Wenxiang Li
Revealing the real-world CO2 emission reduction of ridesplitting and its determinants based on machine learning
Apr 02, 2022



Abstract:Ridesplitting, which is a form of pooled ridesourcing service, has great potential to alleviate the negative impacts of ridesourcing on the environment. However, most existing studies only explored its theoretical environmental benefits based on optimization models and simulations. To put into practice, this study aims to reveal the real-world emission reduction of ridesplitting and its determinants based on the observed data of ridesourcing in Chengdu, China. Integrating the trip data with the COPERT model, this study calculates the CO2 emissions of shared rides (ridesplitting) and their substituted single rides (regular ridesourcing) to estimate the CO2 emission reduction of each ridesplitting trip. The results show that not all ridesplitting trips reduce emissions from ridesourcing in the real world. The CO2 emission reduction rate of ridesplitting varies from trip to trip, averaging at 43.15g/km. Then, the interpretable machine learning models, gradient boosting machines, are applied to explore the relationship between the CO2 emission reduction rate of ridesplitting and its determinants. Based on the SHapley Additive exPlanations method, the overlap rate and detour rate of shared rides are identified to be the most important factors that determine the CO2 emission reduction rate of ridesplitting. Increasing the overlap rate, the number of shared rides, average speed, and ride distance ratio and decreasing the detour rate, actual trip distance, ride distance gap can increase the CO2 emission reduction rate of ridesplitting. In addition, nonlinear effects and interactions of several key factors are examined through the partial dependence plots. This study provides a scientific method for the government and ridesourcing companies to better assess and optimize the environmental benefits of ridesplitting.
Comprehensive and Clinically Accurate Head and Neck Organs at Risk Delineation via Stratified Deep Learning: A Large-scale Multi-Institutional Study
Nov 01, 2021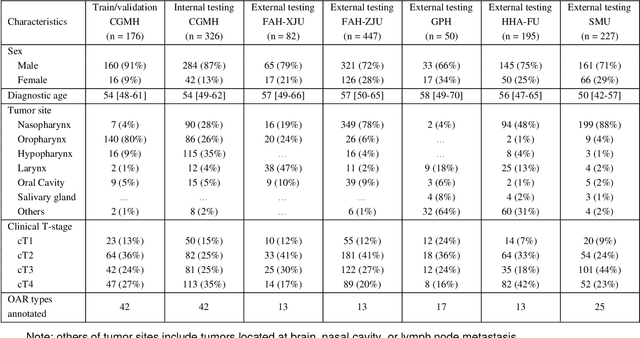
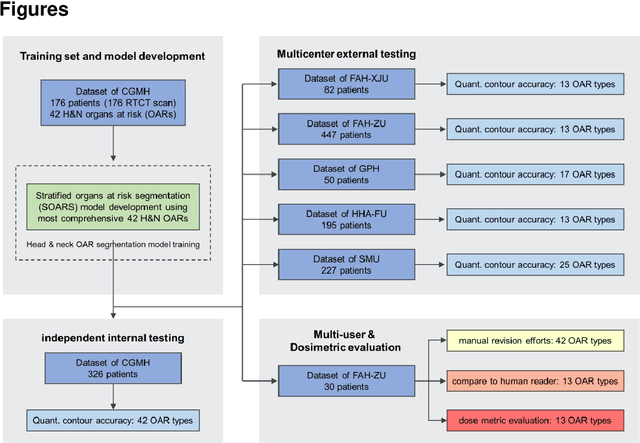
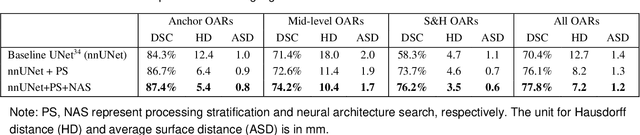
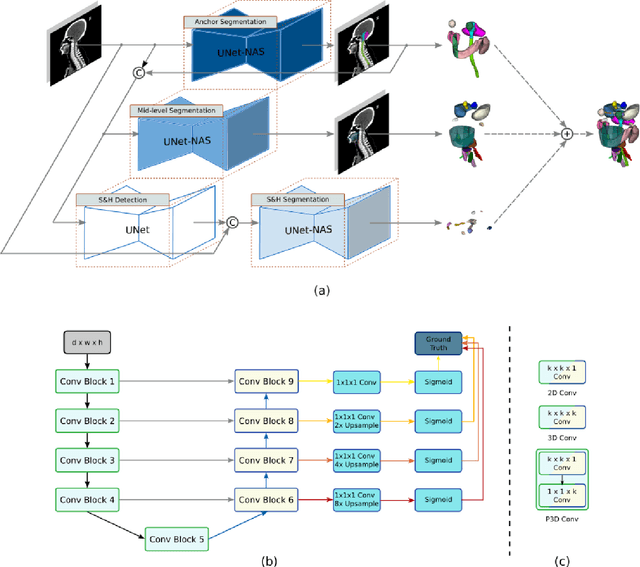
Abstract:Accurate organ at risk (OAR) segmentation is critical to reduce the radiotherapy post-treatment complications. Consensus guidelines recommend a set of more than 40 OARs in the head and neck (H&N) region, however, due to the predictable prohibitive labor-cost of this task, most institutions choose a substantially simplified protocol by delineating a smaller subset of OARs and neglecting the dose distributions associated with other OARs. In this work we propose a novel, automated and highly effective stratified OAR segmentation (SOARS) system using deep learning to precisely delineate a comprehensive set of 42 H&N OARs. SOARS stratifies 42 OARs into anchor, mid-level, and small & hard subcategories, with specifically derived neural network architectures for each category by neural architecture search (NAS) principles. We built SOARS models using 176 training patients in an internal institution and independently evaluated on 1327 external patients across six different institutions. It consistently outperformed other state-of-the-art methods by at least 3-5% in Dice score for each institutional evaluation (up to 36% relative error reduction in other metrics). More importantly, extensive multi-user studies evidently demonstrated that 98% of the SOARS predictions need only very minor or no revisions for direct clinical acceptance (saving 90% radiation oncologists workload), and their segmentation and dosimetric accuracy are within or smaller than the inter-user variation. These findings confirmed the strong clinical applicability of SOARS for the OAR delineation process in H&N cancer radiotherapy workflows, with improved efficiency, comprehensiveness, and quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge