Xiaohe Li
FusionTrack: End-to-End Multi-Object Tracking in Arbitrary Multi-View Environment
May 24, 2025Abstract:Multi-view multi-object tracking (MVMOT) has found widespread applications in intelligent transportation, surveillance systems, and urban management. However, existing studies rarely address genuinely free-viewpoint MVMOT systems, which could significantly enhance the flexibility and scalability of cooperative tracking systems. To bridge this gap, we first construct the Multi-Drone Multi-Object Tracking (MDMOT) dataset, captured by mobile drone swarms across diverse real-world scenarios, initially establishing the first benchmark for multi-object tracking in arbitrary multi-view environment. Building upon this foundation, we propose \textbf{FusionTrack}, an end-to-end framework that reasonably integrates tracking and re-identification to leverage multi-view information for robust trajectory association. Extensive experiments on our MDMOT and other benchmark datasets demonstrate that FusionTrack achieves state-of-the-art performance in both single-view and multi-view tracking.
C$^{2}$INet: Realizing Incremental Trajectory Prediction with Prior-Aware Continual Causal Intervention
Nov 19, 2024Abstract:Trajectory prediction for multi-agents in complex scenarios is crucial for applications like autonomous driving. However, existing methods often overlook environmental biases, which leads to poor generalization. Additionally, hardware constraints limit the use of large-scale data across environments, and continual learning settings exacerbate the challenge of catastrophic forgetting. To address these issues, we propose the Continual Causal Intervention (C$^{2}$INet) method for generalizable multi-agent trajectory prediction within a continual learning framework. Using variational inference, we align environment-related prior with posterior estimator of confounding factors in the latent space, thereby intervening in causal correlations that affect trajectory representation. Furthermore, we store optimal variational priors across various scenarios using a memory queue, ensuring continuous debiasing during incremental task training. The proposed C$^{2}$INet enhances adaptability to diverse tasks while preserving previous task information to prevent catastrophic forgetting. It also incorporates pruning strategies to mitigate overfitting. Comparative evaluations on three real and synthetic complex datasets against state-of-the-art methods demonstrate that our proposed method consistently achieves reliable prediction performance, effectively mitigating confounding factors unique to different scenarios. This highlights the practical value of our method for real-world applications.
MetaTra: Meta-Learning for Generalized Trajectory Prediction in Unseen Domain
Feb 13, 2024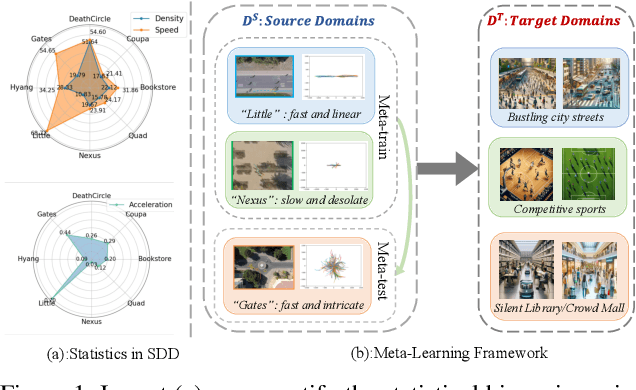
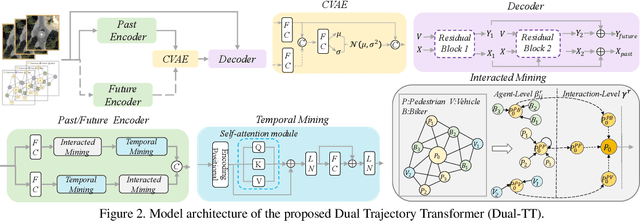
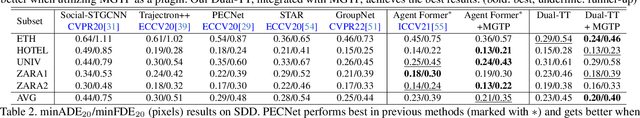
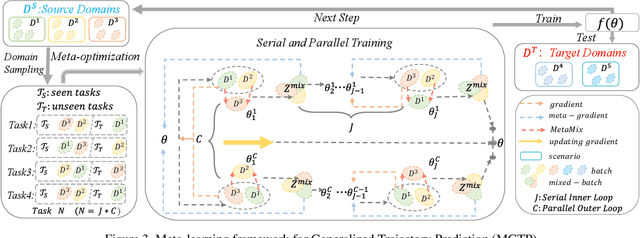
Abstract:Trajectory prediction has garnered widespread attention in different fields, such as autonomous driving and robotic navigation. However, due to the significant variations in trajectory patterns across different scenarios, models trained in known environments often falter in unseen ones. To learn a generalized model that can directly handle unseen domains without requiring any model updating, we propose a novel meta-learning-based trajectory prediction method called MetaTra. This approach incorporates a Dual Trajectory Transformer (Dual-TT), which enables a thorough exploration of the individual intention and the interactions within group motion patterns in diverse scenarios. Building on this, we propose a meta-learning framework to simulate the generalization process between source and target domains. Furthermore, to enhance the stability of our prediction outcomes, we propose a Serial and Parallel Training (SPT) strategy along with a feature augmentation method named MetaMix. Experimental results on several real-world datasets confirm that MetaTra not only surpasses other state-of-the-art methods but also exhibits plug-and-play capabilities, particularly in the realm of domain generalization.
Graph Neural Network with Curriculum Learning for Imbalanced Node Classification
Feb 05, 2022



Abstract:Graph Neural Network (GNN) is an emerging technique for graph-based learning tasks such as node classification. In this work, we reveal the vulnerability of GNN to the imbalance of node labels. Traditional solutions for imbalanced classification (e.g. resampling) are ineffective in node classification without considering the graph structure. Worse still, they may even bring overfitting or underfitting results due to lack of sufficient prior knowledge. To solve these problems, we propose a novel graph neural network framework with curriculum learning (GNN-CL) consisting of two modules. For one thing, we hope to acquire certain reliable interpolation nodes and edges through the novel graph-based oversampling based on smoothness and homophily. For another, we combine graph classification loss and metric learning loss which adjust the distance between different nodes associated with minority class in feature space. Inspired by curriculum learning, we dynamically adjust the weights of different modules during training process to achieve better ability of generalization and discrimination. The proposed framework is evaluated via several widely used graph datasets, showing that our proposed model consistently outperforms the existing state-of-the-art methods.
Gradient Imitation Reinforcement Learning for Low Resource Relation Extraction
Sep 14, 2021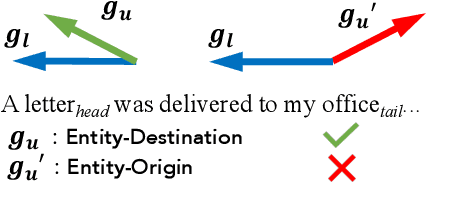
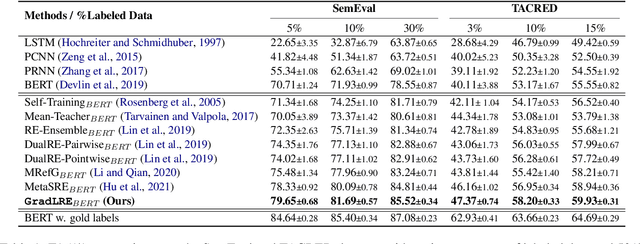
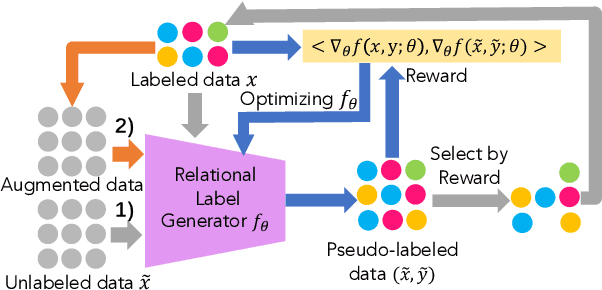

Abstract:Low-resource Relation Extraction (LRE) aims to extract relation facts from limited labeled corpora when human annotation is scarce. Existing works either utilize self-training scheme to generate pseudo labels that will cause the gradual drift problem, or leverage meta-learning scheme which does not solicit feedback explicitly. To alleviate selection bias due to the lack of feedback loops in existing LRE learning paradigms, we developed a Gradient Imitation Reinforcement Learning method to encourage pseudo label data to imitate the gradient descent direction on labeled data and bootstrap its optimization capability through trial and error. We also propose a framework called GradLRE, which handles two major scenarios in low-resource relation extraction. Besides the scenario where unlabeled data is sufficient, GradLRE handles the situation where no unlabeled data is available, by exploiting a contextualized augmentation method to generate data. Experimental results on two public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of GradLRE on low resource relation extraction when comparing with baselines.
GAHNE: Graph-Aggregated Heterogeneous Network Embedding
Dec 23, 2020



Abstract:The real-world networks often compose of different types of nodes and edges with rich semantics, widely known as heterogeneous information network (HIN). Heterogeneous network embedding aims to embed nodes into low-dimensional vectors which capture rich intrinsic information of heterogeneous networks. However, existing models either depend on manually designing meta-paths, ignore mutual effects between different semantics, or omit some aspects of information from global networks. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Graph-Aggregated Heterogeneous Network Embedding (GAHNE), which is designed to extract the semantics of HINs as comprehensively as possible to improve the results of downstream tasks based on graph convolutional neural networks. In GAHNE model, we develop several mechanisms that can aggregate semantic representations from different single-type sub-networks as well as fuse the global information into final embeddings. Extensive experiments on three real-world HIN datasets show that our proposed model consistently outperforms the existing state-of-the-art methods.
Pchatbot: A Large-Scale Dataset for Personalized Chatbot
Sep 28, 2020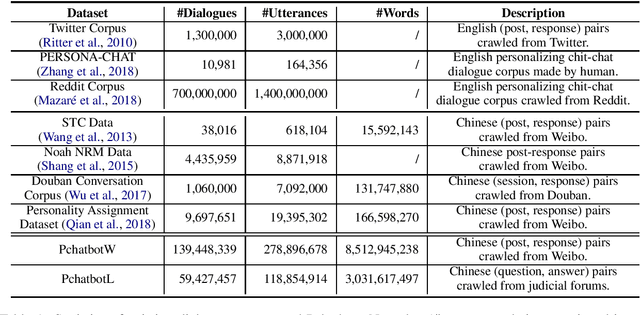
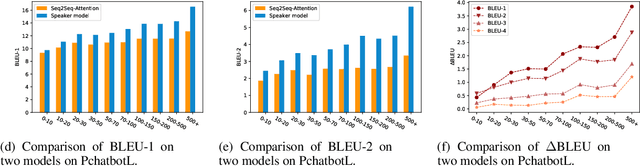
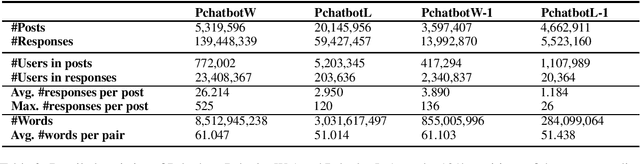

Abstract:Natural language dialogue systems raise great attention recently. As many dialogue models are data-driven, high quality datasets are essential to these systems. In this paper, we introduce Pchatbot, a large scale dialogue dataset which contains two subsets collected from Weibo and Judical forums respectively. Different from existing datasets which only contain post-response pairs, we include anonymized user IDs as well as timestamps. This enables the development of personalized dialogue models which depend on the availability of users' historical conversations. Furthermore, the scale of Pchatbot is significantly larger than existing datasets, which might benefit the data-driven models. Our preliminary experimental study shows that a personalized chatbot model trained on Pchatbot outperforms the corresponding ad-hoc chatbot models. We also demonstrate that using larger dataset improves the quality of dialog models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge