Andrea Asperti
University of Bologna
Does CLIP perceive art the same way we do?
May 08, 2025Abstract:CLIP has emerged as a powerful multimodal model capable of connecting images and text through joint embeddings, but to what extent does it "see" the same way humans do - especially when interpreting artworks? In this paper, we investigate CLIP's ability to extract high-level semantic and stylistic information from paintings, including both human-created and AI-generated imagery. We evaluate its perception across multiple dimensions: content, scene understanding, artistic style, historical period, and the presence of visual deformations or artifacts. By designing targeted probing tasks and comparing CLIP's responses to human annotations and expert benchmarks, we explore its alignment with human perceptual and contextual understanding. Our findings reveal both strengths and limitations in CLIP's visual representations, particularly in relation to aesthetic cues and artistic intent. We further discuss the implications of these insights for using CLIP as a guidance mechanism during generative processes, such as style transfer or prompt-based image synthesis. Our work highlights the need for deeper interpretability in multimodal systems, especially when applied to creative domains where nuance and subjectivity play a central role.
A Critical Assessment of Modern Generative Models' Ability to Replicate Artistic Styles
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:In recent years, advancements in generative artificial intelligence have led to the development of sophisticated tools capable of mimicking diverse artistic styles, opening new possibilities for digital creativity and artistic expression. This paper presents a critical assessment of the style replication capabilities of contemporary generative models, evaluating their strengths and limitations across multiple dimensions. We examine how effectively these models reproduce traditional artistic styles while maintaining structural integrity and compositional balance in the generated images. The analysis is based on a new large dataset of AI-generated works imitating artistic styles of the past, holding potential for a wide range of applications: the "AI-pastiche" dataset. The study is supported by extensive user surveys, collecting diverse opinions on the dataset and investigation both technical and aesthetic challenges, including the ability to generate outputs that are realistic and visually convincing, the versatility of models in handling a wide range of artistic styles, and the extent to which they adhere to the content and stylistic specifications outlined in prompts. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of generative tools in style replication, offering insights into their technical and artistic limitations, potential advancements in model design and training methodologies, and emerging opportunities for enhancing digital artistry, human-AI collaboration, and the broader creative landscape.
Deep Learning for Sea Surface Temperature Reconstruction under Cloud Occlusion
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:Sea Surface Temperature (SST) is crucial for understanding Earth's oceans and climate, significantly influencing weather patterns, ocean currents, marine ecosystem health, and the global energy balance. Large-scale SST monitoring relies on satellite infrared radiation detection, but cloud cover presents a major challenge, creating extensive observational gaps and hampering our ability to fully capture large-scale ocean temperature patterns. Efforts to address these gaps in existing L4 datasets have been made, but they often exhibit notable local and seasonal biases, compromising data reliability and accuracy. To tackle this challenge, we employed deep neural networks to reconstruct cloud-covered portions of satellite imagery while preserving the integrity of observed values in cloud-free areas, using MODIS satellite derived observations of SST. Our best-performing architecture showed significant skill improvements over established methodologies, achieving substantial reductions in error metrics when benchmarked against widely used approaches and datasets. These results underscore the potential of advanced AI techniques to enhance the completeness of satellite observations in Earth-science remote sensing, providing more accurate and reliable datasets for environmental assessments, data-driven model training, climate research, and seamless integration into model data assimilation workflows.
A Notion of Complexity for Theory of Mind via Discrete World Models
Jun 16, 2024Abstract:Theory of Mind (ToM) can be used to assess the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in complex scenarios where social reasoning is required. While the research community has proposed many ToM benchmarks, their hardness varies greatly, and their complexity is not well defined. This work proposes a framework to measure the complexity of ToM tasks. We quantify a problem's complexity as the number of states necessary to solve it correctly. Our complexity measure also accounts for spurious states of a ToM problem designed to make it apparently harder. We use our method to assess the complexity of five widely adopted ToM benchmarks. On top of this framework, we design a prompting technique that augments the information available to a model with a description of how the environment changes with the agents' interactions. We name this technique Discrete World Models (DWM) and show how it elicits superior performance on ToM tasks.
Wind speed super-resolution and validation: from ERA5 to CERRA via diffusion models
Jan 31, 2024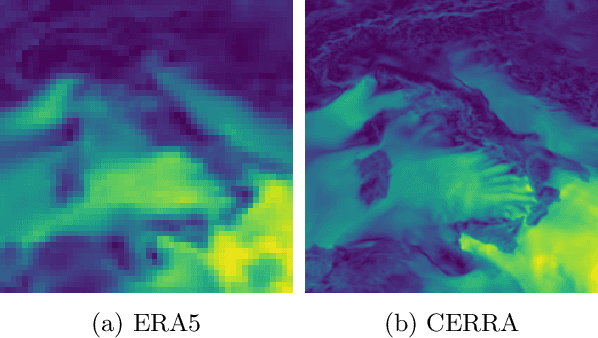
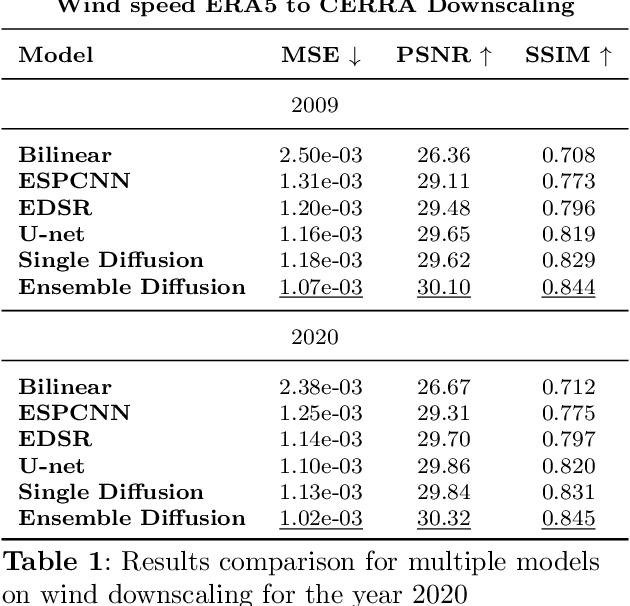
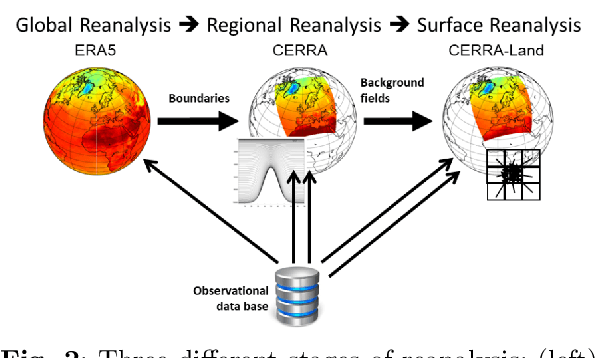
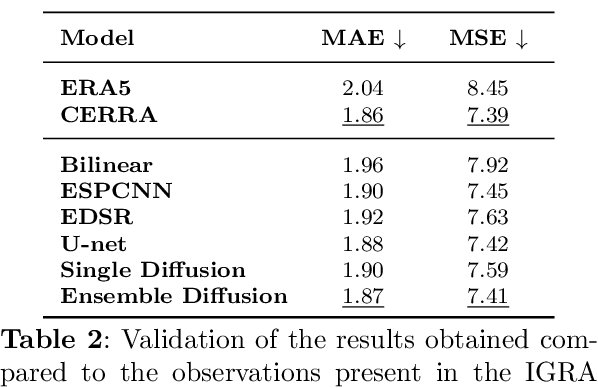
Abstract:The Copernicus Regional Reanalysis for Europe, CERRA, is a high-resolution regional reanalysis dataset for the European domain. In recent years it has shown significant utility across various climate-related tasks, ranging from forecasting and climate change research to renewable energy prediction, resource management, air quality risk assessment, and the forecasting of rare events, among others. Unfortunately, the availability of CERRA is lagging two years behind the current date, due to constraints in acquiring the requisite external data and the intensive computational demands inherent in its generation. As a solution, this paper introduces a novel method using diffusion models to approximate CERRA downscaling in a data-driven manner, without additional informations. By leveraging the lower resolution ERA5 dataset, which provides boundary conditions for CERRA, we approach this as a super-resolution task. Focusing on wind speed around Italy, our model, trained on existing CERRA data, shows promising results, closely mirroring original CERRA data. Validation with in-situ observations further confirms the model's accuracy in approximating ground measurements.
Precipitation nowcasting with generative diffusion models
Aug 13, 2023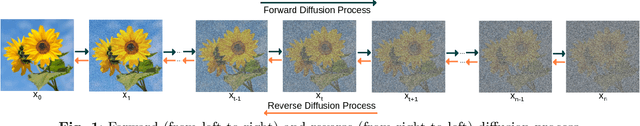
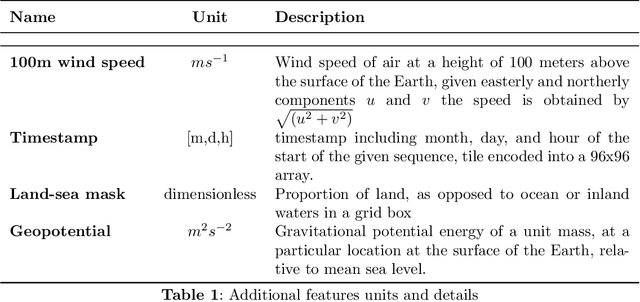
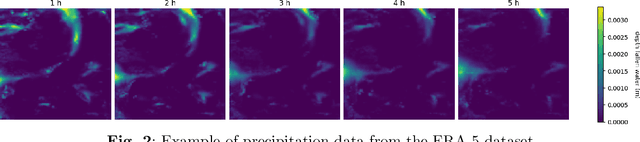
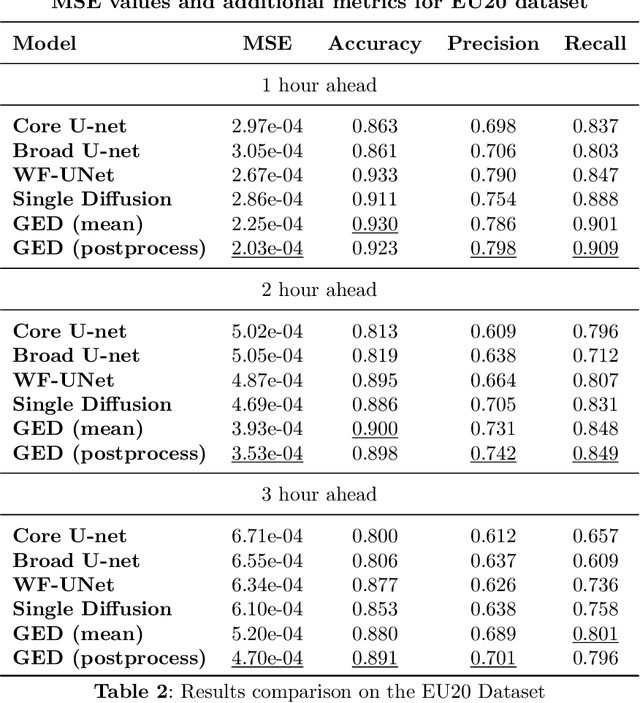
Abstract:In recent years traditional numerical methods for accurate weather prediction have been increasingly challenged by deep learning methods. Numerous historical datasets used for short and medium-range weather forecasts are typically organized into a regular spatial grid structure. This arrangement closely resembles images: each weather variable can be visualized as a map or, when considering the temporal axis, as a video. Several classes of generative models, comprising Generative Adversarial Networks, Variational Autoencoders, or the recent Denoising Diffusion Models have largely proved their applicability to the next-frame prediction problem, and is thus natural to test their performance on the weather prediction benchmarks. Diffusion models are particularly appealing in this context, due to the intrinsically probabilistic nature of weather forecasting: what we are really interested to model is the probability distribution of weather indicators, whose expected value is the most likely prediction. In our study, we focus on a specific subset of the ERA-5 dataset, which includes hourly data pertaining to Central Europe from the years 2016 to 2021. Within this context, we examine the efficacy of diffusion models in handling the task of precipitation nowcasting. Our work is conducted in comparison to the performance of well-established U-Net models, as documented in the existing literature. Our proposed approach of Generative Ensemble Diffusion (GED) utilizes a diffusion model to generate a set of possible weather scenarios which are then amalgamated into a probable prediction via the use of a post-processing network. This approach, in comparison to recent deep learning models, substantially outperformed them in terms of overall performance.
Head Rotation in Denoising Diffusion Models
Aug 11, 2023Abstract:Denoising Diffusion Models (DDM) are emerging as the cutting-edge technology in the realm of deep generative modeling, challenging the dominance of Generative Adversarial Networks. However, effectively exploring the latent space's semantics and identifying compelling trajectories for manipulating and editing important attributes of the generated samples remains challenging, primarily due to the high-dimensional nature of the latent space. In this study, we specifically concentrate on face rotation, which is known to be one of the most intricate editing operations. By leveraging a recent embedding technique for Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIM), we achieve, in many cases, noteworthy manipulations encompassing a wide rotation angle of $\pm 30^o$, preserving the distinct characteristics of the individual. Our methodology exploits the computation of trajectories approximating clouds of latent representations of dataset samples with different yaw rotations through linear regression. Specific trajectories are obtained by restricting the analysis to subsets of data sharing significant attributes with the source image. One of these attributes is the light provenance: a byproduct of our research is a labeling of CelebA, categorizing images into three major groups based on the illumination direction: left, center, and right.
Comparing the latent space of generative models
Jul 14, 2022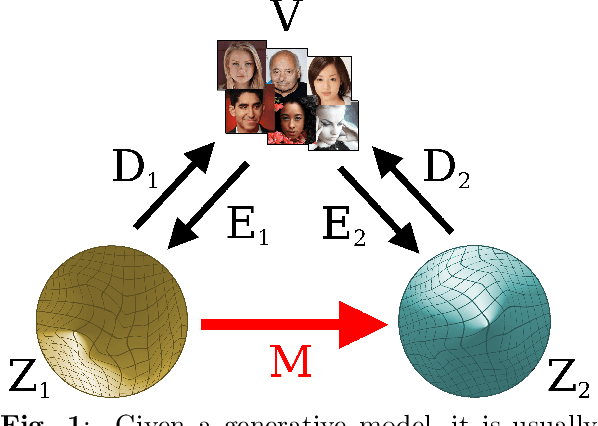
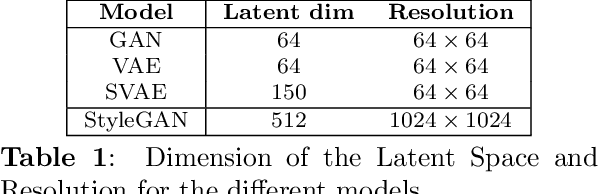

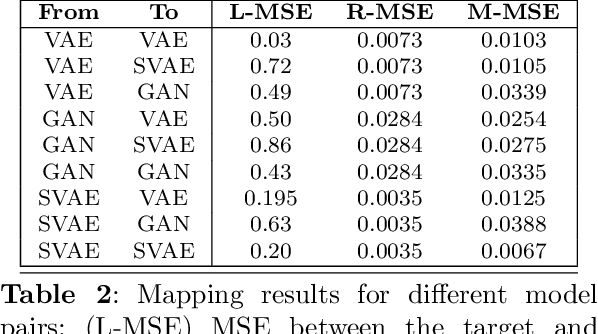
Abstract:Different encodings of datapoints in the latent space of latent-vector generative models may result in more or less effective and disentangled characterizations of the different explanatory factors of variation behind the data. Many works have been recently devoted to the explorationof the latent space of specific models, mostly focused on the study of how features are disentangled and of how trajectories producing desired alterations of data in the visible space can be found. In this work we address the more general problem of comparing the latent spaces of different models, looking for transformations between them. We confined the investigation to the familiar and largely investigated case of generative models for the data manifold of human faces. The surprising, preliminary result reported in this article is that (provided models have not been taught or explicitly conceived to act differently) a simple linear mapping is enough to pass from a latent space to another while preserving most of the information.
MicroRacer: a didactic environment for Deep Reinforcement Learning
Mar 20, 2022
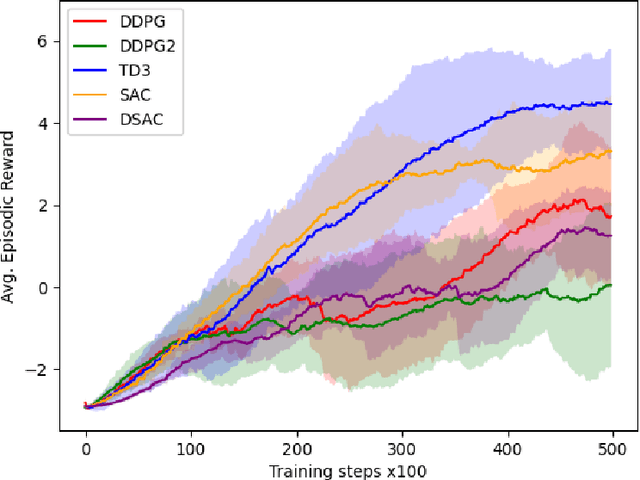
Abstract:MicroRacer is a simple, open source environment inspired by car racing especially meant for the didactics of Deep Reinforcement Learning. The complexity of the environment has been explicitly calibrated to allow users to experiment with many different methods, networks and hyperparameters settings without requiring sophisticated software or the need of exceedingly long training times. Baseline agents for major learning algorithms such as DDPG, PPO, SAC, TD2 and DSAC are provided too, along with a preliminary comparison in terms of training time and performance.
Enhancing variational generation through self-decomposition
Feb 06, 2022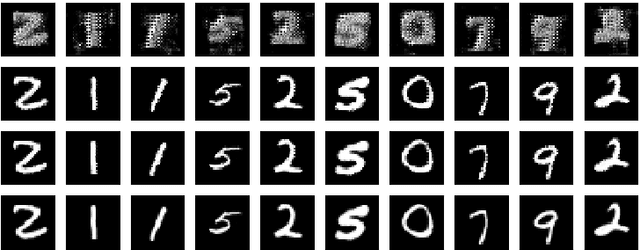
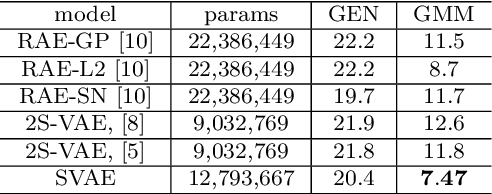
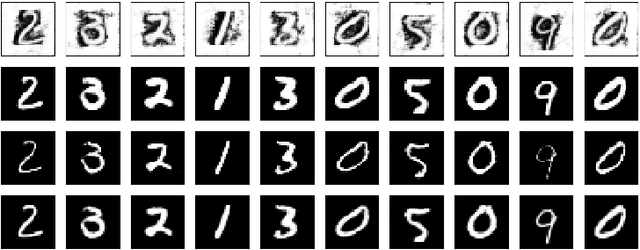
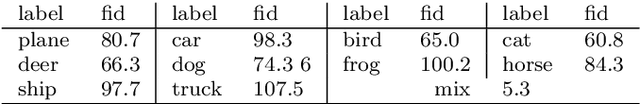
Abstract:In this article we introduce the notion of Split Variational Autoencoder (SVAE), whose output $\hat{x}$ is obtained as a weighted sum $\sigma \odot \hat{x_1} + (1-\sigma) \odot \hat{x_2}$ of two generated images $\hat{x_1},\hat{x_2}$, and $\sigma$ is a learned compositional map. The network is trained as a usual Variational Autoencoder with a negative loglikelihood loss between training and reconstructed images. The decomposition is nondeterministic, but follows two main schemes, that we may roughly categorize as either "syntactic" or "semantic". In the first case, the map tends to exploit the strong correlation between adjacent pixels, splitting the image in two complementary high frequency sub-images. In the second case, the map typically focuses on the contours of objects, splitting the image in interesting variations of its content, with more marked and distinctive features. In this case, the Fr\'echet Inception Distance (FID) of $\hat{x_1}$ and $\hat{x_2}$ is usually lower (hence better) than that of $\hat{x}$, that clearly suffers from being the average of the formers. In a sense, a SVAE forces the Variational Autoencoder to {\em make choices}, in contrast with its intrinsic tendency to average between alternatives with the aim to minimize the reconstruction loss towards a specific sample. According to the FID metric, our technique, tested on typical datasets such as Mnist, Cifar10 and Celeba, allows us to outperform all previous purely variational architectures (not relying on normalization flows).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge