Xuefang Zhao
A Communication Theory Perspective on Prompting Engineering Methods for Large Language Models
Oct 24, 2023



Abstract:The springing up of Large Language Models (LLMs) has shifted the community from single-task-orientated natural language processing (NLP) research to a holistic end-to-end multi-task learning paradigm. Along this line of research endeavors in the area, LLM-based prompting methods have attracted much attention, partially due to the technological advantages brought by prompt engineering (PE) as well as the underlying NLP principles disclosed by various prompting methods. Traditional supervised learning usually requires training a model based on labeled data and then making predictions. In contrast, PE methods directly use the powerful capabilities of existing LLMs (i.e., GPT-3 and GPT-4) via composing appropriate prompts, especially under few-shot or zero-shot scenarios. Facing the abundance of studies related to the prompting and the ever-evolving nature of this field, this article aims to (i) illustrate a novel perspective to review existing PE methods, within the well-established communication theory framework; (ii) facilitate a better/deeper understanding of developing trends of existing PE methods used in four typical tasks; (iii) shed light on promising research directions for future PE methods.
Marrying Dialogue Systems with Data Visualization: Interactive Data Visualization Generation from Natural Language Conversations
Jul 29, 2023



Abstract:Data visualization (DV) has become the prevailing tool in the market due to its effectiveness into illustrating insights in vast amounts of data. To lower the barrier of using DVs, automatic DV tasks, such as natural language question (NLQ) to visualization translation (formally called text-to-vis), have been investigated in the research community. However, text-to-vis assumes the NLQ to be well-organized and expressed in a single sentence. However, in real-world settings, complex DV is needed through consecutive exchanges between the DV system and the users. In this paper, we propose a new task named CoVis, short for Conversational text-to-Visualization, aiming at constructing DVs through a series of interactions between users and the system. Since it is the task which has not been studied in the literature, we first build a benchmark dataset named Dial-NVBench, including dialogue sessions with a sequence of queries from a user and responses from the system. Then, we propose a multi-modal neural network named MMCoVisNet to answer these DV-related queries. In particular, MMCoVisNet first fully understands the dialogue context and determines the corresponding responses. Then, it uses adaptive decoders to provide the appropriate replies: (i) a straightforward text decoder is used to produce general responses, (ii) an SQL-form decoder is applied to synthesize data querying responses, and (iii) a DV-form decoder tries to construct the appropriate DVs. We comparatively evaluate MMCoVisNet with other baselines over our proposed benchmark dataset. Experimental results validate that MMCoVisNet performs better than existing baselines and achieves a state-of-the-art performance.
Speech-to-SQL: Towards Speech-driven SQL Query Generation From Natural Language Question
Jan 04, 2022
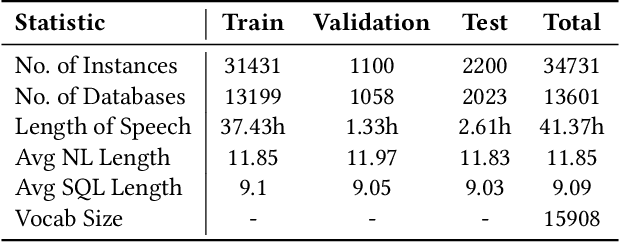
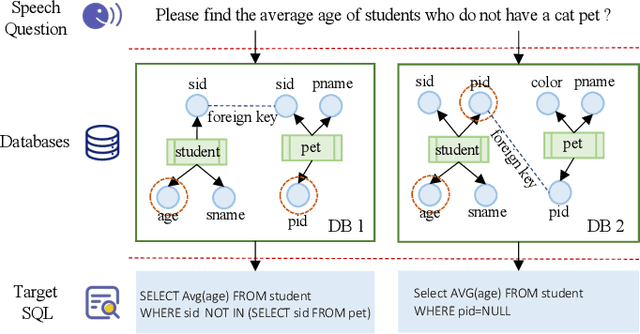
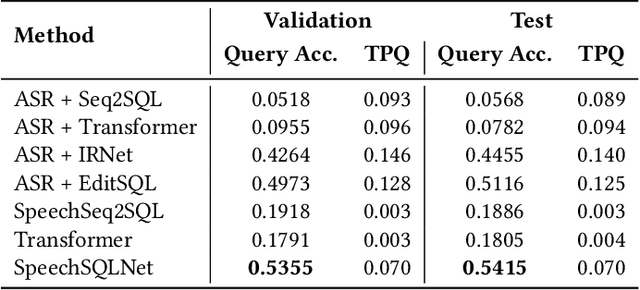
Abstract:Speech-based inputs have been gaining significant momentum with the popularity of smartphones and tablets in our daily lives, since voice is the most easiest and efficient way for human-computer interaction. This paper works towards designing more effective speech-based interfaces to query the structured data in relational databases. We first identify a new task named Speech-to-SQL, which aims to understand the information conveyed by human speech and directly translate it into structured query language (SQL) statements. A naive solution to this problem can work in a cascaded manner, that is, an automatic speech recognition (ASR) component followed by a text-to-SQL component. However, it requires a high-quality ASR system and also suffers from the error compounding problem between the two components, resulting in limited performance. To handle these challenges, we further propose a novel end-to-end neural architecture named SpeechSQLNet to directly translate human speech into SQL queries without an external ASR step. SpeechSQLNet has the advantage of making full use of the rich linguistic information presented in speech. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to directly synthesize SQL based on arbitrary natural language questions, rather than a natural language-based version of SQL or its variants with a limited SQL grammar. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed problem and model, we further construct a dataset named SpeechQL, by piggybacking the widely-used text-to-SQL datasets. Extensive experimental evaluations on this dataset show that SpeechSQLNet can directly synthesize high-quality SQL queries from human speech, outperforming various competitive counterparts as well as the cascaded methods in terms of exact match accuracies.
L2RS: A Learning-to-Rescore Mechanism for Automatic Speech Recognition
Oct 25, 2019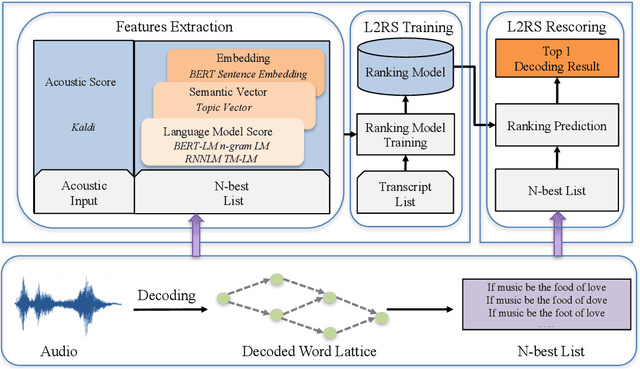
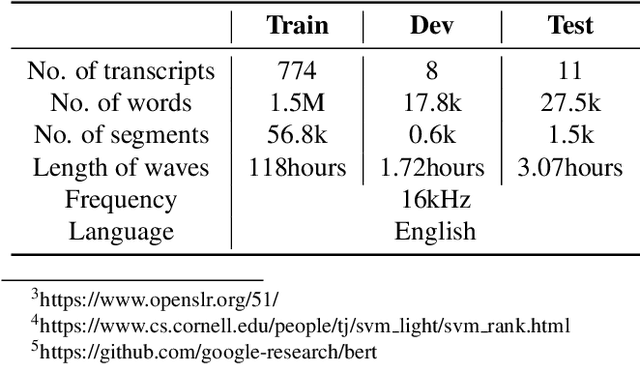

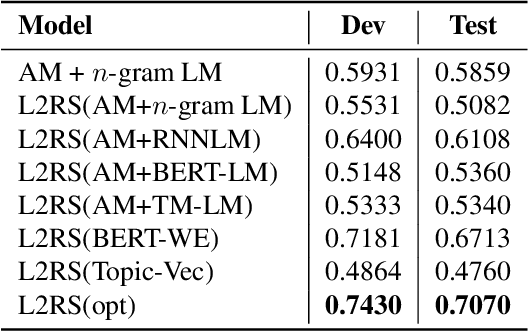
Abstract:Modern Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems primarily rely on scores from an Acoustic Model (AM) and a Language Model (LM) to rescore the N-best lists. With the abundance of recent natural language processing advances, the information utilized by current ASR for evaluating the linguistic and semantic legitimacy of the N-best hypotheses is rather limited. In this paper, we propose a novel Learning-to-Rescore (L2RS) mechanism, which is specialized for utilizing a wide range of textual information from the state-of-the-art NLP models and automatically deciding their weights to rescore the N-best lists for ASR systems. Specifically, we incorporate features including BERT sentence embedding, topic vector, and perplexity scores produced by n-gram LM, topic modeling LM, BERT LM and RNNLM to train a rescoring model. We conduct extensive experiments based on a public dataset, and experimental results show that L2RS outperforms not only traditional rescoring methods but also its deep neural network counterparts by a substantial improvement of 20.67% in terms of NDCG@10. L2RS paves the way for developing more effective rescoring models for ASR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge