Wujian Peng
CoMP: Continual Multimodal Pre-training for Vision Foundation Models
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) provide strong visual representations for a wide range of applications. In this paper, we continually pre-train prevailing VFMs in a multimodal manner such that they can effortlessly process visual inputs of varying sizes and produce visual representations that are more aligned with language representations, regardless of their original pre-training process. To this end, we introduce CoMP, a carefully designed multimodal pre-training pipeline. CoMP uses a Continual Rotary Position Embedding to support native resolution continual pre-training, and an Alignment Loss between visual and textual features through language prototypes to align multimodal representations. By three-stage training, our VFMs achieve remarkable improvements not only in multimodal understanding but also in other downstream tasks such as classification and segmentation. Remarkably, CoMP-SigLIP achieves scores of 66.7 on ChartQA and 75.9 on DocVQA with a 0.5B LLM, while maintaining an 87.4% accuracy on ImageNet-1K and a 49.5 mIoU on ADE20K under frozen chunk evaluation.
Inst-IT: Boosting Multimodal Instance Understanding via Explicit Visual Prompt Instruction Tuning
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have made significant breakthroughs with the advancement of instruction tuning. However, while existing models can understand images and videos at a holistic level, they still struggle with instance-level understanding that requires a more nuanced comprehension and alignment. Instance-level understanding is crucial, as it focuses on the specific elements that we are most interested in. Excitingly, existing works find that the state-of-the-art LMMs exhibit strong instance understanding capabilities when provided with explicit visual cues. Motivated by this, we introduce an automated annotation pipeline assisted by GPT-4o to extract instance-level information from images and videos through explicit visual prompting for instance guidance. Building upon this pipeline, we proposed Inst-IT, a solution to enhance LMMs in Instance understanding via explicit visual prompt Instruction Tuning. Inst-IT consists of a benchmark to diagnose multimodal instance-level understanding, a large-scale instruction-tuning dataset, and a continuous instruction-tuning training paradigm to effectively enhance spatial-temporal instance understanding capabilities of existing LMMs. Experimental results show that, with the boost of Inst-IT, our models not only achieve outstanding performance on Inst-IT Bench but also demonstrate significant improvements across various generic image and video understanding benchmarks. This highlights that our dataset not only boosts instance-level understanding but also strengthens the overall capabilities of generic image and video comprehension.
Synthesize, Diagnose, and Optimize: Towards Fine-Grained Vision-Language Understanding
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:Vision language models (VLM) have demonstrated remarkable performance across various downstream tasks. However, understanding fine-grained visual-linguistic concepts, such as attributes and inter-object relationships, remains a significant challenge. While several benchmarks aim to evaluate VLMs in finer granularity, their primary focus remains on the linguistic aspect, neglecting the visual dimension. Here, we highlight the importance of evaluating VLMs from both a textual and visual perspective. We introduce a progressive pipeline to synthesize images that vary in a specific attribute while ensuring consistency in all other aspects. Utilizing this data engine, we carefully design a benchmark, SPEC, to diagnose the comprehension of object size, position, existence, and count. Subsequently, we conduct a thorough evaluation of four leading VLMs on SPEC. Surprisingly, their performance is close to random guess, revealing significant limitations. With this in mind, we propose a simply yet effective approach to optimize VLMs in fine-grained understanding, achieving significant improvements on SPEC without compromising the zero-shot performance. Results on two additional fine-grained benchmarks also show consistent improvements, further validating the transferability of our approach.
Building an Open-Vocabulary Video CLIP Model with Better Architectures, Optimization and Data
Oct 08, 2023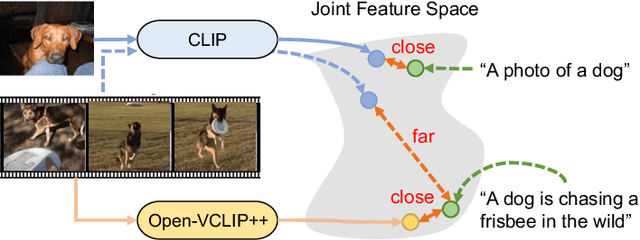
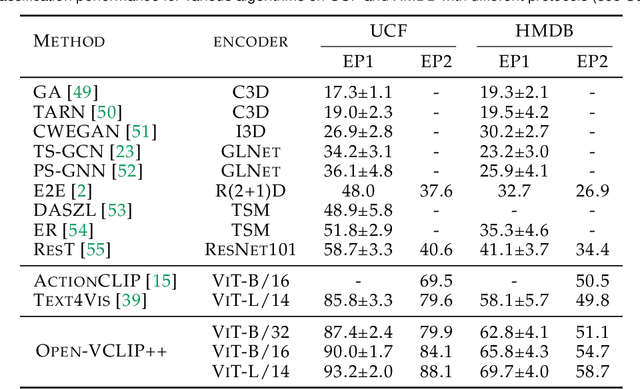
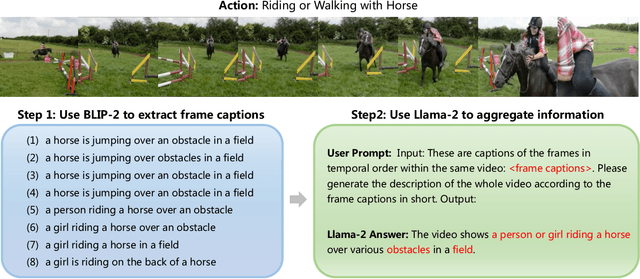
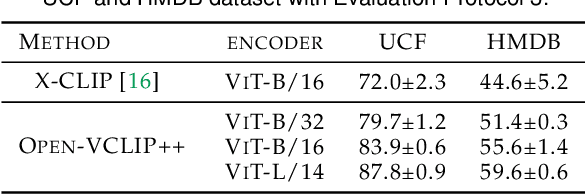
Abstract:Despite significant results achieved by Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) in zero-shot image recognition, limited effort has been made exploring its potential for zero-shot video recognition. This paper presents Open-VCLIP++, a simple yet effective framework that adapts CLIP to a strong zero-shot video classifier, capable of identifying novel actions and events during testing. Open-VCLIP++ minimally modifies CLIP to capture spatial-temporal relationships in videos, thereby creating a specialized video classifier while striving for generalization. We formally demonstrate that training Open-VCLIP++ is tantamount to continual learning with zero historical data. To address this problem, we introduce Interpolated Weight Optimization, a technique that leverages the advantages of weight interpolation during both training and testing. Furthermore, we build upon large language models to produce fine-grained video descriptions. These detailed descriptions are further aligned with video features, facilitating a better transfer of CLIP to the video domain. Our approach is evaluated on three widely used action recognition datasets, following a variety of zero-shot evaluation protocols. The results demonstrate that our method surpasses existing state-of-the-art techniques by significant margins. Specifically, we achieve zero-shot accuracy scores of 88.1%, 58.7%, and 81.2% on UCF, HMDB, and Kinetics-600 datasets respectively, outpacing the best-performing alternative methods by 8.5%, 8.2%, and 12.3%. We also evaluate our approach on the MSR-VTT video-text retrieval dataset, where it delivers competitive video-to-text and text-to-video retrieval performance, while utilizing substantially less fine-tuning data compared to other methods. Code is released at https://github.com/wengzejia1/Open-VCLIP.
BMB: Balanced Memory Bank for Imbalanced Semi-supervised Learning
May 22, 2023Abstract:Exploring a substantial amount of unlabeled data, semi-supervised learning (SSL) boosts the recognition performance when only a limited number of labels are provided. However, traditional methods assume that the data distribution is class-balanced, which is difficult to achieve in reality due to the long-tailed nature of real-world data. While the data imbalance problem has been extensively studied in supervised learning (SL) paradigms, directly transferring existing approaches to SSL is nontrivial, as prior knowledge about data distribution remains unknown in SSL. In light of this, we propose Balanced Memory Bank (BMB), a semi-supervised framework for long-tailed recognition. The core of BMB is an online-updated memory bank that caches historical features with their corresponding pseudo labels, and the memory is also carefully maintained to ensure the data therein are class-rebalanced. Additionally, an adaptive weighting module is introduced to work jointly with the memory bank so as to further re-calibrate the biased training process. We conduct experiments on multiple datasets and demonstrate, among other things, that BMB surpasses state-of-the-art approaches by clear margins, for example 8.2$\%$ on the 1$\%$ labeled subset of ImageNet127 (with a resolution of 64$\times$64) and 4.3$\%$ on the 50$\%$ labeled subset of ImageNet-LT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge