Xiaobin Liu
DEYOLO: Dual-Feature-Enhancement YOLO for Cross-Modality Object Detection
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Object detection in poor-illumination environments is a challenging task as objects are usually not clearly visible in RGB images. As infrared images provide additional clear edge information that complements RGB images, fusing RGB and infrared images has potential to enhance the detection ability in poor-illumination environments. However, existing works involving both visible and infrared images only focus on image fusion, instead of object detection. Moreover, they directly fuse the two kinds of image modalities, which ignores the mutual interference between them. To fuse the two modalities to maximize the advantages of cross-modality, we design a dual-enhancement-based cross-modality object detection network DEYOLO, in which semantic-spatial cross modality and novel bi-directional decoupled focus modules are designed to achieve the detection-centered mutual enhancement of RGB-infrared (RGB-IR). Specifically, a dual semantic enhancing channel weight assignment module (DECA) and a dual spatial enhancing pixel weight assignment module (DEPA) are firstly proposed to aggregate cross-modality information in the feature space to improve the feature representation ability, such that feature fusion can aim at the object detection task. Meanwhile, a dual-enhancement mechanism, including enhancements for two-modality fusion and single modality, is designed in both DECAand DEPAto reduce interference between the two kinds of image modalities. Then, a novel bi-directional decoupled focus is developed to enlarge the receptive field of the backbone network in different directions, which improves the representation quality of DEYOLO. Extensive experiments on M3FD and LLVIP show that our approach outperforms SOTA object detection algorithms by a clear margin. Our code is available at https://github.com/chips96/DEYOLO.
Factor Decomposed Generative Adversarial Networks for Text-to-Image Synthesis
Mar 24, 2023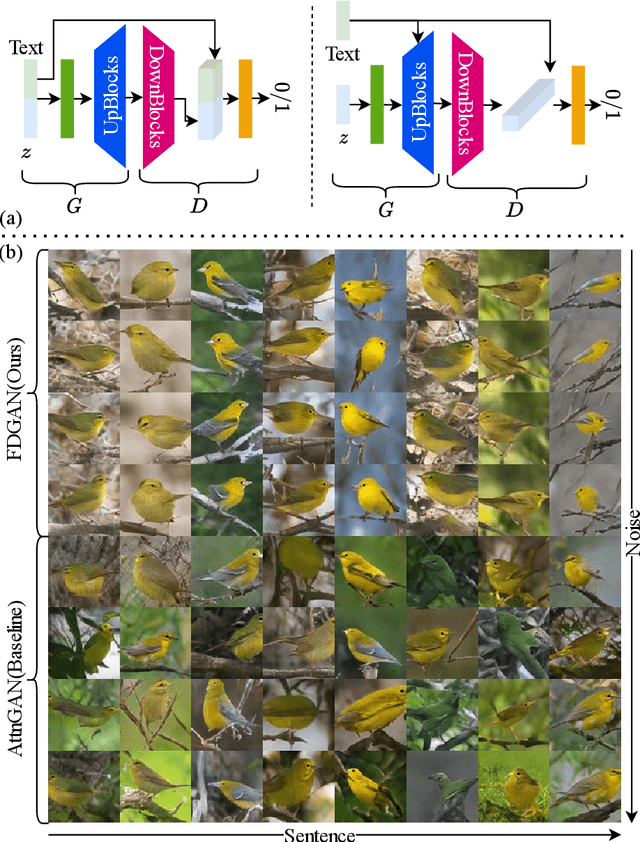

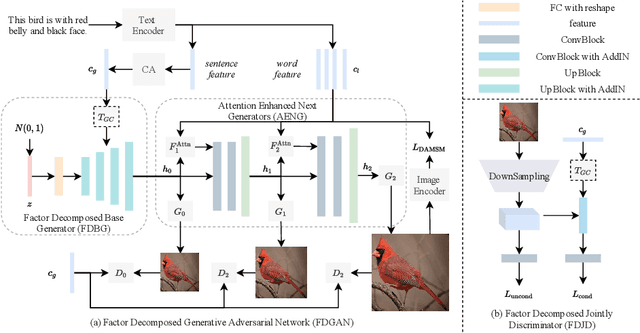

Abstract:Prior works about text-to-image synthesis typically concatenated the sentence embedding with the noise vector, while the sentence embedding and the noise vector are two different factors, which control the different aspects of the generation. Simply concatenating them will entangle the latent factors and encumber the generative model. In this paper, we attempt to decompose these two factors and propose Factor Decomposed Generative Adversarial Networks~(FDGAN). To achieve this, we firstly generate images from the noise vector and then apply the sentence embedding in the normalization layer for both generator and discriminators. We also design an additive norm layer to align and fuse the text-image features. The experimental results show that decomposing the noise and the sentence embedding can disentangle latent factors in text-to-image synthesis, and make the generative model more efficient. Compared with the baseline, FDGAN can achieve better performance, while fewer parameters are used.
Time-frequency Network for Robust Speaker Recognition
Mar 07, 2023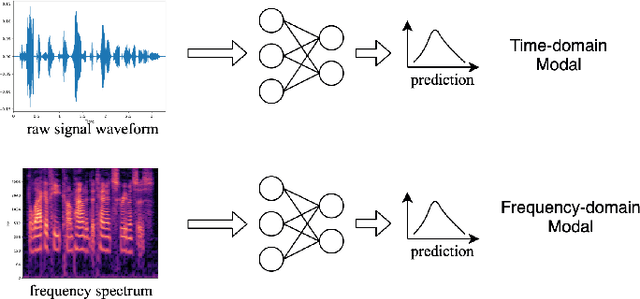
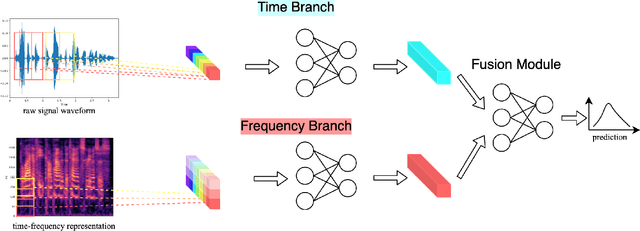
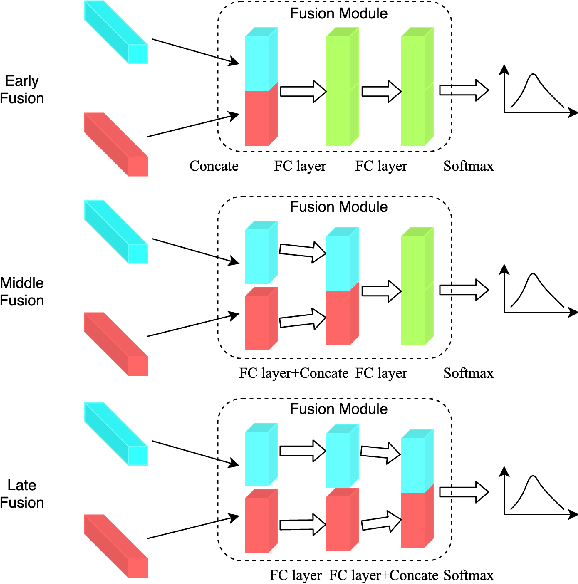
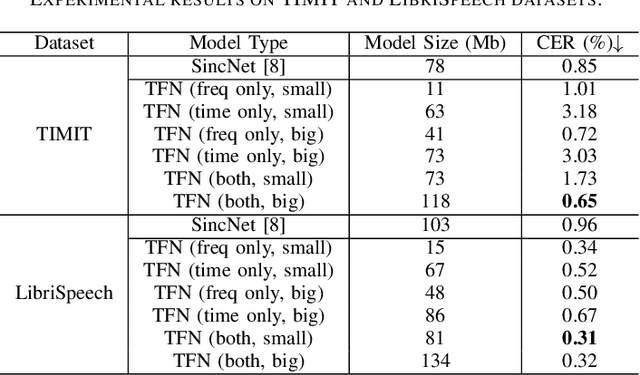
Abstract:The wide deployment of speech-based biometric systems usually demands high-performance speaker recognition algorithms. However, most of the prior works for speaker recognition either process the speech in the frequency domain or time domain, which may produce suboptimal results because both time and frequency domains are important for speaker recognition. In this paper, we attempt to analyze the speech signal in both time and frequency domains and propose the time-frequency network~(TFN) for speaker recognition by extracting and fusing the features in the two domains. Based on the recent advance of deep neural networks, we propose a convolution neural network to encode the raw speech waveform and the frequency spectrum into domain-specific features, which are then fused and transformed into a classification feature space for speaker recognition. Experimental results on the publicly available datasets TIMIT and LibriSpeech show that our framework is effective to combine the information in the two domains and performs better than the state-of-the-art methods for speaker recognition.
Graph Consistency Based Mean-Teaching for Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Person Re-Identification
May 31, 2021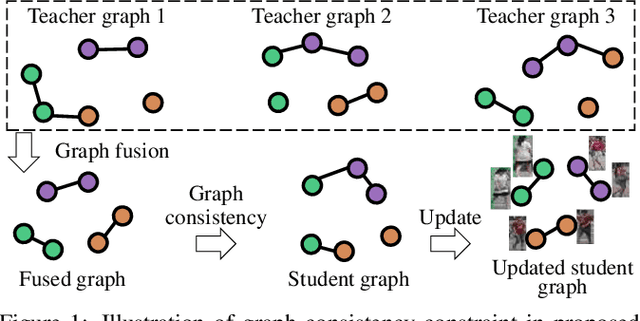
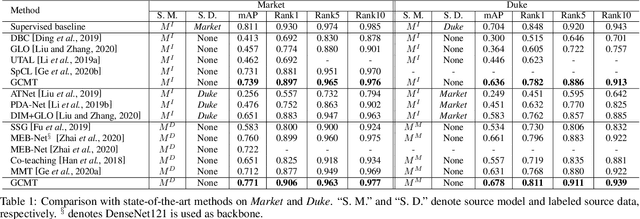
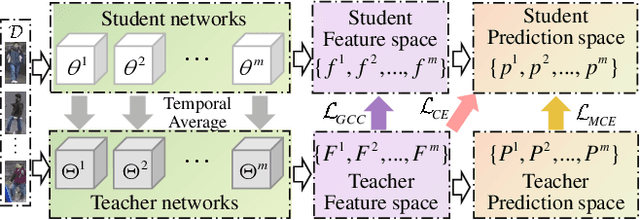
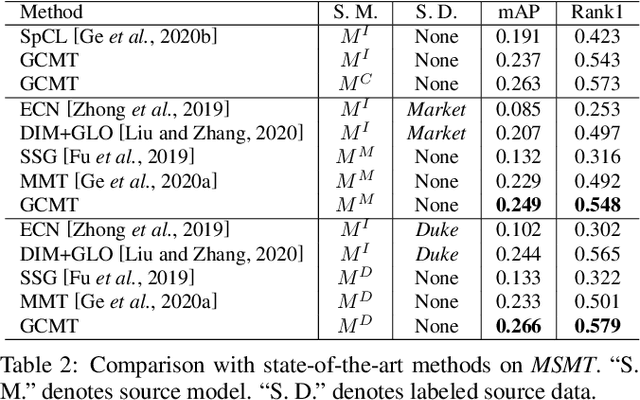
Abstract:Recent works show that mean-teaching is an effective framework for unsupervised domain adaptive person re-identification. However, existing methods perform contrastive learning on selected samples between teacher and student networks, which is sensitive to noises in pseudo labels and neglects the relationship among most samples. Moreover, these methods are not effective in cooperation of different teacher networks. To handle these issues, this paper proposes a Graph Consistency based Mean-Teaching (GCMT) method with constructing the Graph Consistency Constraint (GCC) between teacher and student networks. Specifically, given unlabeled training images, we apply teacher networks to extract corresponding features and further construct a teacher graph for each teacher network to describe the similarity relationships among training images. To boost the representation learning, different teacher graphs are fused to provide the supervise signal for optimizing student networks. GCMT fuses similarity relationships predicted by different teacher networks as supervision and effectively optimizes student networks with more sample relationships involved. Experiments on three datasets, i.e., Market-1501, DukeMTMCreID, and MSMT17, show that proposed GCMT outperforms state-of-the-art methods by clear margin. Specially, GCMT even outperforms the previous method that uses a deeper backbone. Experimental results also show that GCMT can effectively boost the performance with multiple teacher and student networks. Our code is available at https://github.com/liu-xb/GCMT .
Domain Adaptive Person Re-Identification via Coupling Optimization
Nov 06, 2020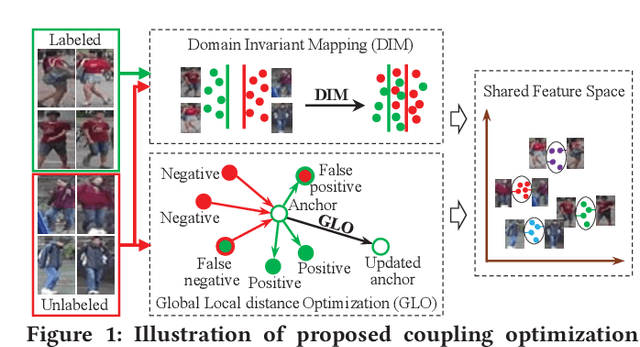
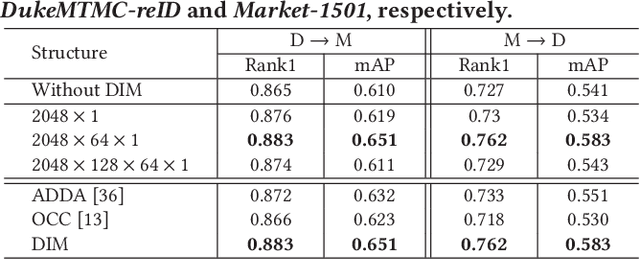

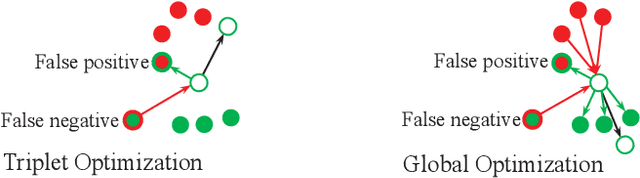
Abstract:Domain adaptive person Re-Identification (ReID) is challenging owing to the domain gap and shortage of annotations on target scenarios. To handle those two challenges, this paper proposes a coupling optimization method including the Domain-Invariant Mapping (DIM) method and the Global-Local distance Optimization (GLO), respectively. Different from previous methods that transfer knowledge in two stages, the DIM achieves a more efficient one-stage knowledge transfer by mapping images in labeled and unlabeled datasets to a shared feature space. GLO is designed to train the ReID model with unsupervised setting on the target domain. Instead of relying on existing optimization strategies designed for supervised training, GLO involves more images in distance optimization, and achieves better robustness to noisy label prediction. GLO also integrates distance optimizations in both the global dataset and local training batch, thus exhibits better training efficiency. Extensive experiments on three large-scale datasets, i.e., Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID, and MSMT17, show that our coupling optimization outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin. Our method also works well in unsupervised training, and even outperforms several recent domain adaptive methods.
RAM: A Region-Aware Deep Model for Vehicle Re-Identification
Jun 25, 2018
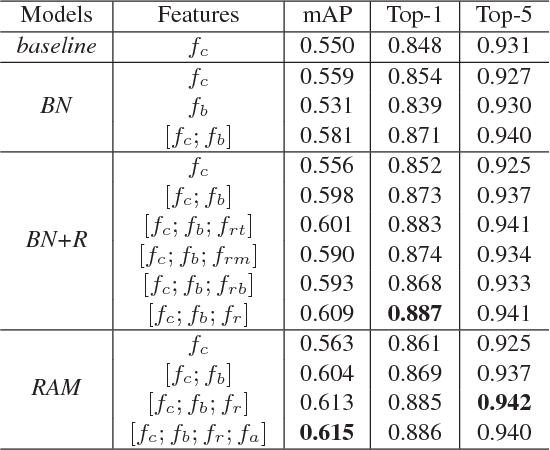
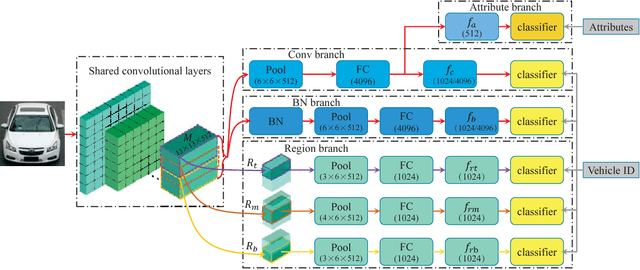
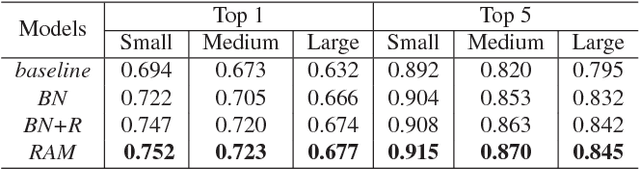
Abstract:Previous works on vehicle Re-ID mainly focus on extracting global features and learning distance metrics. Because some vehicles commonly share same model and maker, it is hard to distinguish them based on their global appearances. Compared with the global appearance, local regions such as decorations and inspection stickers attached to the windshield, may be more distinctive for vehicle Re-ID. To embed the detailed visual cues in those local regions, we propose a Region-Aware deep Model (RAM). Specifically, in addition to extracting global features, RAM also extracts features from a series of local regions. As each local region conveys more distinctive visual cues, RAM encourages the deep model to learn discriminative features. We also introduce a novel learning algorithm to jointly use vehicle IDs, types/models, and colors to train the RAM. This strategy fuses more cues for training and results in more discriminative global and regional features. We evaluate our methods on two large-scale vehicle Re-ID datasets, i.e., VeRi and VehicleID. Experimental results show our methods achieve promising performance in comparison with recent works.
E$^2$BoWs: An End-to-End Bag-of-Words Model via Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Sep 20, 2017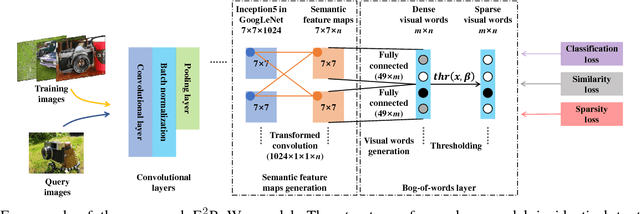

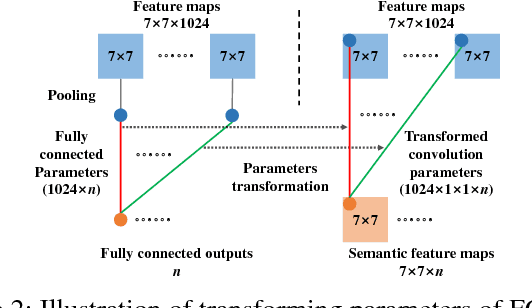
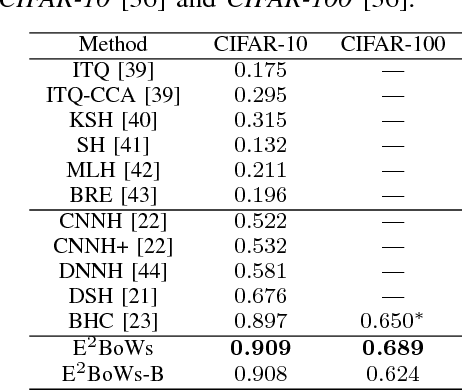
Abstract:Traditional Bag-of-visual Words (BoWs) model is commonly generated with many steps including local feature extraction, codebook generation, and feature quantization, etc. Those steps are relatively independent with each other and are hard to be jointly optimized. Moreover, the dependency on hand-crafted local feature makes BoWs model not effective in conveying high-level semantics. These issues largely hinder the performance of BoWs model in large-scale image applications. To conquer these issues, we propose an End-to-End BoWs (E$^2$BoWs) model based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN). Our model takes an image as input, then identifies and separates the semantic objects in it, and finally outputs the visual words with high semantic discriminative power. Specifically, our model firstly generates Semantic Feature Maps (SFMs) corresponding to different object categories through convolutional layers, then introduces Bag-of-Words Layers (BoWL) to generate visual words for each individual feature map. We also introduce a novel learning algorithm to reinforce the sparsity of the generated E$^2$BoWs model, which further ensures the time and memory efficiency. We evaluate the proposed E$^2$BoWs model on several image search datasets including CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, MIRFLICKR-25K and NUS-WIDE. Experimental results show that our method achieves promising accuracy and efficiency compared with recent deep learning based retrieval works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge