William Wong
Detecting misinformation through Framing Theory: the Frame Element-based Model
Feb 19, 2024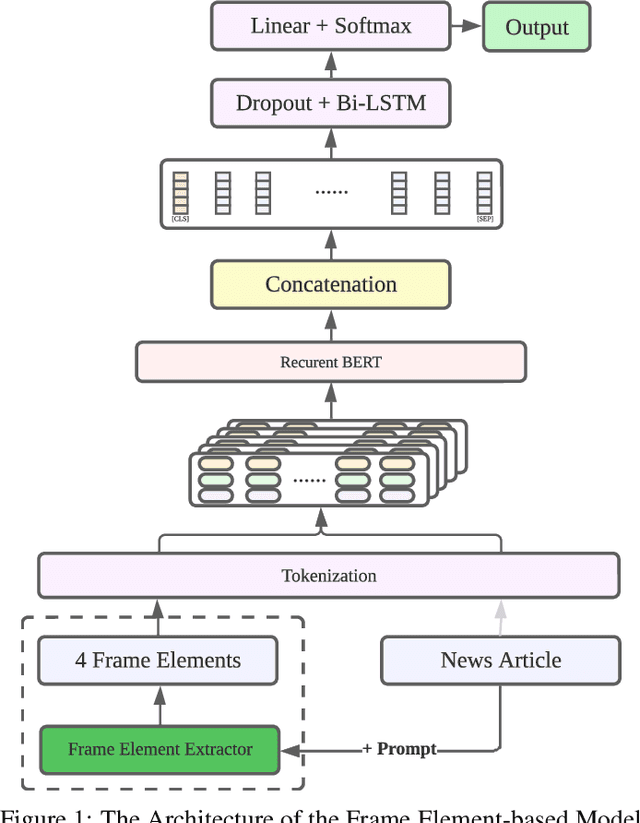
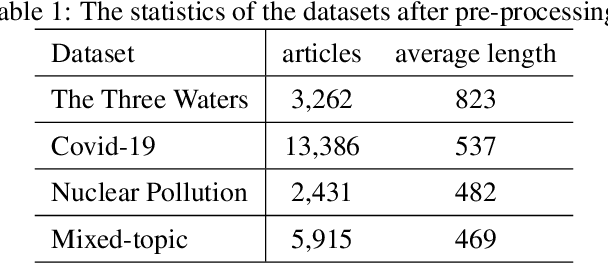
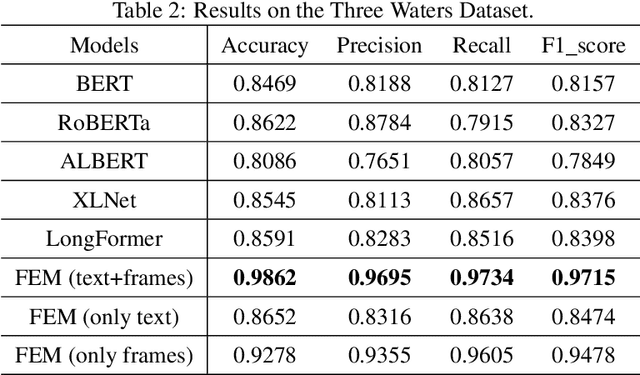
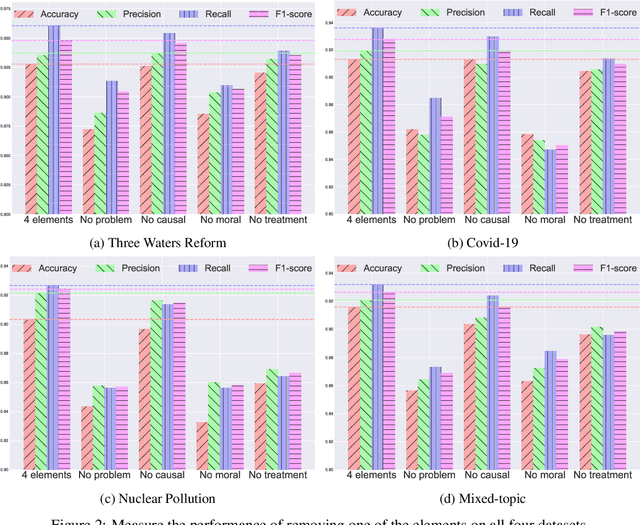
Abstract:In this paper, we delve into the rapidly evolving challenge of misinformation detection, with a specific focus on the nuanced manipulation of narrative frames - an under-explored area within the AI community. The potential for Generative AI models to generate misleading narratives underscores the urgency of this problem. Drawing from communication and framing theories, we posit that the presentation or 'framing' of accurate information can dramatically alter its interpretation, potentially leading to misinformation. We highlight this issue through real-world examples, demonstrating how shifts in narrative frames can transmute fact-based information into misinformation. To tackle this challenge, we propose an innovative approach leveraging the power of pre-trained Large Language Models and deep neural networks to detect misinformation originating from accurate facts portrayed under different frames. These advanced AI techniques offer unprecedented capabilities in identifying complex patterns within unstructured data critical for examining the subtleties of narrative frames. The objective of this paper is to bridge a significant research gap in the AI domain, providing valuable insights and methodologies for tackling framing-induced misinformation, thus contributing to the advancement of responsible and trustworthy AI technologies. Several experiments are intensively conducted and experimental results explicitly demonstrate the various impact of elements of framing theory proving the rationale of applying framing theory to increase the performance in misinformation detection.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Optimizing Industrial HVAC Systems with Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning
Sep 16, 2022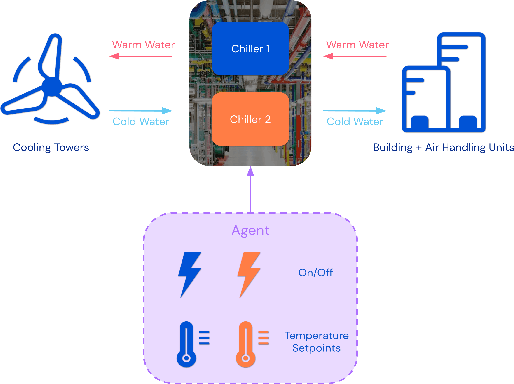
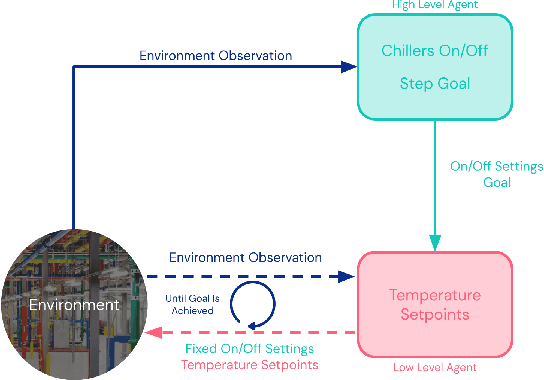
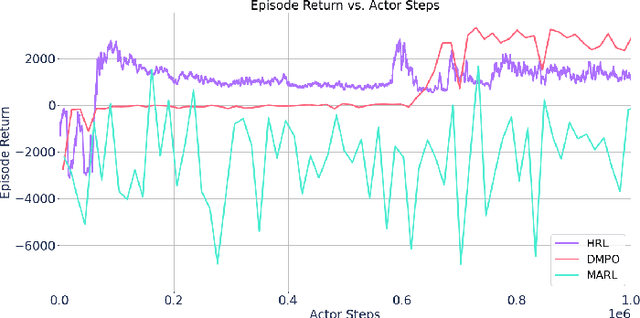
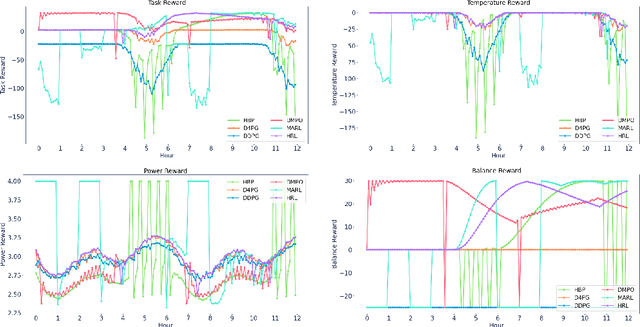
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) techniques have been developed to optimize industrial cooling systems, offering substantial energy savings compared to traditional heuristic policies. A major challenge in industrial control involves learning behaviors that are feasible in the real world due to machinery constraints. For example, certain actions can only be executed every few hours while other actions can be taken more frequently. Without extensive reward engineering and experimentation, an RL agent may not learn realistic operation of machinery. To address this, we use hierarchical reinforcement learning with multiple agents that control subsets of actions according to their operation time scales. Our hierarchical approach achieves energy savings over existing baselines while maintaining constraints such as operating chillers within safe bounds in a simulated HVAC control environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge