Wenrui Wang
ECN
FLAM: Foundation Model-Based Body Stabilization for Humanoid Locomotion and Manipulation
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots have attracted significant attention in recent years. Reinforcement Learning (RL) is one of the main ways to control the whole body of humanoid robots. RL enables agents to complete tasks by learning from environment interactions, guided by task rewards. However, existing RL methods rarely explicitly consider the impact of body stability on humanoid locomotion and manipulation. Achieving high performance in whole-body control remains a challenge for RL methods that rely solely on task rewards. In this paper, we propose a Foundation model-based method for humanoid Locomotion And Manipulation (FLAM for short). FLAM integrates a stabilizing reward function with a basic policy. The stabilizing reward function is designed to encourage the robot to learn stable postures, thereby accelerating the learning process and facilitating task completion. Specifically, the robot pose is first mapped to the 3D virtual human model. Then, the human pose is stabilized and reconstructed through a human motion reconstruction model. Finally, the pose before and after reconstruction is used to compute the stabilizing reward. By combining this stabilizing reward with the task reward, FLAM effectively guides policy learning. Experimental results on a humanoid robot benchmark demonstrate that FLAM outperforms state-of-the-art RL methods, highlighting its effectiveness in improving stability and overall performance.
Abnormality Forecasting: Time Series Anomaly Prediction via Future Context Modeling
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:Identifying anomalies from time series data plays an important role in various fields such as infrastructure security, intelligent operation and maintenance, and space exploration. Current research focuses on detecting the anomalies after they occur, which can lead to significant financial/reputation loss or infrastructure damage. In this work we instead study a more practical yet very challenging problem, time series anomaly prediction, aiming at providing early warnings for abnormal events before their occurrence. To tackle this problem, we introduce a novel principled approach, namely future context modeling (FCM). Its key insight is that the future abnormal events in a target window can be accurately predicted if their preceding observation window exhibits any subtle difference to normal data. To effectively capture such differences, FCM first leverages long-term forecasting models to generate a discriminative future context based on the observation data, aiming to amplify those subtle but unusual difference. It then models a normality correlation of the observation data with the forecasting future context to complement the normality modeling of the observation data in foreseeing possible abnormality in the target window. A joint variate-time attention learning is also introduced in FCM to leverage both temporal signals and features of the time series data for more discriminative normality modeling in the aforementioned two views. Comprehensive experiments on five datasets demonstrate that FCM gains good recall rate (70\%+) on multiple datasets and significantly outperforms all baselines in F1 score. Code is available at https://github.com/mala-lab/FCM.
Evaluating the Effect of Crutch-using on Trunk Muscle Loads
Aug 25, 2020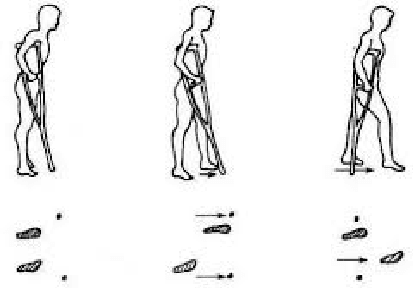
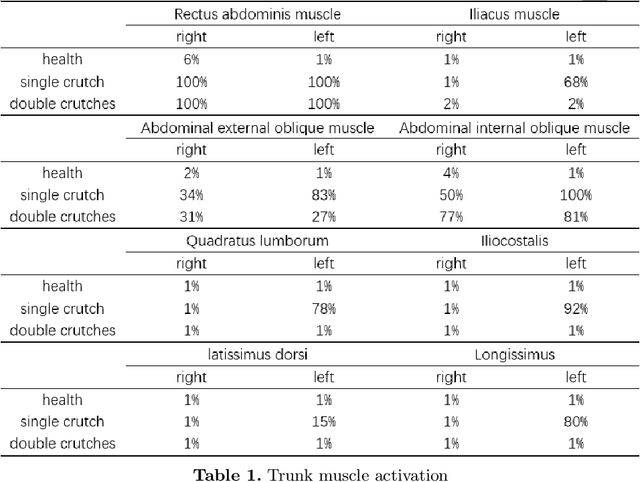
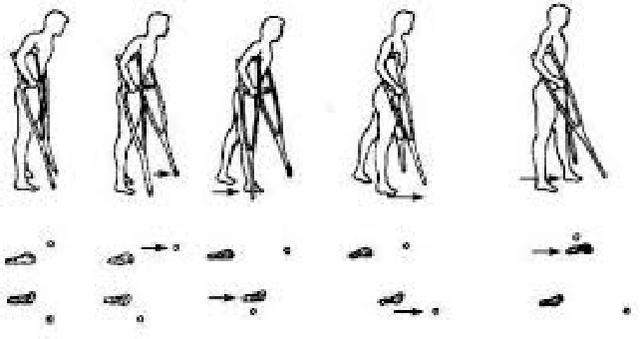
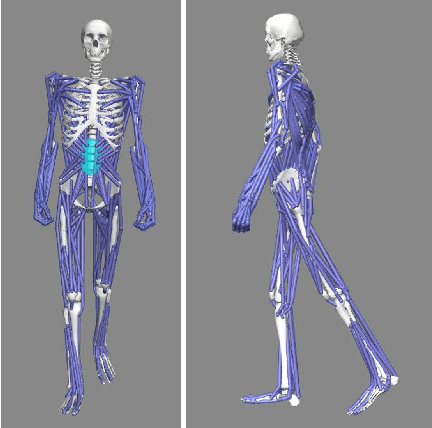
Abstract:As a traditional tool of external assistance, crutches play an important role in society. They have a wide range of applications to help either the elderly and disabled to walk or to treat certain illnesses or for post-operative rehabilitation. But there are many different types of crutches, including shoulder crutches and elbow crutches. How to choose has become an issue that deserves to be debated. Because while crutches help people walk, they also have an impact on the body. Inappropriate choice of crutches or long-term misuse can lead to problems such as scoliosis. Previous studies were mainly experimental measurements or the construction of dynamic models to calculate the load on joints with crutches. These studies focus only on the level of the joints, ignoring the role that muscles play in this process. Although some also take into account the degree of muscle activation, there is still a lack of quantitative analysis. The traditional dynamic model can be used to calculate the load on each joint. However, due to the activation of the muscle, this situation only causes part of the load transmitted to the joint, and the work of the chair will compensate the other part of the load. Analysis at the muscle level allows a better understanding of the impact of crutches on the body. By comparing the levels of activation of the trunk muscles, it was found that the use of crutches for walking, especially a single crutch, can cause a large difference in the activation of the back muscles on the left and right sides, and this difference will cause muscle degeneration for a long time, leading to scoliosis. In this article taking scoliosis as an example, by analyzing the muscles around the spine, we can better understand the pathology and can better prevent diseases. The objective of this article is to analyze normal walking compared to walking with one or two crutches using OpenSim software to obtain the degree of activation of different muscles in order to analyze the impact of crutches on the body.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge