Xinhang Zhang
Machine vision detection to daily facial fatigue with a nonlocal 3D attention network
Apr 21, 2021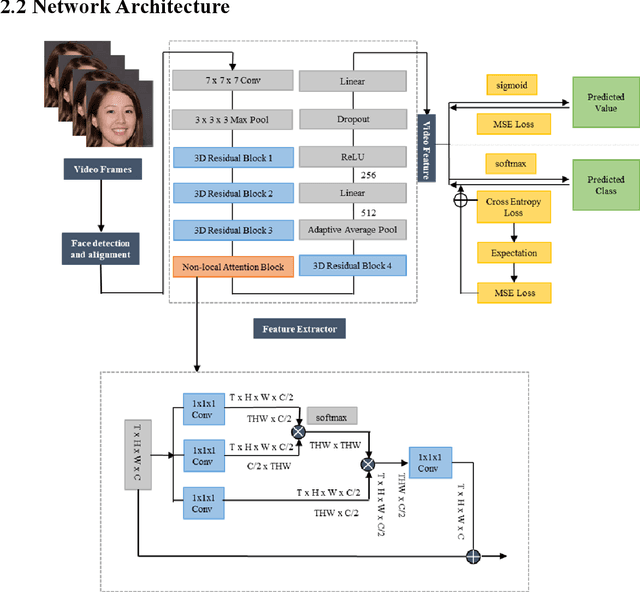
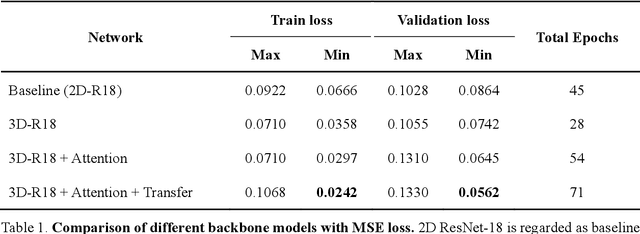
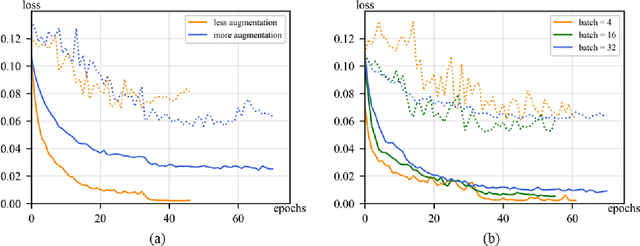
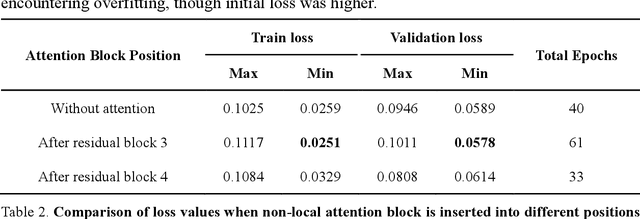
Abstract:Fatigue detection is valued for people to keep mental health and prevent safety accidents. However, detecting facial fatigue, especially mild fatigue in the real world via machine vision is still a challenging issue due to lack of non-lab dataset and well-defined algorithms. In order to improve the detection capability on facial fatigue that can be used widely in daily life, this paper provided an audiovisual dataset named DLFD (daily-life fatigue dataset) which reflected people's facial fatigue state in the wild. A framework using 3D-ResNet along with non-local attention mechanism was training for extraction of local and long-range features in spatial and temporal dimensions. Then, a compacted loss function combining mean squared error and cross-entropy was designed to predict both continuous and categorical fatigue degrees. Our proposed framework has reached an average accuracy of 90.8% on validation set and 72.5% on test set for binary classification, standing a good position compared to other state-of-the-art methods. The analysis of feature map visualization revealed that our framework captured facial dynamics and attempted to build a connection with fatigue state. Our experimental results in multiple metrics proved that our framework captured some typical, micro and dynamic facial features along spatiotemporal dimensions, contributing to the mild fatigue detection in the wild.
Balanced Order Batching with Task-Oriented Graph Clustering
Aug 19, 2020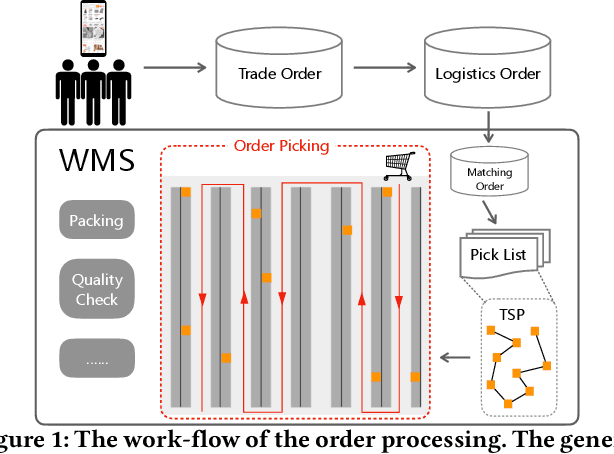
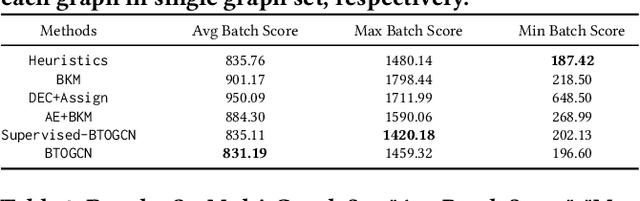
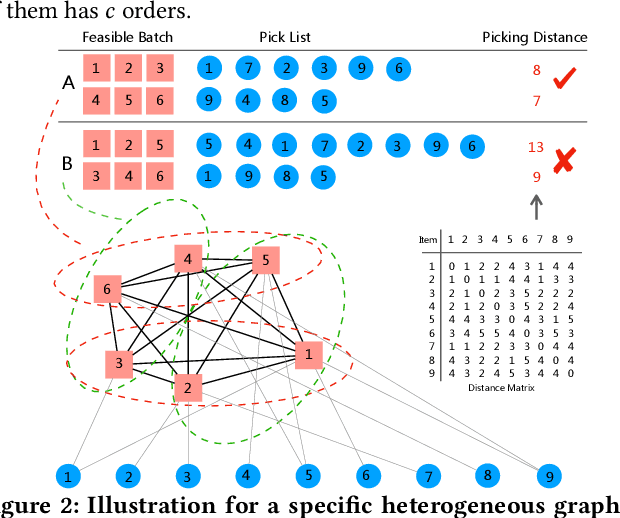
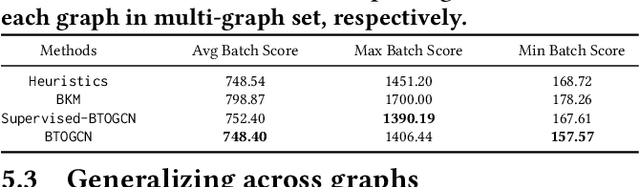
Abstract:Balanced order batching problem (BOBP) arises from the process of warehouse picking in Cainiao, the largest logistics platform in China. Batching orders together in the picking process to form a single picking route, reduces travel distance. The reason for its importance is that order picking is a labor intensive process and, by using good batching methods, substantial savings can be obtained. The BOBP is a NP-hard combinational optimization problem and designing a good problem-specific heuristic under the quasi-real-time system response requirement is non-trivial. In this paper, rather than designing heuristics, we propose an end-to-end learning and optimization framework named Balanced Task-orientated Graph Clustering Network (BTOGCN) to solve the BOBP by reducing it to balanced graph clustering optimization problem. In BTOGCN, a task-oriented estimator network is introduced to guide the type-aware heterogeneous graph clustering networks to find a better clustering result related to the BOBP objective. Through comprehensive experiments on single-graph and multi-graphs, we show: 1) our balanced task-oriented graph clustering network can directly utilize the guidance of target signal and outperforms the two-stage deep embedding and deep clustering method; 2) our method obtains an average 4.57m and 0.13m picking distance ("m" is the abbreviation of the meter (the SI base unit of length)) reduction than the expert-designed algorithm on single and multi-graph set and has a good generalization ability to apply in practical scenario.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge