Jingxuan Ni
Machine vision detection to daily facial fatigue with a nonlocal 3D attention network
Apr 21, 2021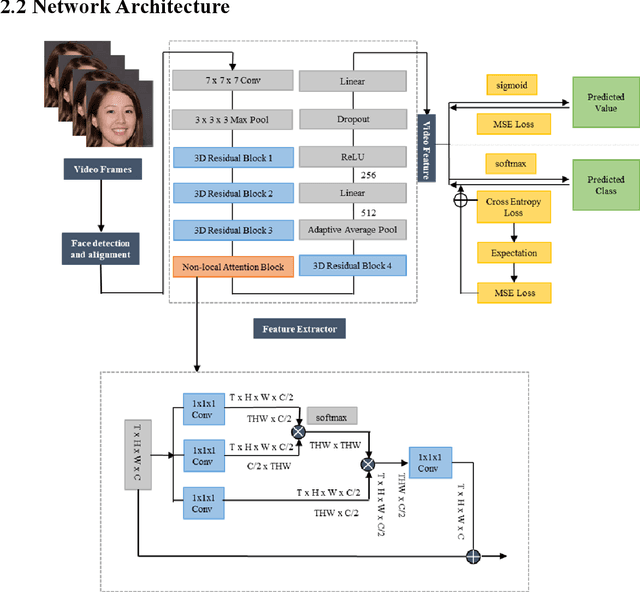
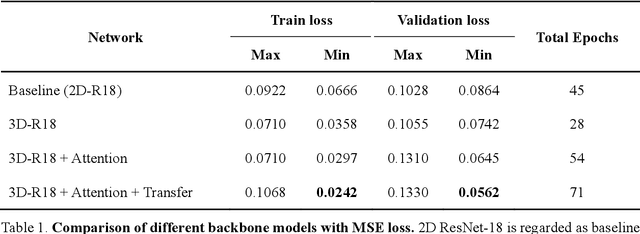
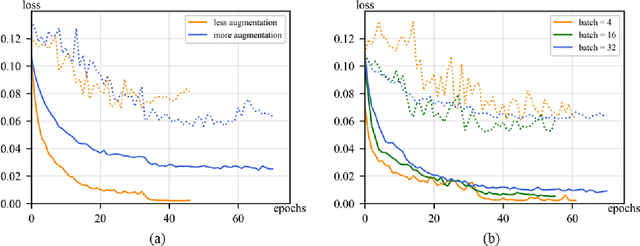
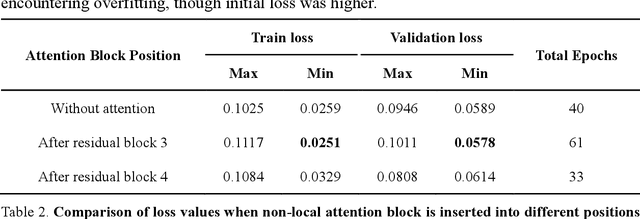
Abstract:Fatigue detection is valued for people to keep mental health and prevent safety accidents. However, detecting facial fatigue, especially mild fatigue in the real world via machine vision is still a challenging issue due to lack of non-lab dataset and well-defined algorithms. In order to improve the detection capability on facial fatigue that can be used widely in daily life, this paper provided an audiovisual dataset named DLFD (daily-life fatigue dataset) which reflected people's facial fatigue state in the wild. A framework using 3D-ResNet along with non-local attention mechanism was training for extraction of local and long-range features in spatial and temporal dimensions. Then, a compacted loss function combining mean squared error and cross-entropy was designed to predict both continuous and categorical fatigue degrees. Our proposed framework has reached an average accuracy of 90.8% on validation set and 72.5% on test set for binary classification, standing a good position compared to other state-of-the-art methods. The analysis of feature map visualization revealed that our framework captured facial dynamics and attempted to build a connection with fatigue state. Our experimental results in multiple metrics proved that our framework captured some typical, micro and dynamic facial features along spatiotemporal dimensions, contributing to the mild fatigue detection in the wild.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge