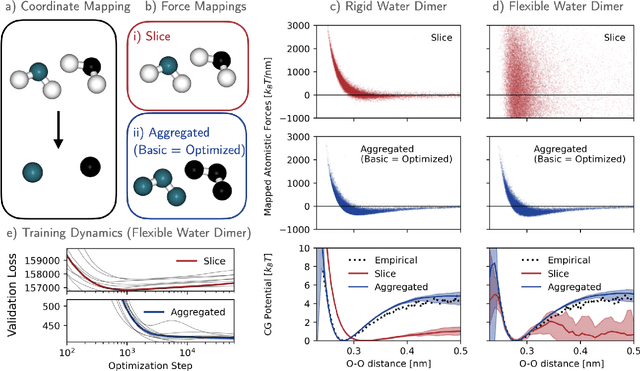
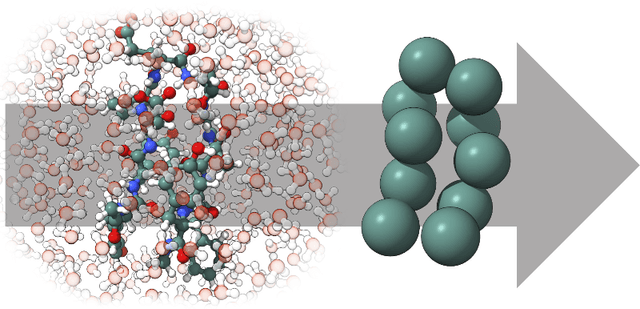
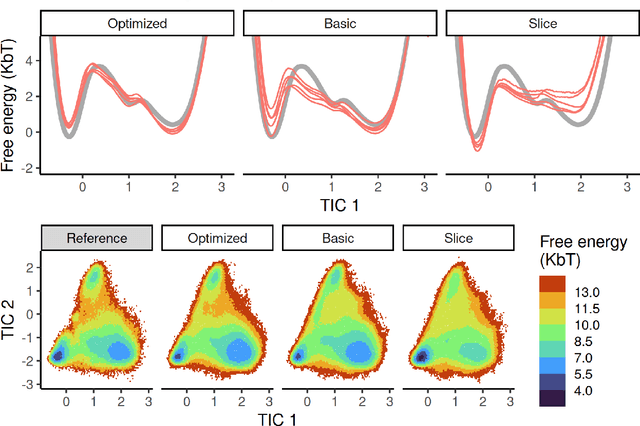
Abstract:Machine-learned coarse-grained (CG) models have the potential for simulating large molecular complexes beyond what is possible with atomistic molecular dynamics. However, training accurate CG models remains a challenge. A widely used methodology for learning CG force-fields maps forces from all-atom molecular dynamics to the CG representation and matches them with a CG force-field on average. We show that there is flexibility in how to map all-atom forces to the CG representation, and that the most commonly used mapping methods are statistically inefficient and potentially even incorrect in the presence of constraints in the all-atom simulation. We define an optimization statement for force mappings and demonstrate that substantially improved CG force-fields can be learned from the same simulation data when using optimized force maps. The method is demonstrated on the miniproteins Chignolin and Tryptophan Cage and published as open-source code.
Force-matching Coarse-Graining without Forces
Mar 21, 2022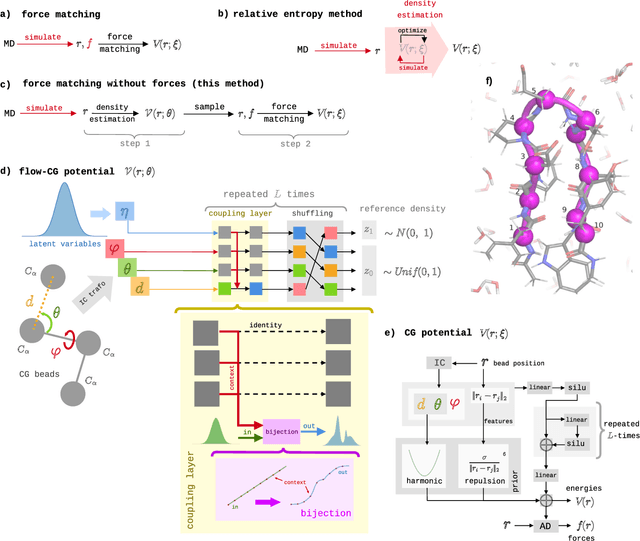
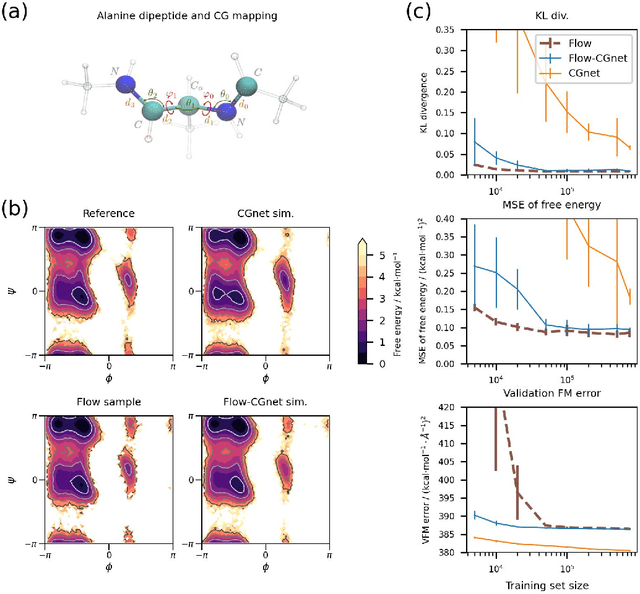
Abstract:Coarse-grained (CG) molecular simulations have become a standard tool to study molecular processes on time-~and length-scales inaccessible to all-atom simulations. Learning CG force fields from all-atom data has mainly relied on force-matching and relative entropy minimization. Force-matching is straightforward to implement but requires the forces on the CG particles to be saved during all-atom simulation, and because these instantaneous forces depend on all degrees of freedom, they provide a very noisy signal that makes training the CG force field data inefficient. Relative entropy minimization does not require forces to be saved and is more data-efficient, but requires the CG model to be re-simulated during the iterative training procedure, which can make the training procedure extremely costly or lead to failure to converge. Here we present \emph{flow-matching}, a new training method for CG force fields that combines the advantages of force-matching and relative entropy minimization by leveraging normalizing flows, a generative deep learning method. Flow-matching first trains a normalizing flow to represent the CG probability density by using relative entropy minimization without suffering from the re-simulation problem because flows can directly sample from the equilibrium distribution they represent. Subsequently, the forces of the flow are used to train a CG force field by matching the coarse-grained forces directly, which is a much easier problem than traditional force-matching as it does not suffer from the noise problem. Besides not requiring forces, flow-matching also outperforms classical force-matching by an order of magnitude in terms of data efficiency and produces CG models that can capture the folding and unfolding of small proteins.
Machine Learning Implicit Solvation for Molecular Dynamics
Jun 14, 2021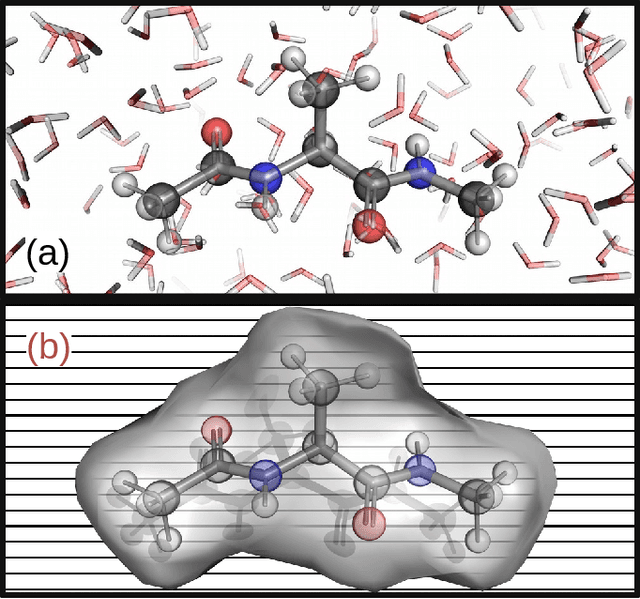
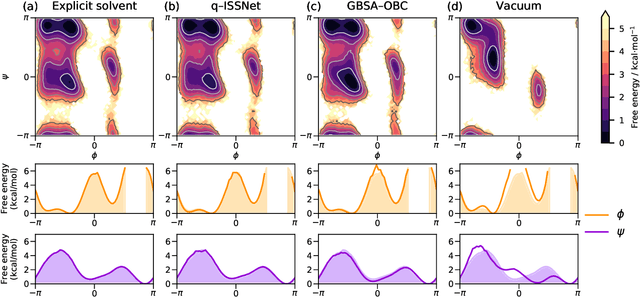
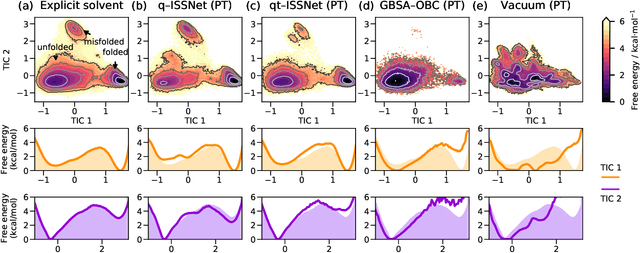
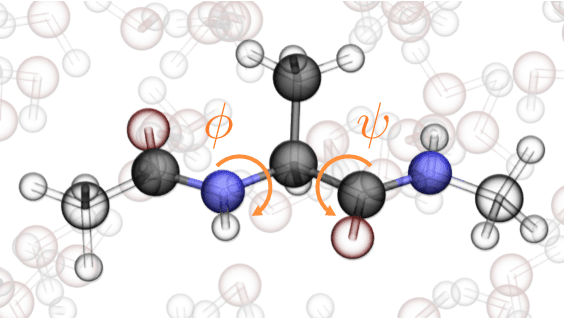
Abstract:Accurate modeling of the solvent environment for biological molecules is crucial for computational biology and drug design. A popular approach to achieve long simulation time scales for large system sizes is to incorporate the effect of the solvent in a mean-field fashion with implicit solvent models. However, a challenge with existing implicit solvent models is that they often lack accuracy or certain physical properties compared to explicit solvent models, as the many-body effects of the neglected solvent molecules is difficult to model as a mean field. Here, we leverage machine learning (ML) and multi-scale coarse graining (CG) in order to learn implicit solvent models that can approximate the energetic and thermodynamic properties of a given explicit solvent model with arbitrary accuracy, given enough training data. Following the previous ML--CG models CGnet and CGSchnet, we introduce ISSNet, a graph neural network, to model the implicit solvent potential of mean force. ISSNet can learn from explicit solvent simulation data and be readily applied to MD simulations. We compare the solute conformational distributions under different solvation treatments for two peptide systems. The results indicate that ISSNet models can outperform widely-used generalized Born and surface area models in reproducing the thermodynamics of small protein systems with respect to explicit solvent. The success of this novel method demonstrates the potential benefit of applying machine learning methods in accurate modeling of solvent effects for in silico research and biomedical applications.
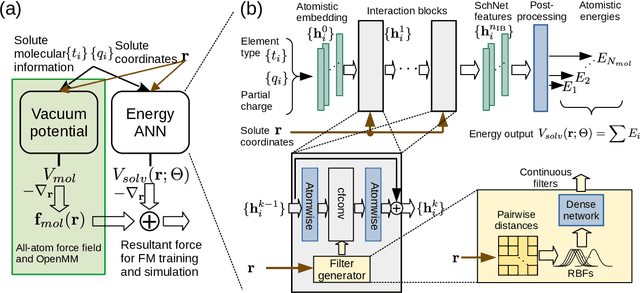
Coarse Graining Molecular Dynamics with Graph Neural Networks
Aug 21, 2020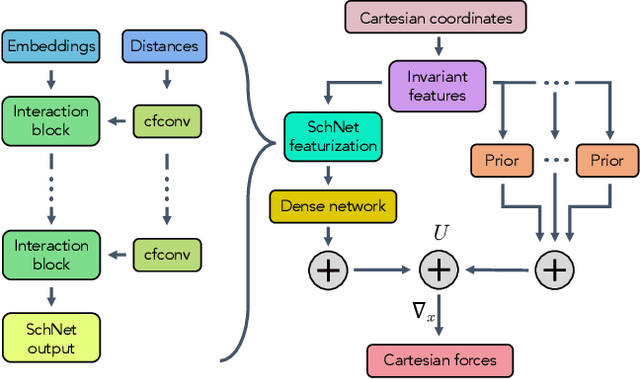
Abstract:Coarse graining enables the investigation of molecular dynamics for larger systems and at longer timescales than is possible at atomic resolution. However, a coarse graining model must be formulated such that the conclusions we draw from it are consistent with the conclusions we would draw from a model at a finer level of detail. It has been proven that a force matching scheme defines a thermodynamically consistent coarse-grained model for an atomistic system in the variational limit. Wang et al. [ACS Cent. Sci. 5, 755 (2019)] demonstrated that the existence of such a variational limit enables the use of a supervised machine learning framework to generate a coarse-grained force field, which can then be used for simulation in the coarse-grained space. Their framework, however, requires the manual input of molecular features upon which to machine learn the force field. In the present contribution, we build upon the advance of Wang et al.and introduce a hybrid architecture for the machine learning of coarse-grained force fields that learns their own features via a subnetwork that leverages continuous filter convolutions on a graph neural network architecture. We demonstrate that this framework succeeds at reproducing the thermodynamics for small biomolecular systems. Since the learned molecular representations are inherently transferable, the architecture presented here sets the stage for the development of machine-learned, coarse-grained force fields that are transferable across molecular systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge