William B. Langdon
Improving a Parallel C++ Intel AVX-512 SIMD Linear Genetic Programming Interpreter
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:We extend recent 256 SSE vector work to 512 AVX giving a four fold speedup. We use MAGPIE (Machine Automated General Performance Improvement via Evolution of software) to speedup a C++ linear genetic programming interpreter. Local search is provided with three alternative hand optimised codes, revision history and the Intel 512 bit AVX512VL documentation as C++ XML. Magpie is applied to the new Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) parallel interpreter for Peter Nordin's linear genetic programming GPengine. Linux mprotect sandboxes whilst performance is given by perf instruction count. In both cases, in a matter of hours local search reliably sped up 114 or 310 lines of manually written parallel SIMD code for the Intel Advanced Vector Extensions (AVX) by 2 percent.
GreenStableYolo: Optimizing Inference Time and Image Quality of Text-to-Image Generation
Jul 20, 2024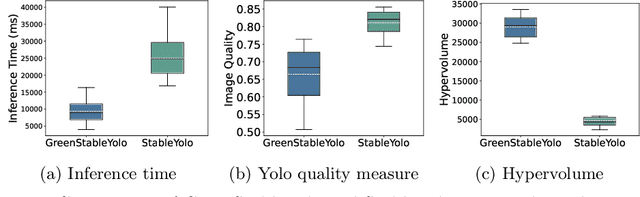
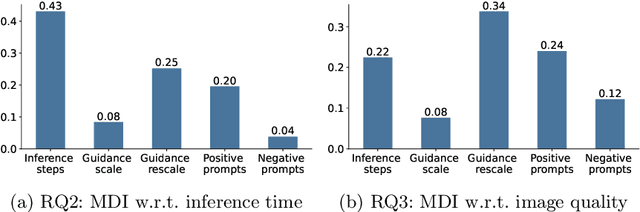
Abstract:Tuning the parameters and prompts for improving AI-based text-to-image generation has remained a substantial yet unaddressed challenge. Hence we introduce GreenStableYolo, which improves the parameters and prompts for Stable Diffusion to both reduce GPU inference time and increase image generation quality using NSGA-II and Yolo. Our experiments show that despite a relatively slight trade-off (18%) in image quality compared to StableYolo (which only considers image quality), GreenStableYolo achieves a substantial reduction in inference time (266% less) and a 526% higher hypervolume, thereby advancing the state-of-the-art for text-to-image generation.
GI Software with fewer Data Cache Misses
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:By their very name caches are often overlooked and yet play a vital role in the performance of modern and indeed future hardware. Using MAGPIE (Machine Automated General Performance Improvement via Evolution of software) we show genetic improvement GI can reduce the cache load of existing computer programs. Operating on lines of C and C++ source code using local search, Magpie can generate new functionally equivalent variants which generate fewer L1 data cache misses. Cache miss reduction is tested on two industrial open source programs (Google's Open Location Code OLC and Uber's Hexagonal Hierarchical Spatial Index H3) and two 2D photograph image processing tasks, counting pixels and OpenCV's SEEDS segmentation algorithm. Magpie's patches functionally generalise. In one case they reduce data misses on the highest performance L1 cache dramatically by 47 percent.
Genetic Improvement @ ICSE 2020
Jul 31, 2020
Abstract:Following Prof. Mark Harman of Facebook's keynote and formal presentations (which are recorded in the proceedings) there was a wide ranging discussion at the eighth international Genetic Improvement workshop, GI-2020 @ ICSE (held as part of the 42nd ACM/IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering on Friday 3rd July 2020). Topics included industry take up, human factors, explainabiloity (explainability, justifyability, exploitability) and GI benchmarks. We also contrast various recent online approaches (e.g. SBST 2020) to holding virtual computer science conferences and workshops via the WWW on the Internet without face-2-face interaction. Finally we speculate on how the Coronavirus Covid-19 Pandemic will affect research next year and into the future.
Fast Generation of Big Random Binary Trees
Jan 13, 2020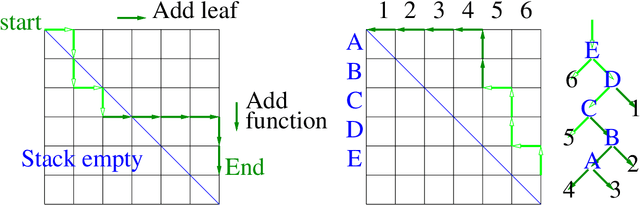
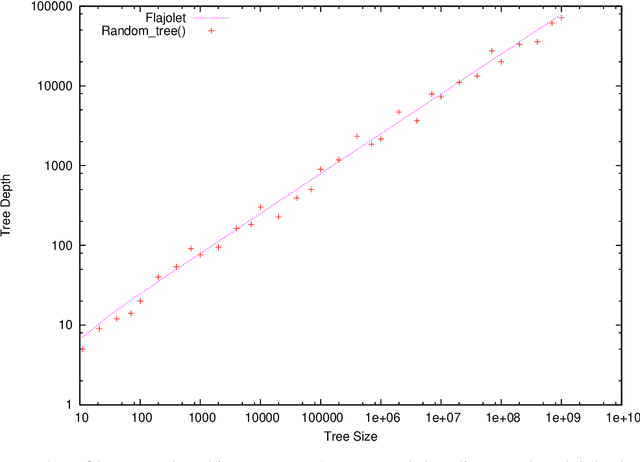
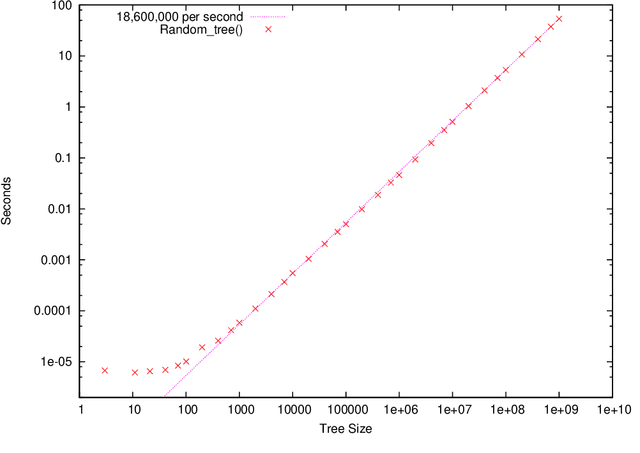
Abstract:random_tree() is a linear time and space C++ implementation able to create trees of up to a billion nodes for genetic programming and genetic improvement experiments. A 3.60GHz CPU can generate more than 18 million random nodes for GP program trees per second.
The State and Future of Genetic Improvement
Jun 27, 2019Abstract:We report the discussion session at the sixth international Genetic Improvement workshop, GI-2019 @ ICSE, which was held as part of the 41st ACM/IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering on Tuesday 28th May 2019. Topics included GI representations, the maintainability of evolved code, automated software testing, future areas of GI research, such as co-evolution, and existing GI tools and benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge