William Anderson
mLaSDI: Multi-stage latent space dynamics identification
Jun 12, 2025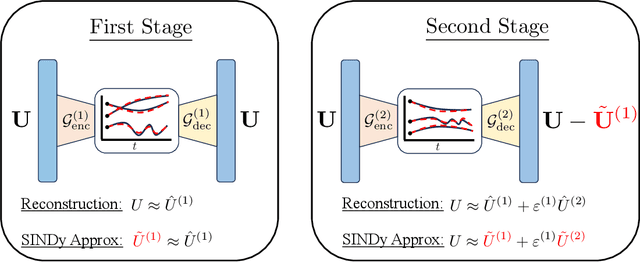
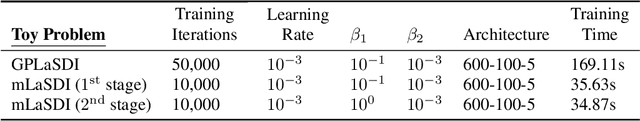
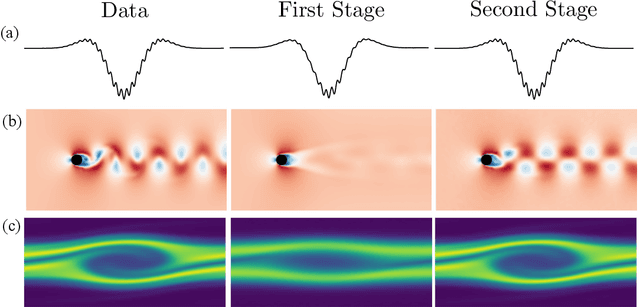
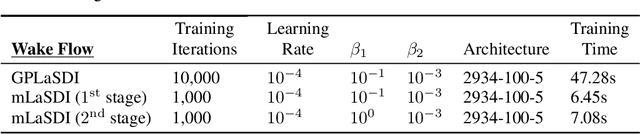
Abstract:Determining accurate numerical solutions of partial differential equations (PDEs) is an important task in many scientific disciplines. However, solvers can be computationally expensive, leading to the development of reduced-order models (ROMs). Recently, Latent Space Dynamics Identification (LaSDI) was proposed as a data-driven, non-intrusive ROM framework. LaSDI compresses the training data using an autoencoder and learns a system of user-chosen ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which govern the latent space dynamics. This allows for rapid predictions by interpolating and evolving the low-dimensional ODEs in the latent space. While LaSDI has produced effective ROMs for numerous problems, the autoencoder can have difficulty accurately reconstructing training data while also satisfying the imposed dynamics in the latent space, particularly in complex or high-frequency regimes. To address this, we propose multi-stage Latent Space Dynamics Identification (mLaSDI). With mLaSDI, several autoencoders are trained sequentially in stages, where each autoencoder learns to correct the error of the previous stages. We find that applying mLaSDI with small autoencoders results in lower prediction and reconstruction errors, while also reducing training time compared to LaSDI.
Defining Foundation Models for Computational Science: A Call for Clarity and Rigor
May 28, 2025Abstract:The widespread success of foundation models in natural language processing and computer vision has inspired researchers to extend the concept to scientific machine learning and computational science. However, this position paper argues that as the term "foundation model" is an evolving concept, its application in computational science is increasingly used without a universally accepted definition, potentially creating confusion and diluting its precise scientific meaning. In this paper, we address this gap by proposing a formal definition of foundation models in computational science, grounded in the core values of generality, reusability, and scalability. We articulate a set of essential and desirable characteristics that such models must exhibit, drawing parallels with traditional foundational methods, like the finite element and finite volume methods. Furthermore, we introduce the Data-Driven Finite Element Method (DD-FEM), a framework that fuses the modular structure of classical FEM with the representational power of data-driven learning. We demonstrate how DD-FEM addresses many of the key challenges in realizing foundation models for computational science, including scalability, adaptability, and physics consistency. By bridging traditional numerical methods with modern AI paradigms, this work provides a rigorous foundation for evaluating and developing novel approaches toward future foundation models in computational science.
Eclectic Rule Extraction for Explainability of Deep Neural Network based Intrusion Detection Systems
Jan 18, 2024



Abstract:This paper addresses trust issues created from the ubiquity of black box algorithms and surrogate explainers in Explainable Intrusion Detection Systems (X-IDS). While Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) aims to enhance transparency, black box surrogate explainers, such as Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanation (LIME) and SHapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP), are difficult to trust. The black box nature of these surrogate explainers makes the process behind explanation generation opaque and difficult to understand. To avoid this problem, one can use transparent white box algorithms such as Rule Extraction (RE). There are three types of RE algorithms: pedagogical, decompositional, and eclectic. Pedagogical methods offer fast but untrustworthy white-box explanations, while decompositional RE provides trustworthy explanations with poor scalability. This work explores eclectic rule extraction, which strikes a balance between scalability and trustworthiness. By combining techniques from pedagogical and decompositional approaches, eclectic rule extraction leverages the advantages of both, while mitigating some of their drawbacks. The proposed Hybrid X-IDS architecture features eclectic RE as a white box surrogate explainer for black box Deep Neural Networks (DNN). The presented eclectic RE algorithm extracts human-readable rules from hidden layers, facilitating explainable and trustworthy rulesets. Evaluations on UNSW-NB15 and CIC-IDS-2017 datasets demonstrate the algorithm's ability to generate rulesets with 99.9% accuracy, mimicking DNN outputs. The contributions of this work include the hybrid X-IDS architecture, the eclectic rule extraction algorithm applicable to intrusion detection datasets, and a thorough analysis of performance and explainability, demonstrating the trade-offs involved in rule extraction speed and accuracy.
REGARD: Rules of EngaGement for Automated cybeR Defense to aid in Intrusion Response
May 23, 2023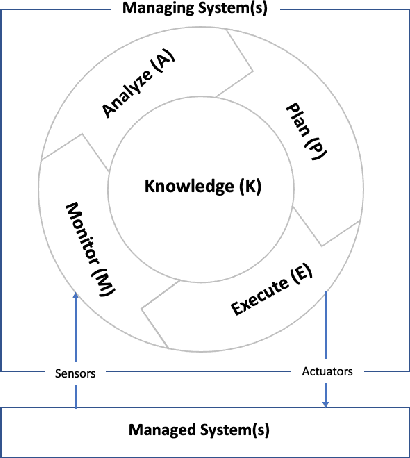
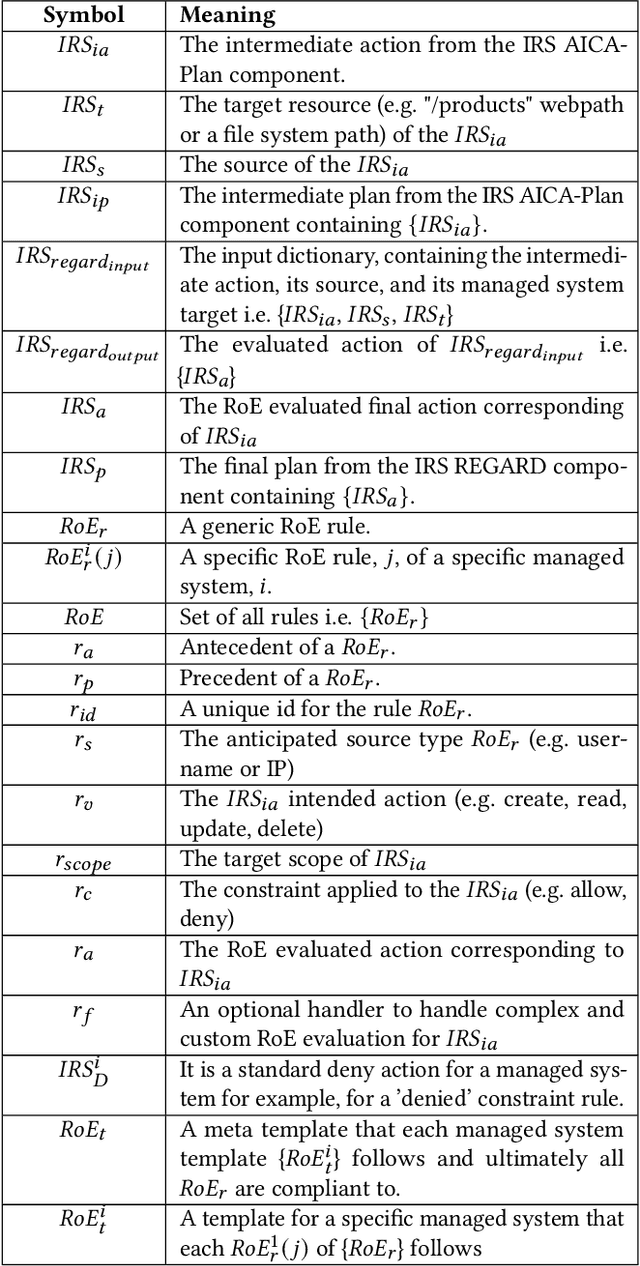
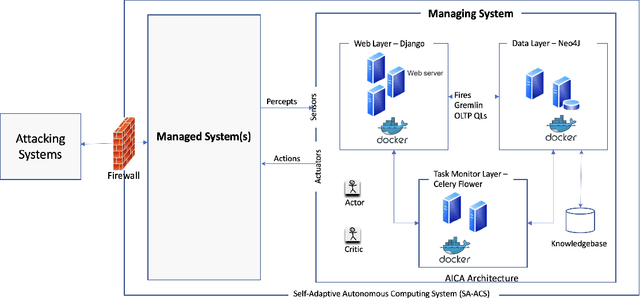
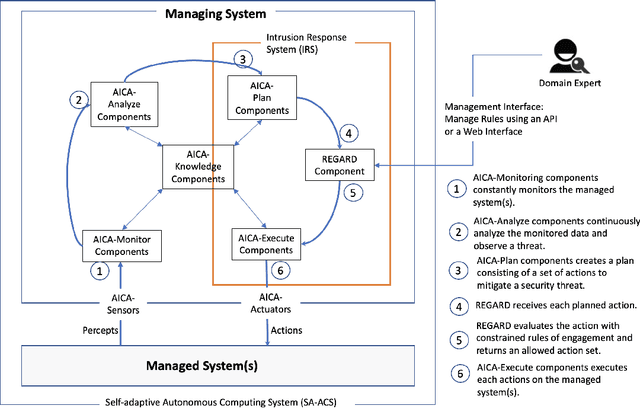
Abstract:Automated Intelligent Cyberdefense Agents (AICAs) that are part Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and part Intrusion Response Systems (IRS) are being designed to protect against sophisticated and automated cyber-attacks. An AICA based on the ideas of Self-Adaptive Autonomic Computing Systems (SA-ACS) can be considered as a managing system that protects a managed system like a personal computer, web application, critical infrastructure, etc. An AICA, specifically the IRS components, can compute a wide range of potential responses to meet its security goals and objectives, such as taking actions to prevent the attack from completing, restoring the system to comply with the organizational security policy, containing or confining an attack, attack eradication, deploying forensics measures to enable future attack analysis, counterattack, and so on. To restrict its activities in order to minimize collateral/organizational damage, such an automated system must have set Rules of Engagement (RoE). Automated systems must determine which operations can be completely automated (and when), which actions require human operator confirmation, and which actions must never be undertaken. In this paper, to enable this control functionality over an IRS, we create Rules of EngaGement for Automated cybeR Defense (REGARD) system which holds a set of Rules of Engagement (RoE) to protect the managed system according to the instructions provided by the human operator. These rules help limit the action of the IRS on the managed system in compliance with the recommendations of the domain expert. We provide details of execution, management, operation, and conflict resolution for Rules of Engagement (RoE) to constrain the actions of an automated IRS. We also describe REGARD system implementation, security case studies for cyber defense, and RoE demonstrations.
Explainable Intrusion Detection Systems Using Competitive Learning Techniques
Mar 30, 2023
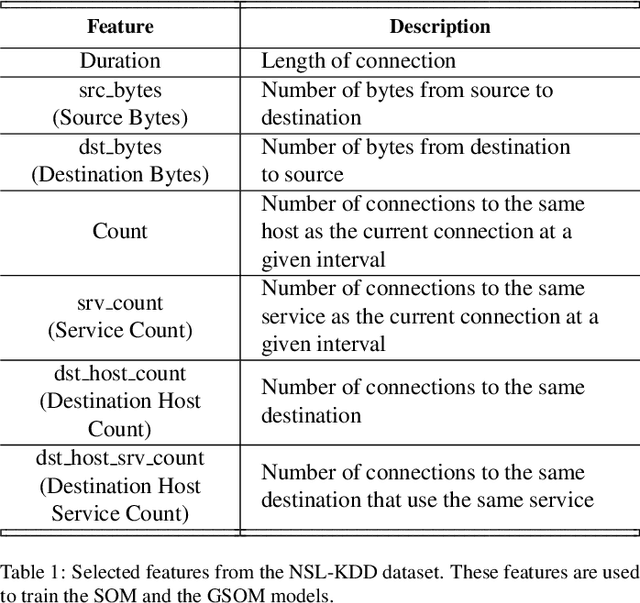

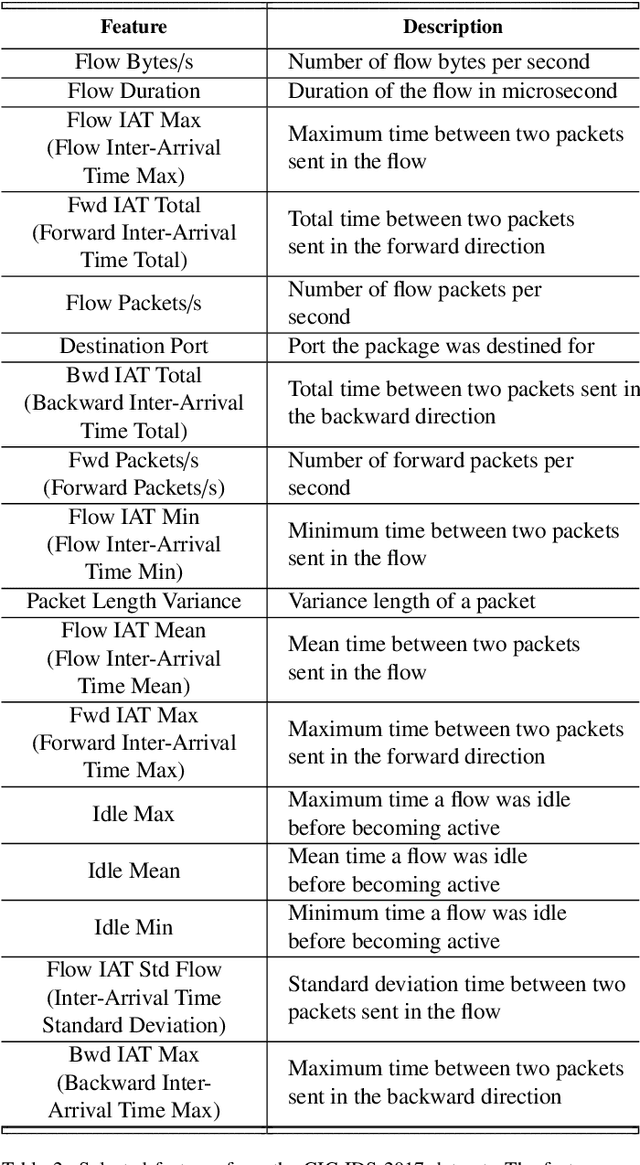
Abstract:The current state of the art systems in Artificial Intelligence (AI) enabled intrusion detection use a variety of black box methods. These black box methods are generally trained using Error Based Learning (EBL) techniques with a focus on creating accurate models. These models have high performative costs and are not easily explainable. A white box Competitive Learning (CL) based eXplainable Intrusion Detection System (X-IDS) offers a potential solution to these problem. CL models utilize an entirely different learning paradigm than EBL approaches. This different learning process makes the CL family of algorithms innately explainable and less resource intensive. In this paper, we create an X-IDS architecture that is based on DARPA's recommendation for explainable systems. In our architecture we leverage CL algorithms like, Self Organizing Maps (SOM), Growing Self Organizing Maps (GSOM), and Growing Hierarchical Self Organizing Map (GHSOM). The resulting models can be data-mined to create statistical and visual explanations. Our architecture is tested using NSL-KDD and CIC-IDS-2017 benchmark datasets, and produces accuracies that are 1% - 3% less than EBL models. However, CL models are much more explainable than EBL models. Additionally, we use a pruning process that is able to significantly reduce the size of these CL based models. By pruning our models, we are able to increase prediction speeds. Lastly, we analyze the statistical and visual explanations generated by our architecture, and we give a strategy that users could use to help navigate the set of explanations. These explanations will help users build trust with an Intrusion Detection System (IDS), and allow users to discover ways to increase the IDS's potency.
Designing an Artificial Immune System inspired Intrusion Detection System
Aug 16, 2022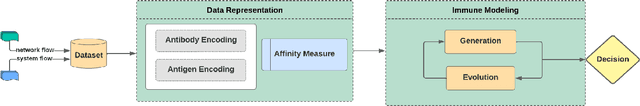
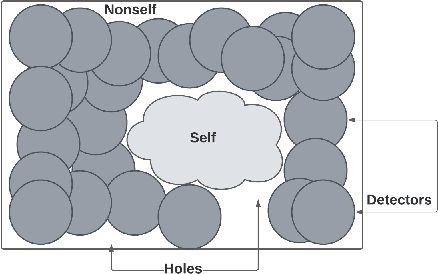
Abstract:The Human Immune System (HIS) works to protect a body from infection, illness, and disease. This system can inspire cybersecurity professionals to design an Artificial Immune System (AIS) based Intrusion Detection System (IDS). These biologically inspired algorithms using Self/Nonself and Danger Theory can directly augmentIDS designs and implementations. In this paper, we include an examination into the elements of design necessary for building an AIS-IDS framework and present an architecture to create such systems.
Creating an Explainable Intrusion Detection System Using Self Organizing Maps
Jul 15, 2022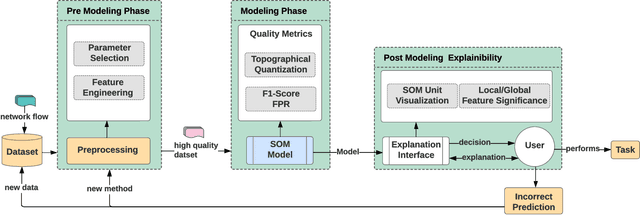
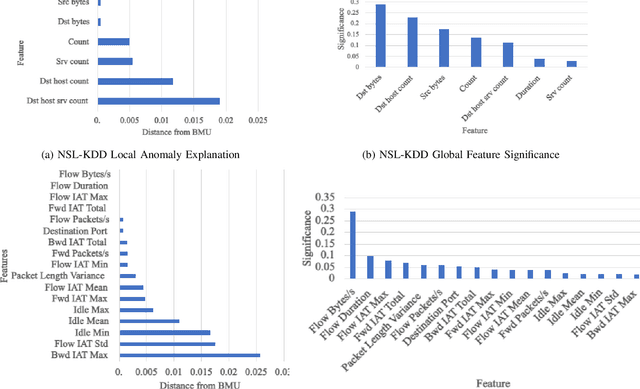
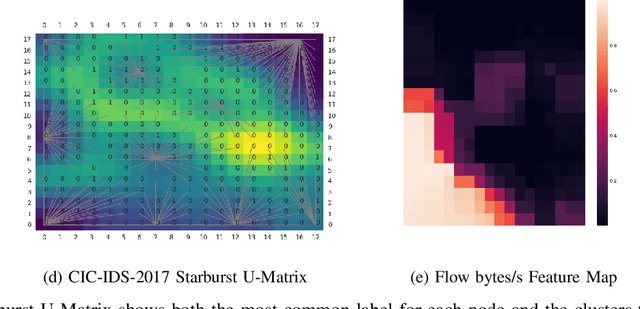
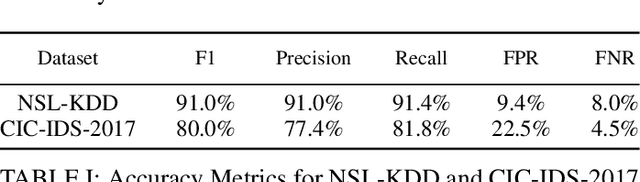
Abstract:Modern Artificial Intelligence (AI) enabled Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are complex black boxes. This means that a security analyst will have little to no explanation or clarification on why an IDS model made a particular prediction. A potential solution to this problem is to research and develop Explainable Intrusion Detection Systems (X-IDS) based on current capabilities in Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). In this paper, we create a Self Organizing Maps (SOMs) based X-IDS system that is capable of producing explanatory visualizations. We leverage SOM's explainability to create both global and local explanations. An analyst can use global explanations to get a general idea of how a particular IDS model computes predictions. Local explanations are generated for individual datapoints to explain why a certain prediction value was computed. Furthermore, our SOM based X-IDS was evaluated on both explanation generation and traditional accuracy tests using the NSL-KDD and the CIC-IDS-2017 datasets.
Explainable Intrusion Detection Systems (X-IDS): A Survey of Current Methods, Challenges, and Opportunities
Jul 13, 2022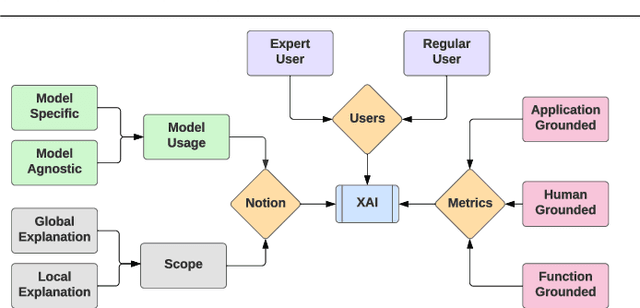
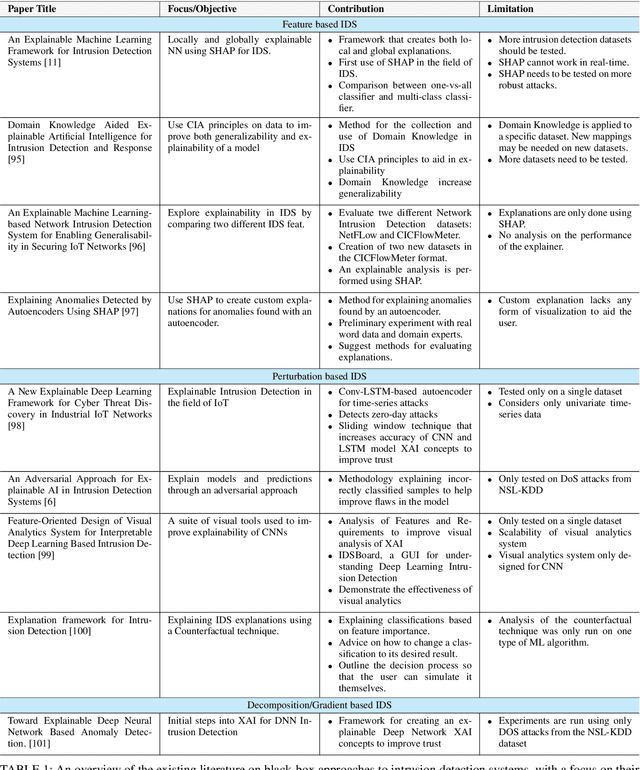
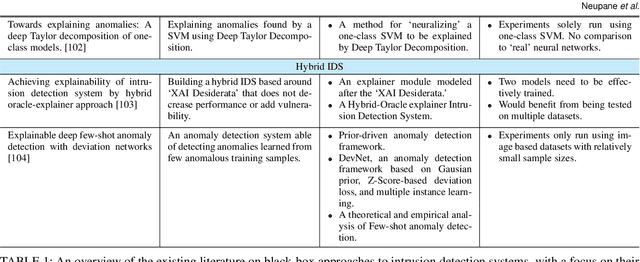
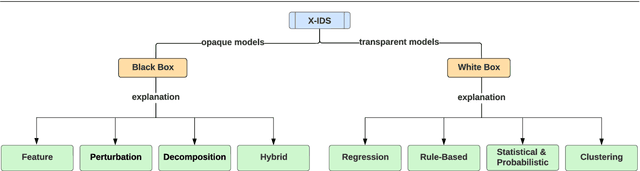
Abstract:The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to cybersecurity challenges has gained traction in industry and academia, partially as a result of widespread malware attacks on critical systems such as cloud infrastructures and government institutions. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), using some forms of AI, have received widespread adoption due to their ability to handle vast amounts of data with a high prediction accuracy. These systems are hosted in the organizational Cyber Security Operation Center (CSoC) as a defense tool to monitor and detect malicious network flow that would otherwise impact the Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA). CSoC analysts rely on these systems to make decisions about the detected threats. However, IDSs designed using Deep Learning (DL) techniques are often treated as black box models and do not provide a justification for their predictions. This creates a barrier for CSoC analysts, as they are unable to improve their decisions based on the model's predictions. One solution to this problem is to design explainable IDS (X-IDS). This survey reviews the state-of-the-art in explainable AI (XAI) for IDS, its current challenges, and discusses how these challenges span to the design of an X-IDS. In particular, we discuss black box and white box approaches comprehensively. We also present the tradeoff between these approaches in terms of their performance and ability to produce explanations. Furthermore, we propose a generic architecture that considers human-in-the-loop which can be used as a guideline when designing an X-IDS. Research recommendations are given from three critical viewpoints: the need to define explainability for IDS, the need to create explanations tailored to various stakeholders, and the need to design metrics to evaluate explanations.
Using Uncertainty in Deep Learning Reconstruction for Cone-Beam CT of the Brain
Aug 20, 2021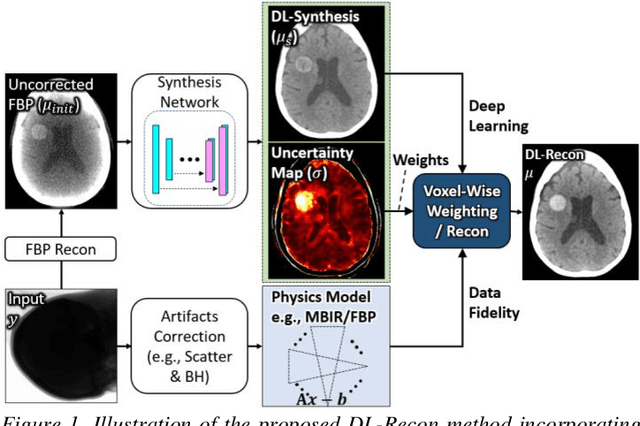
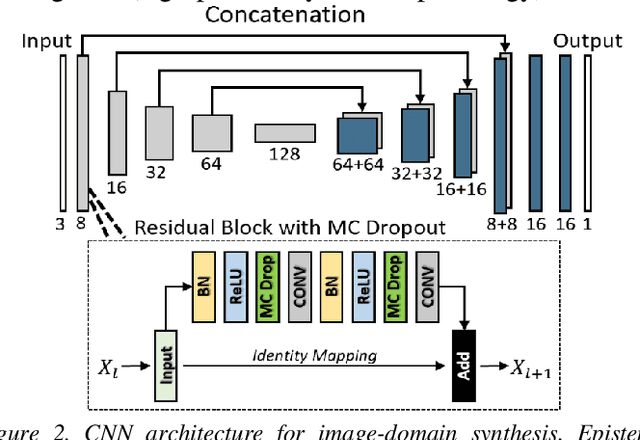
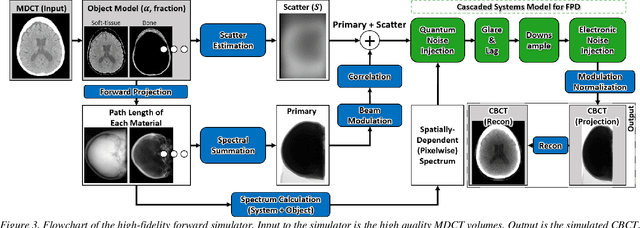
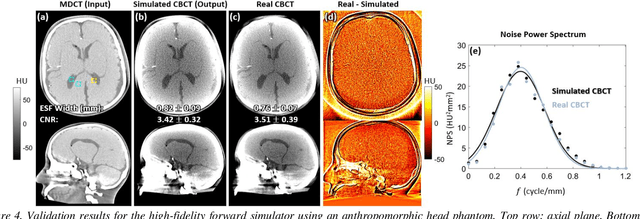
Abstract:Contrast resolution beyond the limits of conventional cone-beam CT (CBCT) systems is essential to high-quality imaging of the brain. We present a deep learning reconstruction method (dubbed DL-Recon) that integrates physically principled reconstruction models with DL-based image synthesis based on the statistical uncertainty in the synthesis image. A synthesis network was developed to generate a synthesized CBCT image (DL-Synthesis) from an uncorrected filtered back-projection (FBP) image. To improve generalizability (including accurate representation of lesions not seen in training), voxel-wise epistemic uncertainty of DL-Synthesis was computed using a Bayesian inference technique (Monte-Carlo dropout). In regions of high uncertainty, the DL-Recon method incorporates information from a physics-based reconstruction model and artifact-corrected projection data. Two forms of the DL-Recon method are proposed: (i) image-domain fusion of DL-Synthesis and FBP (DL-FBP) weighted by DL uncertainty; and (ii) a model-based iterative image reconstruction (MBIR) optimization using DL-Synthesis to compute a spatially varying regularization term based on DL uncertainty (DL-MBIR). The error in DL-Synthesis images was correlated with the uncertainty in the synthesis estimate. Compared to FBP and PWLS, the DL-Recon methods (both DL-FBP and DL-MBIR) showed ~50% reduction in noise (at matched spatial resolution) and ~40-70% improvement in image uniformity. Conventional DL-Synthesis alone exhibited ~10-60% under-estimation of lesion contrast and ~5-40% reduction in lesion segmentation accuracy (Dice coefficient) in simulated and real brain lesions, suggesting a lack of reliability / generalizability for structures unseen in the training data. DL-FBP and DL-MBIR improved the accuracy of reconstruction by directly incorporating information from the measurements in regions of high uncertainty.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge