X. Angelo Huang
Language Models Are Implicitly Continuous
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Language is typically modelled with discrete sequences. However, the most successful approaches to language modelling, namely neural networks, are continuous and smooth function approximators. In this work, we show that Transformer-based language models implicitly learn to represent sentences as continuous-time functions defined over a continuous input space. This phenomenon occurs in most state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs), including Llama2, Llama3, Phi3, Gemma, Gemma2, and Mistral, and suggests that LLMs reason about language in ways that fundamentally differ from humans. Our work formally extends Transformers to capture the nuances of time and space continuity in both input and output space. Our results challenge the traditional interpretation of how LLMs understand language, with several linguistic and engineering implications.
Code Simulation as a Proxy for High-order Tasks in Large Language Models
Feb 05, 2025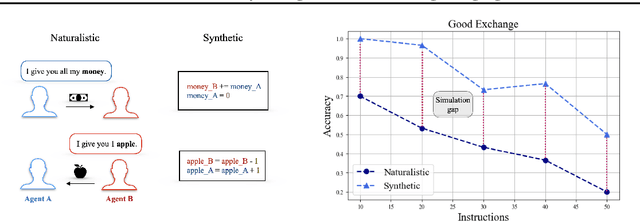

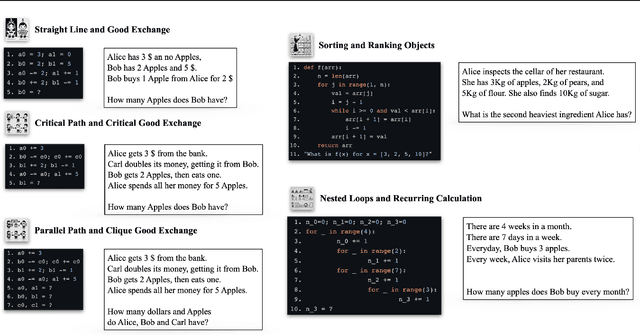
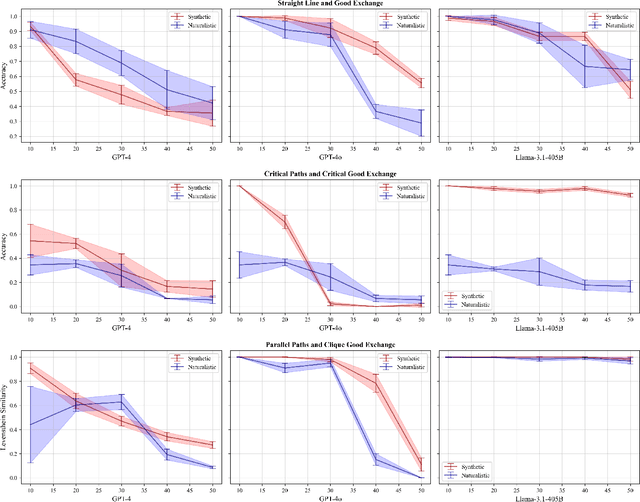
Abstract:Many reasoning, planning, and problem-solving tasks share an intrinsic algorithmic nature: correctly simulating each step is a sufficient condition to solve them correctly. We collect pairs of naturalistic and synthetic reasoning tasks to assess the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLM). While naturalistic tasks often require careful human handcrafting, we show that synthetic data is, in many cases, a good proxy that is much easier to collect at scale. We leverage common constructs in programming as the counterpart of the building blocks of naturalistic reasoning tasks, such as straight-line programs, code that contains critical paths, and approximate and redundant instructions. We further assess the capabilities of LLMs on sorting problems and repeated operations via sorting algorithms and nested loops. Our synthetic datasets further reveal that while the most powerful LLMs exhibit relatively strong execution capabilities, the process is fragile: it is negatively affected by memorisation and seems to rely heavily on pattern recognition. Our contribution builds upon synthetically testing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs as a scalable complement to handcrafted human-annotated problems.
A Notion of Complexity for Theory of Mind via Discrete World Models
Jun 16, 2024Abstract:Theory of Mind (ToM) can be used to assess the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in complex scenarios where social reasoning is required. While the research community has proposed many ToM benchmarks, their hardness varies greatly, and their complexity is not well defined. This work proposes a framework to measure the complexity of ToM tasks. We quantify a problem's complexity as the number of states necessary to solve it correctly. Our complexity measure also accounts for spurious states of a ToM problem designed to make it apparently harder. We use our method to assess the complexity of five widely adopted ToM benchmarks. On top of this framework, we design a prompting technique that augments the information available to a model with a description of how the environment changes with the agents' interactions. We name this technique Discrete World Models (DWM) and show how it elicits superior performance on ToM tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge