Xingdong Sheng
LoGoSeg: Integrating Local and Global Features for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Open-vocabulary semantic segmentation (OVSS) extends traditional closed-set segmentation by enabling pixel-wise annotation for both seen and unseen categories using arbitrary textual descriptions. While existing methods leverage vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP, their reliance on image-level pretraining often results in imprecise spatial alignment, leading to mismatched segmentations in ambiguous or cluttered scenes. However, most existing approaches lack strong object priors and region-level constraints, which can lead to object hallucination or missed detections, further degrading performance. To address these challenges, we propose LoGoSeg, an efficient single-stage framework that integrates three key innovations: (i) an object existence prior that dynamically weights relevant categories through global image-text similarity, effectively reducing hallucinations; (ii) a region-aware alignment module that establishes precise region-level visual-textual correspondences; and (iii) a dual-stream fusion mechanism that optimally combines local structural information with global semantic context. Unlike prior works, LoGoSeg eliminates the need for external mask proposals, additional backbones, or extra datasets, ensuring efficiency. Extensive experiments on six benchmarks (A-847, PC-459, A-150, PC-59, PAS-20, and PAS-20b) demonstrate its competitive performance and strong generalization in open-vocabulary settings.
Perceiving and Acting in First-Person: A Dataset and Benchmark for Egocentric Human-Object-Human Interactions
Aug 06, 2025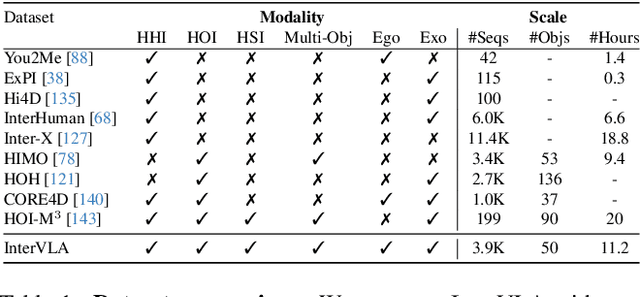
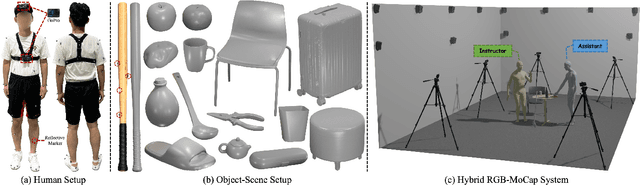
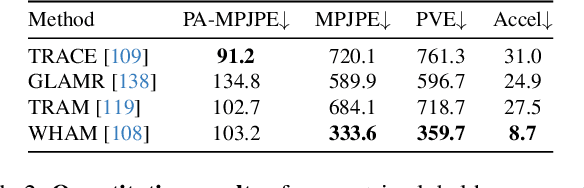

Abstract:Learning action models from real-world human-centric interaction datasets is important towards building general-purpose intelligent assistants with efficiency. However, most existing datasets only offer specialist interaction category and ignore that AI assistants perceive and act based on first-person acquisition. We urge that both the generalist interaction knowledge and egocentric modality are indispensable. In this paper, we embed the manual-assisted task into a vision-language-action framework, where the assistant provides services to the instructor following egocentric vision and commands. With our hybrid RGB-MoCap system, pairs of assistants and instructors engage with multiple objects and the scene following GPT-generated scripts. Under this setting, we accomplish InterVLA, the first large-scale human-object-human interaction dataset with 11.4 hours and 1.2M frames of multimodal data, spanning 2 egocentric and 5 exocentric videos, accurate human/object motions and verbal commands. Furthermore, we establish novel benchmarks on egocentric human motion estimation, interaction synthesis, and interaction prediction with comprehensive analysis. We believe that our InterVLA testbed and the benchmarks will foster future works on building AI agents in the physical world.
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection: Methods and Results
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection (CD-FSOD) poses significant challenges to existing object detection and few-shot detection models when applied across domains. In conjunction with NTIRE 2025, we organized the 1st CD-FSOD Challenge, aiming to advance the performance of current object detectors on entirely novel target domains with only limited labeled data. The challenge attracted 152 registered participants, received submissions from 42 teams, and concluded with 13 teams making valid final submissions. Participants approached the task from diverse perspectives, proposing novel models that achieved new state-of-the-art (SOTA) results under both open-source and closed-source settings. In this report, we present an overview of the 1st NTIRE 2025 CD-FSOD Challenge, highlighting the proposed solutions and summarizing the results submitted by the participants.
$E^{3}$Gen: Efficient, Expressive and Editable Avatars Generation
May 29, 2024



Abstract:This paper aims to introduce 3D Gaussian for efficient, expressive, and editable digital avatar generation. This task faces two major challenges: (1) The unstructured nature of 3D Gaussian makes it incompatible with current generation pipelines; (2) the expressive animation of 3D Gaussian in a generative setting that involves training with multiple subjects remains unexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel avatar generation method named $E^3$Gen, to effectively address these challenges. First, we propose a novel generative UV features plane representation that encodes unstructured 3D Gaussian onto a structured 2D UV space defined by the SMPL-X parametric model. This novel representation not only preserves the representation ability of the original 3D Gaussian but also introduces a shared structure among subjects to enable generative learning of the diffusion model. To tackle the second challenge, we propose a part-aware deformation module to achieve robust and accurate full-body expressive pose control. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance in avatar generation and enables expressive full-body pose control and editing.
IPAD: Industrial Process Anomaly Detection Dataset
Apr 23, 2024



Abstract:Video anomaly detection (VAD) is a challenging task aiming to recognize anomalies in video frames, and existing large-scale VAD researches primarily focus on road traffic and human activity scenes. In industrial scenes, there are often a variety of unpredictable anomalies, and the VAD method can play a significant role in these scenarios. However, there is a lack of applicable datasets and methods specifically tailored for industrial production scenarios due to concerns regarding privacy and security. To bridge this gap, we propose a new dataset, IPAD, specifically designed for VAD in industrial scenarios. The industrial processes in our dataset are chosen through on-site factory research and discussions with engineers. This dataset covers 16 different industrial devices and contains over 6 hours of both synthetic and real-world video footage. Moreover, we annotate the key feature of the industrial process, ie, periodicity. Based on the proposed dataset, we introduce a period memory module and a sliding window inspection mechanism to effectively investigate the periodic information in a basic reconstruction model. Our framework leverages LoRA adapter to explore the effective migration of pretrained models, which are initially trained using synthetic data, into real-world scenarios. Our proposed dataset and method will fill the gap in the field of industrial video anomaly detection and drive the process of video understanding tasks as well as smart factory deployment.
Rethinking Clothes Changing Person ReID: Conflicts, Synthesis, and Optimization
Apr 19, 2024



Abstract:Clothes-changing person re-identification (CC-ReID) aims to retrieve images of the same person wearing different outfits. Mainstream researches focus on designing advanced model structures and strategies to capture identity information independent of clothing. However, the same-clothes discrimination as the standard ReID learning objective in CC-ReID is persistently ignored in previous researches. In this study, we dive into the relationship between standard and clothes-changing~(CC) learning objectives, and bring the inner conflicts between these two objectives to the fore. We try to magnify the proportion of CC training pairs by supplementing high-fidelity clothes-varying synthesis, produced by our proposed Clothes-Changing Diffusion model. By incorporating the synthetic images into CC-ReID model training, we observe a significant improvement under CC protocol. However, such improvement sacrifices the performance under the standard protocol, caused by the inner conflict between standard and CC. For conflict mitigation, we decouple these objectives and re-formulate CC-ReID learning as a multi-objective optimization (MOO) problem. By effectively regularizing the gradient curvature across multiple objectives and introducing preference restrictions, our MOO solution surpasses the single-task training paradigm. Our framework is model-agnostic, and demonstrates superior performance under both CC and standard ReID protocols.
Inter-X: Towards Versatile Human-Human Interaction Analysis
Dec 26, 2023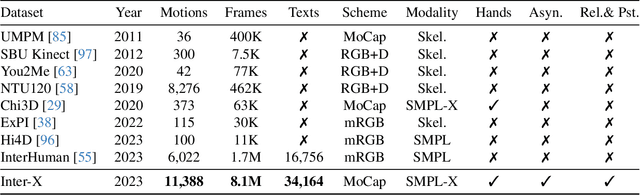
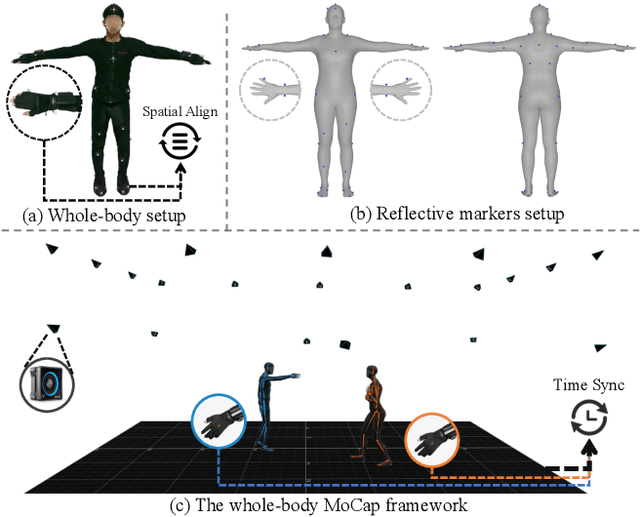
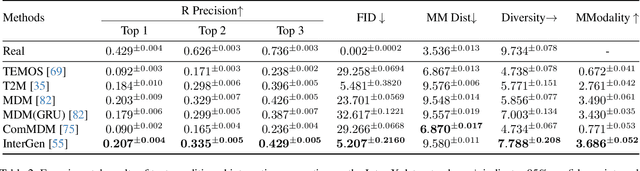
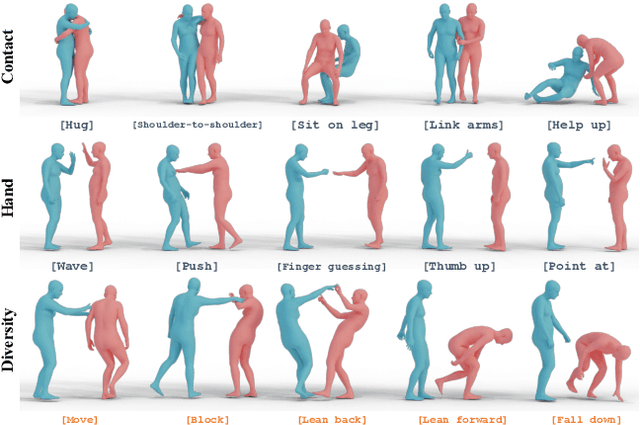
Abstract:The analysis of the ubiquitous human-human interactions is pivotal for understanding humans as social beings. Existing human-human interaction datasets typically suffer from inaccurate body motions, lack of hand gestures and fine-grained textual descriptions. To better perceive and generate human-human interactions, we propose Inter-X, a currently largest human-human interaction dataset with accurate body movements and diverse interaction patterns, together with detailed hand gestures. The dataset includes ~11K interaction sequences and more than 8.1M frames. We also equip Inter-X with versatile annotations of more than 34K fine-grained human part-level textual descriptions, semantic interaction categories, interaction order, and the relationship and personality of the subjects. Based on the elaborate annotations, we propose a unified benchmark composed of 4 categories of downstream tasks from both the perceptual and generative directions. Extensive experiments and comprehensive analysis show that Inter-X serves as a testbed for promoting the development of versatile human-human interaction analysis. Our dataset and benchmark will be publicly available for research purposes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge