Xilei Zhu
ESVQA: Perceptual Quality Assessment of Egocentric Spatial Videos
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid development of eXtended Reality (XR), egocentric spatial shooting and display technologies have further enhanced immersion and engagement for users. Assessing the quality of experience (QoE) of egocentric spatial videos is crucial to ensure a high-quality viewing experience. However, the corresponding research is still lacking. In this paper, we use the embodied experience to highlight this more immersive experience and study the new problem, i.e., embodied perceptual quality assessment for egocentric spatial videos. Specifically, we introduce the first Egocentric Spatial Video Quality Assessment Database (ESVQAD), which comprises 600 egocentric spatial videos and their mean opinion scores (MOSs). Furthermore, we propose a novel multi-dimensional binocular feature fusion model, termed ESVQAnet, which integrates binocular spatial, motion, and semantic features to predict the perceptual quality. Experimental results demonstrate the ESVQAnet outperforms 16 state-of-the-art VQA models on the embodied perceptual quality assessment task, and exhibits strong generalization capability on traditional VQA tasks. The database and codes will be released upon the publication.
How Does Audio Influence Visual Attention in Omnidirectional Videos? Database and Model
Aug 10, 2024



Abstract:Understanding and predicting viewer attention in omnidirectional videos (ODVs) is crucial for enhancing user engagement in virtual and augmented reality applications. Although both audio and visual modalities are essential for saliency prediction in ODVs, the joint exploitation of these two modalities has been limited, primarily due to the absence of large-scale audio-visual saliency databases and comprehensive analyses. This paper comprehensively investigates audio-visual attention in ODVs from both subjective and objective perspectives. Specifically, we first introduce a new audio-visual saliency database for omnidirectional videos, termed AVS-ODV database, containing 162 ODVs and corresponding eye movement data collected from 60 subjects under three audio modes including mute, mono, and ambisonics. Based on the constructed AVS-ODV database, we perform an in-depth analysis of how audio influences visual attention in ODVs. To advance the research on audio-visual saliency prediction for ODVs, we further establish a new benchmark based on the AVS-ODV database by testing numerous state-of-the-art saliency models, including visual-only models and audio-visual models. In addition, given the limitations of current models, we propose an innovative omnidirectional audio-visual saliency prediction network (OmniAVS), which is built based on the U-Net architecture, and hierarchically fuses audio and visual features from the multimodal aligned embedding space. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed OmniAVS model outperforms other state-of-the-art models on both ODV AVS prediction and traditional AVS predcition tasks. The AVS-ODV database and OmniAVS model will be released to facilitate future research.
ESIQA: Perceptual Quality Assessment of Vision-Pro-based Egocentric Spatial Images
Jul 31, 2024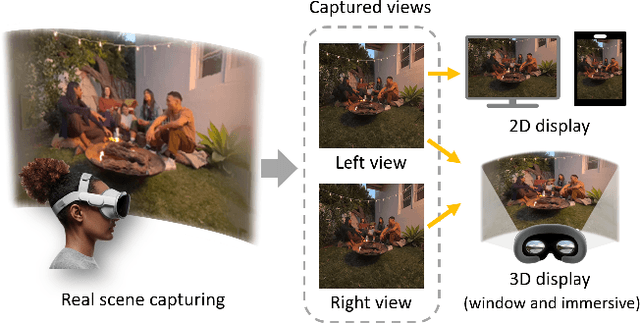



Abstract:With the development of eXtended Reality (XR), head-mounted shooting and display technology have experienced significant advancement and gained considerable attention. Egocentric spatial images and videos are emerging as a compelling form of stereoscopic XR content. Different from traditional 2D images, egocentric spatial images present challenges for perceptual quality assessment due to their special shooting, processing methods, and stereoscopic characteristics. However, the corresponding image quality assessment (IQA) research for egocentric spatial images is still lacking. In this paper, we establish the Egocentric Spatial Images Quality Assessment Database (ESIQAD), the first IQA database dedicated for egocentric spatial images as far as we know. Our ESIQAD includes 500 egocentric spatial images, containing 400 images captured with the Apple Vision Pro and 100 images generated via an iPhone's "Spatial Camera" app. The corresponding mean opinion scores (MOSs) are collected under three viewing modes, including 2D display, 3D-window display, and 3D-immersive display. Furthermore, based on our database, we conduct a benchmark experiment and evaluate the performance of 22 state-of-the-art IQA models under three different viewing modes. We hope this research can facilitate future IQA research on egocentric spatial images. The database is available at https://github.com/IntMeGroup/ESIQA.
Audio-visual Saliency for Omnidirectional Videos
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:Visual saliency prediction for omnidirectional videos (ODVs) has shown great significance and necessity for omnidirectional videos to help ODV coding, ODV transmission, ODV rendering, etc.. However, most studies only consider visual information for ODV saliency prediction while audio is rarely considered despite its significant influence on the viewing behavior of ODV. This is mainly due to the lack of large-scale audio-visual ODV datasets and corresponding analysis. Thus, in this paper, we first establish the largest audio-visual saliency dataset for omnidirectional videos (AVS-ODV), which comprises the omnidirectional videos, audios, and corresponding captured eye-tracking data for three video sound modalities including mute, mono, and ambisonics. Then we analyze the visual attention behavior of the observers under various omnidirectional audio modalities and visual scenes based on the AVS-ODV dataset. Furthermore, we compare the performance of several state-of-the-art saliency prediction models on the AVS-ODV dataset and construct a new benchmark. Our AVS-ODV datasets and the benchmark will be released to facilitate future research.
Perceptual Quality Assessment of Omnidirectional Audio-visual Signals
Jul 20, 2023Abstract:Omnidirectional videos (ODVs) play an increasingly important role in the application fields of medical, education, advertising, tourism, etc. Assessing the quality of ODVs is significant for service-providers to improve the user's Quality of Experience (QoE). However, most existing quality assessment studies for ODVs only focus on the visual distortions of videos, while ignoring that the overall QoE also depends on the accompanying audio signals. In this paper, we first establish a large-scale audio-visual quality assessment dataset for omnidirectional videos, which includes 375 distorted omnidirectional audio-visual (A/V) sequences generated from 15 high-quality pristine omnidirectional A/V contents, and the corresponding perceptual audio-visual quality scores. Then, we design three baseline methods for full-reference omnidirectional audio-visual quality assessment (OAVQA), which combine existing state-of-the-art single-mode audio and video QA models via multimodal fusion strategies. We validate the effectiveness of the A/V multimodal fusion method for OAVQA on our dataset, which provides a new benchmark for omnidirectional QoE evaluation. Our dataset is available at https://github.com/iamazxl/OAVQA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge