Yaosen Chen
GeoMVD: Geometry-Enhanced Multi-View Generation Model Based on Geometric Information Extraction
Nov 19, 2025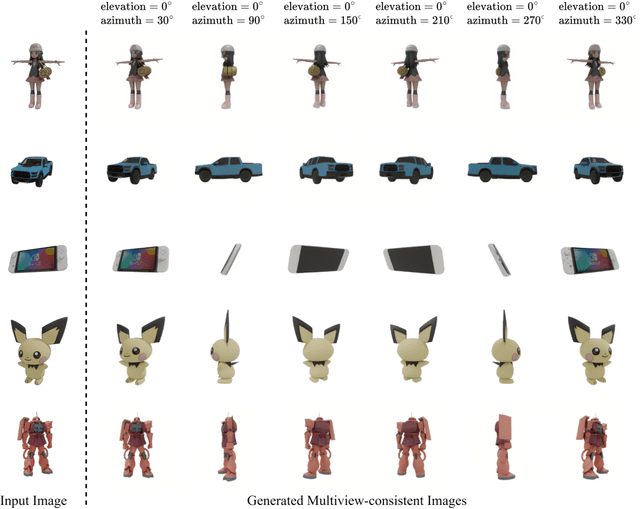
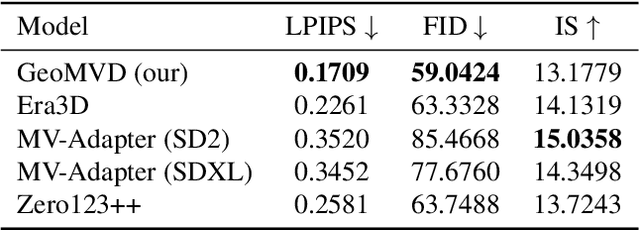
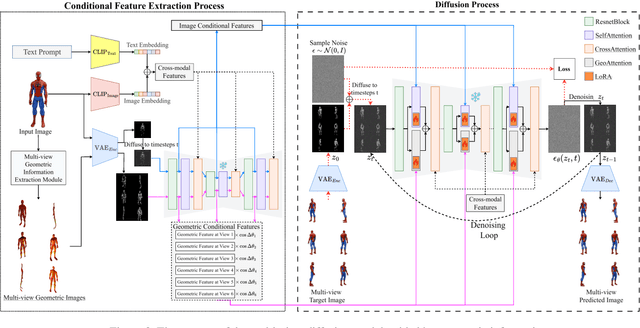
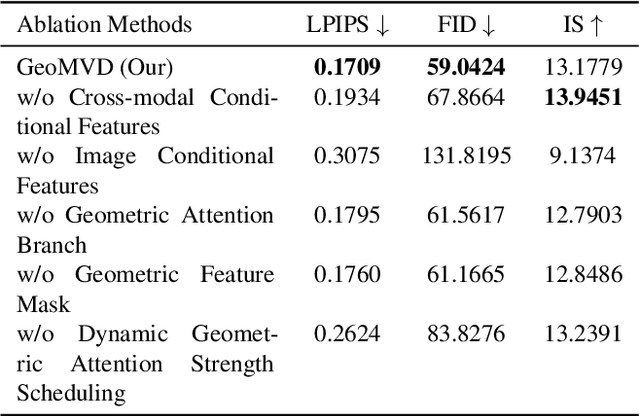
Abstract:Multi-view image generation holds significant application value in computer vision, particularly in domains like 3D reconstruction, virtual reality, and augmented reality. Most existing methods, which rely on extending single images, face notable computational challenges in maintaining cross-view consistency and generating high-resolution outputs. To address these issues, we propose the Geometry-guided Multi-View Diffusion Model, which incorporates mechanisms for extracting multi-view geometric information and adjusting the intensity of geometric features to generate images that are both consistent across views and rich in detail. Specifically, we design a multi-view geometry information extraction module that leverages depth maps, normal maps, and foreground segmentation masks to construct a shared geometric structure, ensuring shape and structural consistency across different views. To enhance consistency and detail restoration during generation, we develop a decoupled geometry-enhanced attention mechanism that strengthens feature focus on key geometric details, thereby improving overall image quality and detail preservation. Furthermore, we apply an adaptive learning strategy that fine-tunes the model to better capture spatial relationships and visual coherence between the generated views, ensuring realistic results. Our model also incorporates an iterative refinement process that progressively improves the output quality through multiple stages of image generation. Finally, a dynamic geometry information intensity adjustment mechanism is proposed to adaptively regulate the influence of geometric data, optimizing overall quality while ensuring the naturalness of generated images. More details can be found on the project page: https://sobeymil.github.io/GeoMVD.com.
NCST: Neural-based Color Style Transfer for Video Retouching
Nov 01, 2024



Abstract:Video color style transfer aims to transform the color style of an original video by using a reference style image. Most existing methods employ neural networks, which come with challenges like opaque transfer processes and limited user control over the outcomes. Typically, users cannot fine-tune the resulting images or videos. To tackle this issue, we introduce a method that predicts specific parameters for color style transfer using two images. Initially, we train a neural network to learn the corresponding color adjustment parameters. When applying style transfer to a video, we fine-tune the network with key frames from the video and the chosen style image, generating precise transformation parameters. These are then applied to convert the color style of both images and videos. Our experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm surpasses current methods in color style transfer quality. Moreover, each parameter in our method has a specific, interpretable meaning, enabling users to understand the color style transfer process and allowing them to perform manual fine-tuning if desired.
TVG: A Training-free Transition Video Generation Method with Diffusion Models
Aug 24, 2024Abstract:Transition videos play a crucial role in media production, enhancing the flow and coherence of visual narratives. Traditional methods like morphing often lack artistic appeal and require specialized skills, limiting their effectiveness. Recent advances in diffusion model-based video generation offer new possibilities for creating transitions but face challenges such as poor inter-frame relationship modeling and abrupt content changes. We propose a novel training-free Transition Video Generation (TVG) approach using video-level diffusion models that addresses these limitations without additional training. Our method leverages Gaussian Process Regression ($\mathcal{GPR}$) to model latent representations, ensuring smooth and dynamic transitions between frames. Additionally, we introduce interpolation-based conditional controls and a Frequency-aware Bidirectional Fusion (FBiF) architecture to enhance temporal control and transition reliability. Evaluations of benchmark datasets and custom image pairs demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in generating high-quality smooth transition videos. The code are provided in https://sobeymil.github.io/tvg.com.
MVOC: a training-free multiple video object composition method with diffusion models
Jun 22, 2024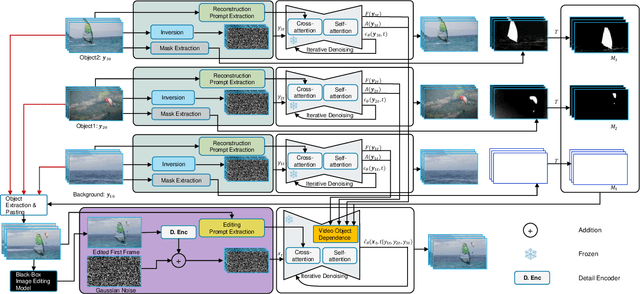
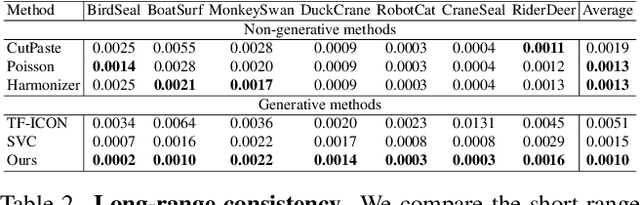
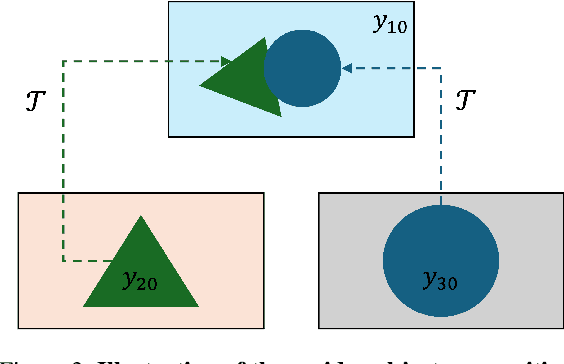
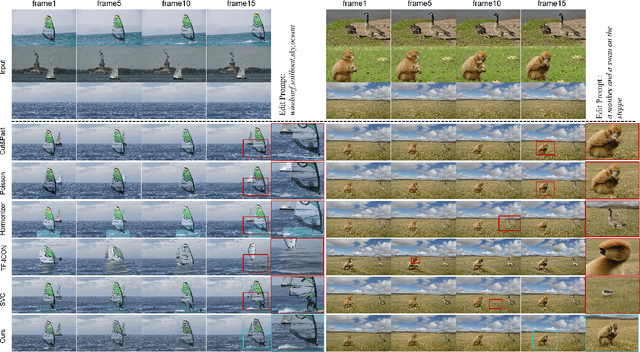
Abstract:Video composition is the core task of video editing. Although image composition based on diffusion models has been highly successful, it is not straightforward to extend the achievement to video object composition tasks, which not only exhibit corresponding interaction effects but also ensure that the objects in the composited video maintain motion and identity consistency, which is necessary to composite a physical harmony video. To address this challenge, we propose a Multiple Video Object Composition (MVOC) method based on diffusion models. Specifically, we first perform DDIM inversion on each video object to obtain the corresponding noise features. Secondly, we combine and edit each object by image editing methods to obtain the first frame of the composited video. Finally, we use the image-to-video generation model to composite the video with feature and attention injections in the Video Object Dependence Module, which is a training-free conditional guidance operation for video generation, and enables the coordination of features and attention maps between various objects that can be non-independent in the composited video. The final generative model not only constrains the objects in the generated video to be consistent with the original object motion and identity, but also introduces interaction effects between objects. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that the proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches. Project page: https://sobeymil.github.io/mvoc.com.
HyperLips: Hyper Control Lips with High Resolution Decoder for Talking Face Generation
Oct 15, 2023



Abstract:Talking face generation has a wide range of potential applications in the field of virtual digital humans. However, rendering high-fidelity facial video while ensuring lip synchronization is still a challenge for existing audio-driven talking face generation approaches. To address this issue, we propose HyperLips, a two-stage framework consisting of a hypernetwork for controlling lips and a high-resolution decoder for rendering high-fidelity faces. In the first stage, we construct a base face generation network that uses the hypernetwork to control the encoding latent code of the visual face information over audio. First, FaceEncoder is used to obtain latent code by extracting features from the visual face information taken from the video source containing the face frame.Then, HyperConv, which weighting parameters are updated by HyperNet with the audio features as input, will modify the latent code to synchronize the lip movement with the audio. Finally, FaceDecoder will decode the modified and synchronized latent code into visual face content. In the second stage, we obtain higher quality face videos through a high-resolution decoder. To further improve the quality of face generation, we trained a high-resolution decoder, HRDecoder, using face images and detected sketches generated from the first stage as input.Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art work with more realistic, high-fidelity, and lip synchronization. Project page: https://semchan.github.io/HyperLips Project/
NLUT: Neural-based 3D Lookup Tables for Video Photorealistic Style Transfer
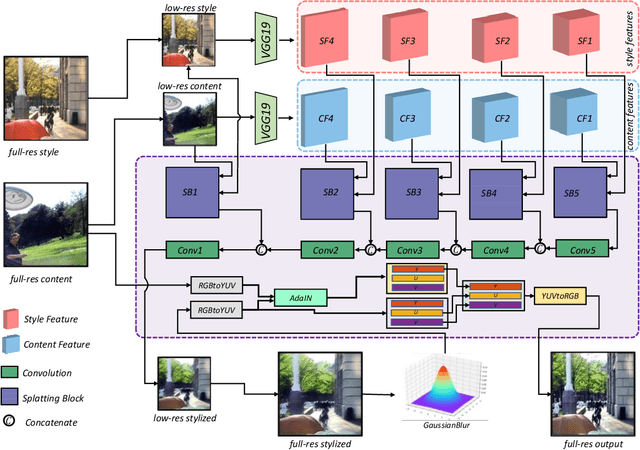
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:Video photorealistic style transfer is desired to generate videos with a similar photorealistic style to the style image while maintaining temporal consistency. However, existing methods obtain stylized video sequences by performing frame-by-frame photorealistic style transfer, which is inefficient and does not ensure the temporal consistency of the stylized video. To address this issue, we use neural network-based 3D Lookup Tables (LUTs) for the photorealistic transfer of videos, achieving a balance between efficiency and effectiveness. We first train a neural network for generating photorealistic stylized 3D LUTs on a large-scale dataset; then, when performing photorealistic style transfer for a specific video, we select a keyframe and style image in the video as the data source and fine-turn the neural network; finally, we query the 3D LUTs generated by the fine-tuned neural network for the colors in the video, resulting in a super-fast photorealistic style transfer, even processing 8K video takes less than 2 millisecond per frame. The experimental results show that our method not only realizes the photorealistic style transfer of arbitrary style images but also outperforms the existing methods in terms of visual quality and consistency. Project page:https://semchan.github.io/NLUT_Project.
UPST-NeRF: Universal Photorealistic Style Transfer of Neural Radiance Fields for 3D Scene
Aug 21, 2022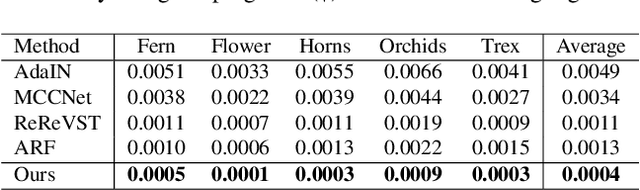
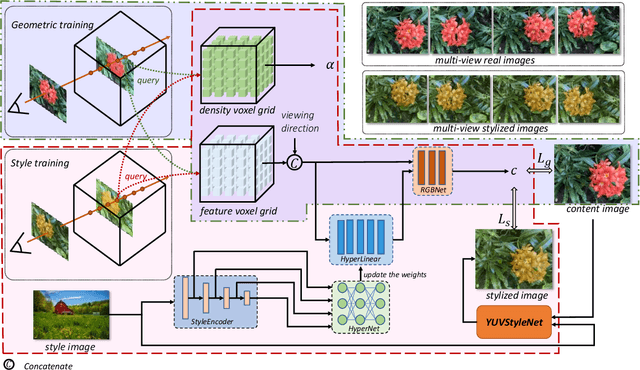
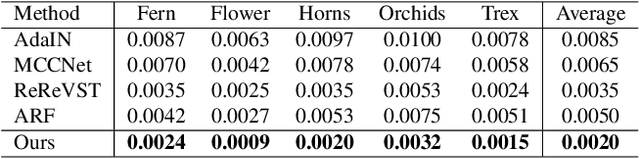
Abstract:3D scenes photorealistic stylization aims to generate photorealistic images from arbitrary novel views according to a given style image while ensuring consistency when rendering from different viewpoints. Some existing stylization methods with neural radiance fields can effectively predict stylized scenes by combining the features of the style image with multi-view images to train 3D scenes. However, these methods generate novel view images that contain objectionable artifacts. Besides, they cannot achieve universal photorealistic stylization for a 3D scene. Therefore, a styling image must retrain a 3D scene representation network based on a neural radiation field. We propose a novel 3D scene photorealistic style transfer framework to address these issues. It can realize photorealistic 3D scene style transfer with a 2D style image. We first pre-trained a 2D photorealistic style transfer network, which can meet the photorealistic style transfer between any given content image and style image. Then, we use voxel features to optimize a 3D scene and get the geometric representation of the scene. Finally, we jointly optimize a hyper network to realize the scene photorealistic style transfer of arbitrary style images. In the transfer stage, we use a pre-trained 2D photorealistic network to constrain the photorealistic style of different views and different style images in the 3D scene. The experimental results show that our method not only realizes the 3D photorealistic style transfer of arbitrary style images but also outperforms the existing methods in terms of visual quality and consistency. Project page:https://semchan.github.io/UPST_NeRF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge