Fouad Bennis
ReV, LS2N
A new simple dynamic muscle fatigue model and its validation
Jan 04, 2022Abstract:Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is one of the major health problems in physical work especially in manual handling jobs. In several literatures, muscle fatigue is considered to be closely related to MSD, especially for muscle related disorders. In addition to many existing analysis techniques for muscle fatigue assessment and MSD risk analysis, in this paper, a new muscle fatigue model was proposed. The new proposed model reflects the influence of external load, workload history, and individual differences. This model is simple in mathematics and can be easily applied in realtime calculation, such as the application in realtime virtual work simulation and evaluation. The new model was mathematically validated with 24 existing static models by comparing the calculated METs, and qualitatively or quantitatively validated with 3 existing dynamic models. The proposed model shows high or moderate similarities in predicting the METs with all the 24 static models. Validation results with the three dynamic models were also promising. The main limitation of the model is that it still lacks experimental validation for more dynamic situations. Relevance to industry Muscle fatigue is one of the main reasons causing MSDs in industry, especially for physical work. Correct evaluation of muscle fatigue is necessary to determine work-rest regimens and reduce the risks of MSD.
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:0901.0222
Evaluating the Effect of Crutch-using on Trunk Muscle Loads
Aug 25, 2020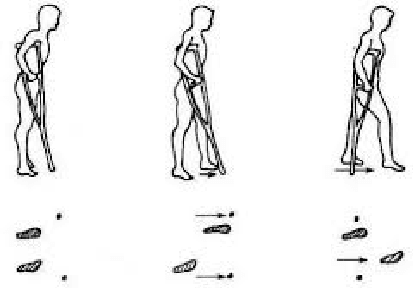
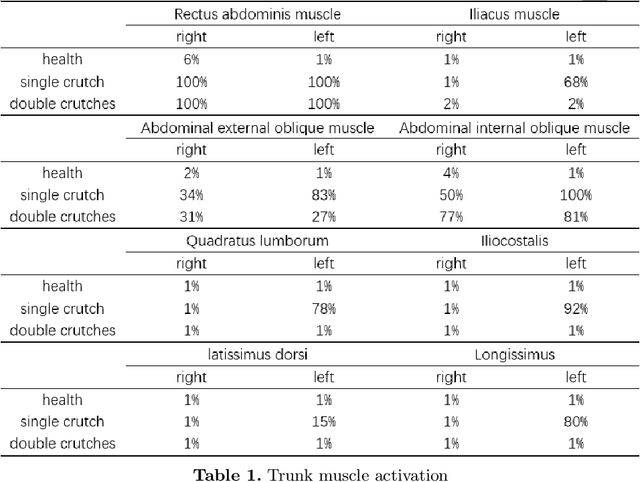
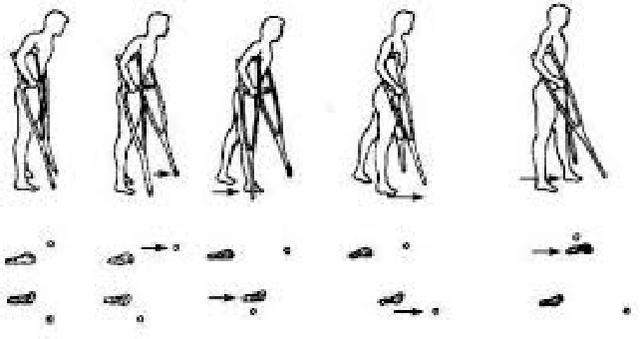
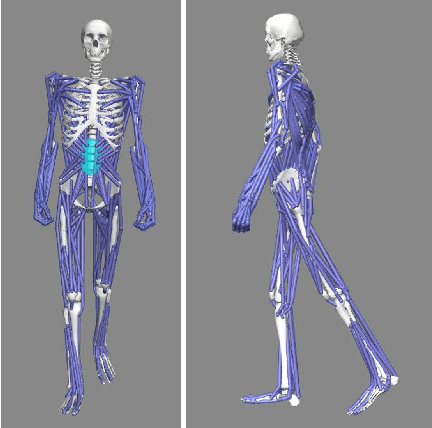
Abstract:As a traditional tool of external assistance, crutches play an important role in society. They have a wide range of applications to help either the elderly and disabled to walk or to treat certain illnesses or for post-operative rehabilitation. But there are many different types of crutches, including shoulder crutches and elbow crutches. How to choose has become an issue that deserves to be debated. Because while crutches help people walk, they also have an impact on the body. Inappropriate choice of crutches or long-term misuse can lead to problems such as scoliosis. Previous studies were mainly experimental measurements or the construction of dynamic models to calculate the load on joints with crutches. These studies focus only on the level of the joints, ignoring the role that muscles play in this process. Although some also take into account the degree of muscle activation, there is still a lack of quantitative analysis. The traditional dynamic model can be used to calculate the load on each joint. However, due to the activation of the muscle, this situation only causes part of the load transmitted to the joint, and the work of the chair will compensate the other part of the load. Analysis at the muscle level allows a better understanding of the impact of crutches on the body. By comparing the levels of activation of the trunk muscles, it was found that the use of crutches for walking, especially a single crutch, can cause a large difference in the activation of the back muscles on the left and right sides, and this difference will cause muscle degeneration for a long time, leading to scoliosis. In this article taking scoliosis as an example, by analyzing the muscles around the spine, we can better understand the pathology and can better prevent diseases. The objective of this article is to analyze normal walking compared to walking with one or two crutches using OpenSim software to obtain the degree of activation of different muscles in order to analyze the impact of crutches on the body.
Branch-and-Bound Method for Just-in-Time Optimization of Radar Search Patterns
Feb 12, 2020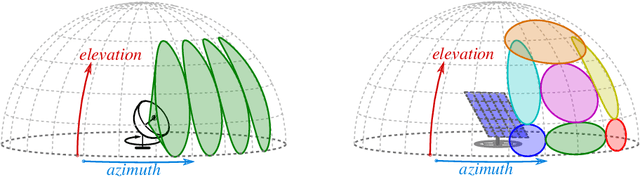

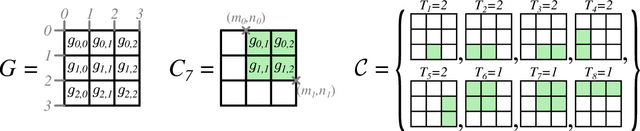
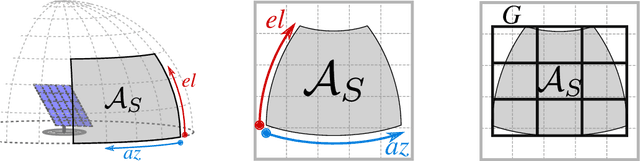
Abstract:Electronic phased-array radars offer new possibilities for radar search pattern optimization by using bi-dimensional beam-forming and beam-steering. Radar search pattern optimization can be approximated as a set cover problem and solved using integer programming, while accounting for localized clutter and terrain masks in detection constraints. We present a set cover problem approximation for time-budget minimization of radar search patterns, under constraints of range, detection probability and direction-specific scan update rates. Branch\&Bound is a classical optimization procedure for solving combinatorial problems. It is known mainly as an exact algorithm, but features interesting characteristics, making it particularly fit for solving optimization problems in real-time applications and producing just-in-time solutions.
Predictive model of the human muscle fatigue: application to repetitive push-pull tasks with light external load
Mar 22, 2015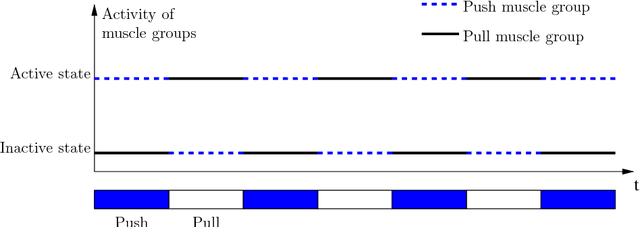
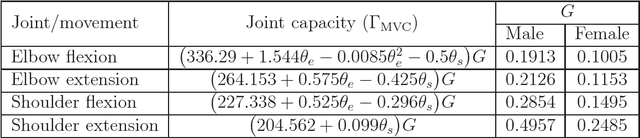
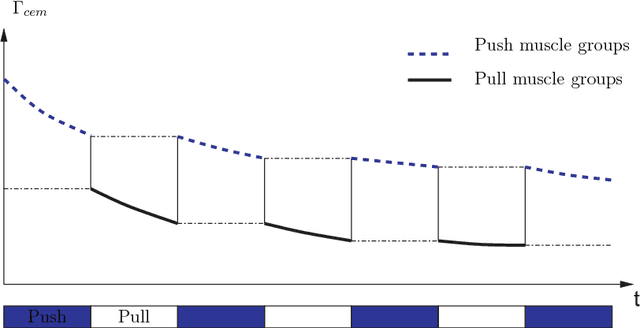
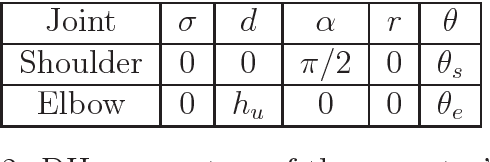
Abstract:Repetitive tasks in industrial works may contribute to health problems among operators, such as musculo-skeletal disorders, in part due to insufficient control of muscle fatigue. In this paper, a predictive model of fatigue is proposed for repetitive push/pull operations. Assumptions generally accepted in the literature are first explicitly set in this framework. Then, an earlier static fatigue model is recalled and extended to quasi-static situations. Specifically, the maximal torque that can be generated at a joint is not considered as constant, but instead varies over time accordingly to the operator's changing posture. The fatigue model is implemented with this new consideration and evaluated in a simulation of push/pull operation. Reference to this paper should be made as follows: Sakka, S., Chablat, D., Ma, R. and Bennis, F. (2015) 'Predictive model of the human muscle fatigue: application to repetitive push-pull tasks with light external load', Int.
Determination of subject-specific muscle fatigue rates under static fatiguing operations
Feb 07, 2014


Abstract:Cumulative local muscle fatigue may lead to potential musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) risks {\color{red}, and subject-specific muscle fatigability needs to be considered to reduce potential MSD risks.} This study was conducted to determine local muscle fatigue rate at shoulder joint level based on an exponential function derived from a muscle fatigue model. Forty male subjects participated in a fatiguing operation under a static posture with a range of relative force levels (14% - 33%). Remaining maximum muscle strengths were measured after different fatiguing sessions. The time course of strength decline was fitted to the exponential function. Subject-specific fatigue rates of shoulder joint moment strength were determined. Good correspondence ($R^2>0.8$) was found in the regression of the majority (35 out of 40 subjects). Substantial inter-individual variability in fatigue rate was found and discussed.
Sensitivity Analysis of the Orthoglide, a 3-DOF Translational Parallel Kinematic Machine
Dec 04, 2013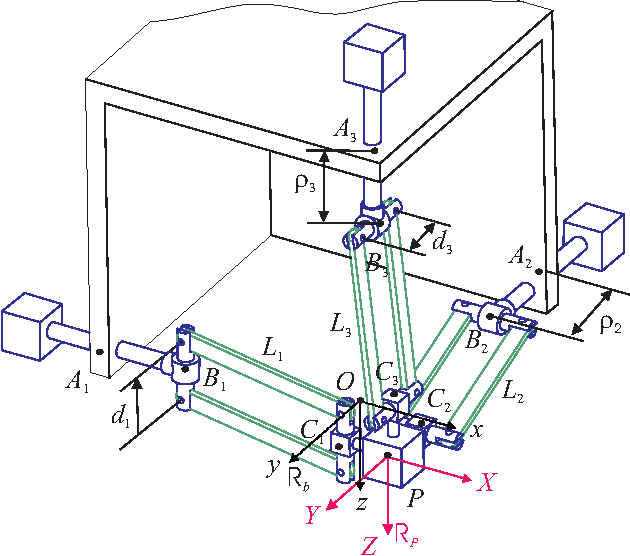
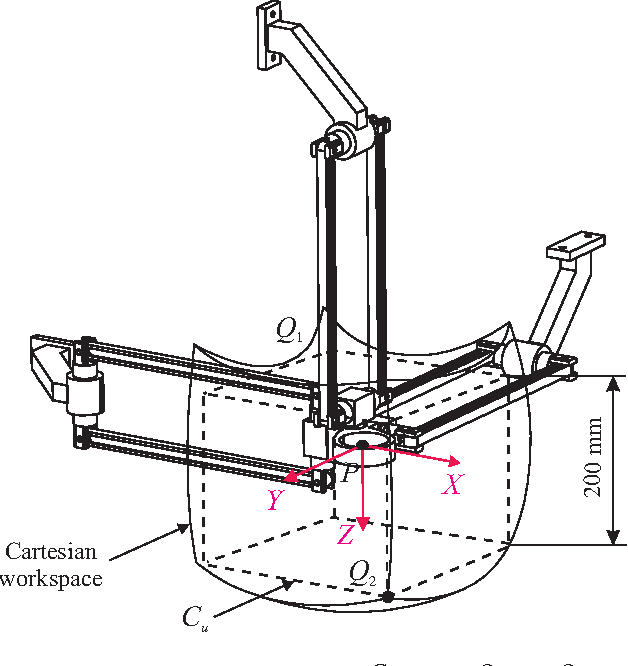

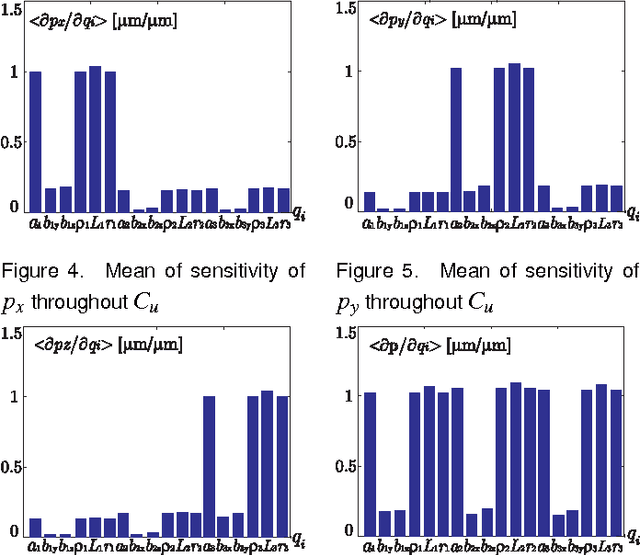
Abstract:This paper presents a sensitivity analysis of the Orthoglide, a 3-DOF translational Parallel Kinematic Machine. Two complementary methods are developed to analyze its sensitivity to its dimensional and angular variations. First, a linkage kinematic analysis method is used to have a rough idea of the influence of the dimensional variations on the location of the end-effector. Besides, this method shows that variations in the design parameters of the same type from one leg to the other have the same influence on the end-effector. However, this method does not take into account the variations in the parallelograms. Thus, a differential vector method is used to study the influence of the dimensional and angular variations in the parts of the manipulator on the position and orientation of the end-effector, and particularly the influence of the variations in the parallelograms. It turns out that the kinematic isotropic configuration of the manipulator is the least sensitive one to its dimensional and angular variations. On the contrary, the closest configurations to its kinematic singular configurations are the most sensitive ones to geometrical variations.
A new approach to muscle fatigue evaluation for Push/Pull task
Jun 07, 2012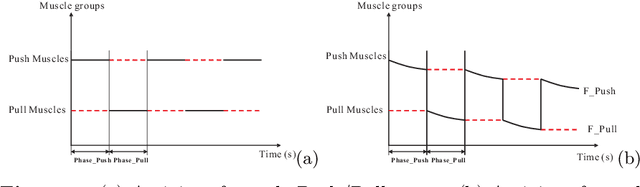
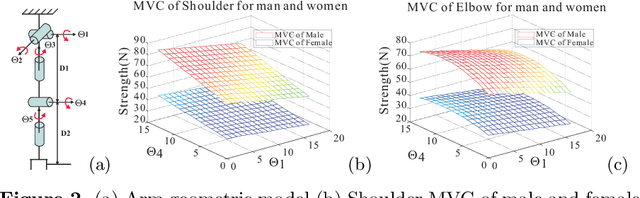
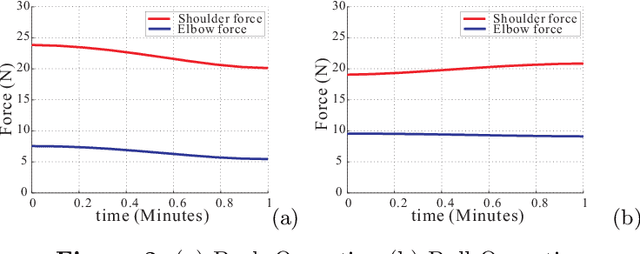
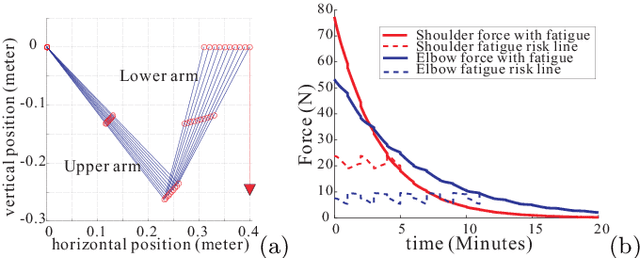
Abstract:Pushing/Pulling tasks is an important part of work in many industries. Usually, most researchers study the Push/Pull tasks by analyzing different posture conditions, force requirements, velocity factors, etc. However few studies have reported the effects of fatigue. Fatigue caused by physical loading is one of the main reasons responsible for MusculoSkeletal Disorders (MSD). In this paper, muscle groups of articulation is considered and from joint level a new approach is proposed for muscle fatigue evaluation in the arms Push/Pull operations. The objective of this work is to predict the muscle fatigue situation in the Push/Pull tasks in order to reduce the probability of MSD problems for workers. A case study is presented to use this new approach for analyzing arm fatigue in Pushing/Pulling.
Human Arm simulation for interactive constrained environment design
Jun 07, 2012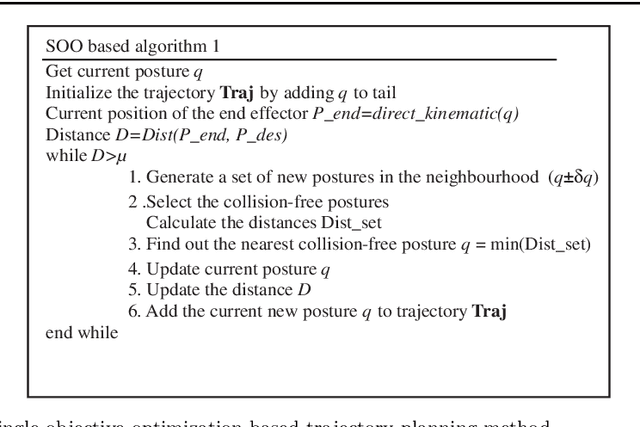

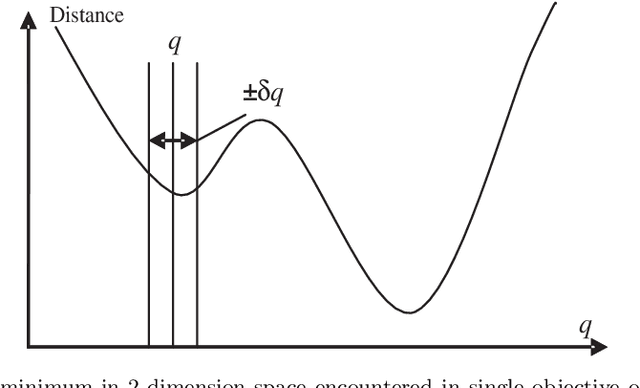
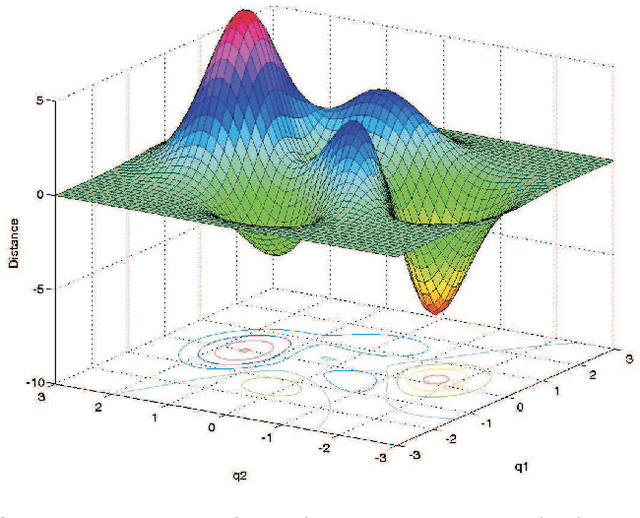
Abstract:During the conceptual and prototype design stage of an industrial product, it is crucial to take assembly/disassembly and maintenance operations in advance. A well-designed system should enable relatively easy access of operating manipulators in the constrained environment and reduce musculoskeletal disorder risks for those manual handling operations. Trajectory planning comes up as an important issue for those assembly and maintenance operations under a constrained environment, since it determines the accessibility and the other ergonomics issues, such as muscle effort and its related fatigue. In this paper, a customer-oriented interactive approach is proposed to partially solve ergonomic related issues encountered during the design stage under a constrained system for the operator's convenience. Based on a single objective optimization method, trajectory planning for different operators could be generated automatically. Meanwhile, a motion capture based method assists the operator to guide the trajectory planning interactively when either a local minimum is encountered within the single objective optimization or the operator prefers guiding the virtual human manually. Besides that, a physical engine is integrated into this approach to provide physically realistic simulation in real time manner, so that collision free path and related dynamic information could be computed to determine further muscle fatigue and accessibility of a product design
Human Muscle Fatigue Model in Dynamic Motions
Apr 08, 2012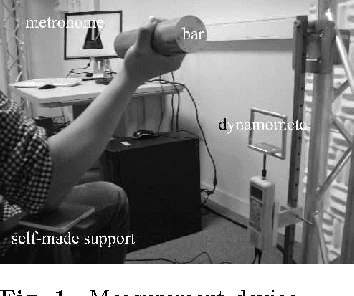
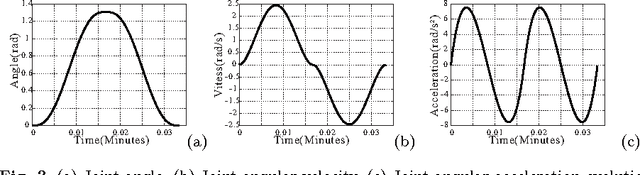
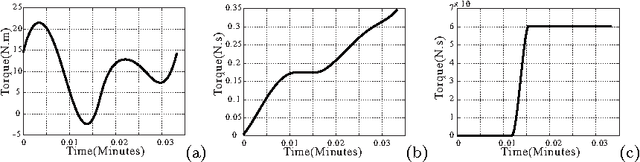
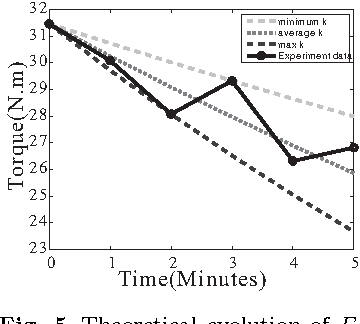
Abstract:Human muscle fatigue is considered to be one of the main reasons for Musculoskeletal Disorder (MSD). Recent models have been introduced to define muscle fatigue for static postures. However, the main drawbacks of these models are that the dynamic effect of the human and the external load are not taken into account. In this paper, each human joint is assumed to be controlled by two muscle groups to generate motions such as push/pull. The joint torques are computed using Lagrange's formulation to evaluate the dynamic factors of the muscle fatigue model. An experiment is defined to validate this assumption and the result for one person confirms its feasibility. The evaluation of this model can predict the fatigue and MSD risk in industry production quickly.
Can virtual reality predict body part discomfort and performance of people in realistic world for assembling tasks?
Apr 06, 2011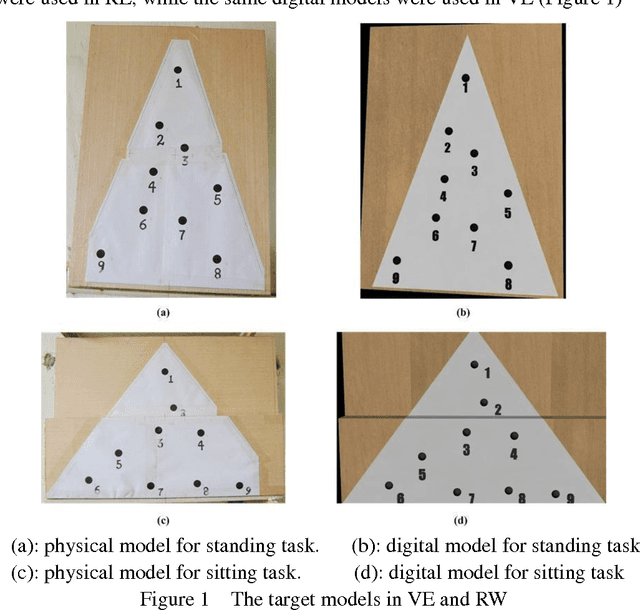
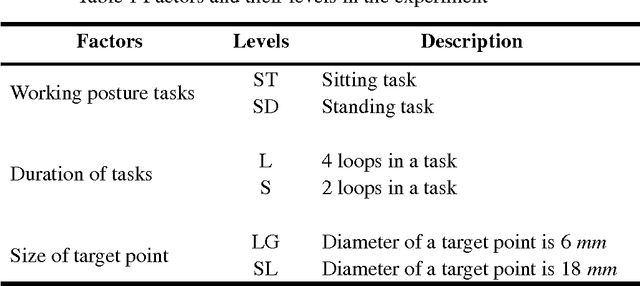
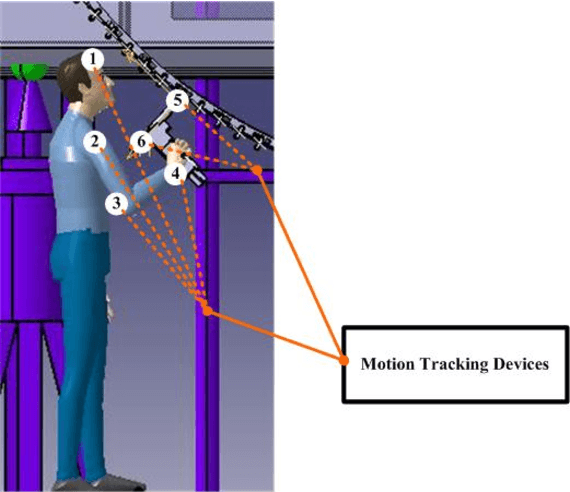
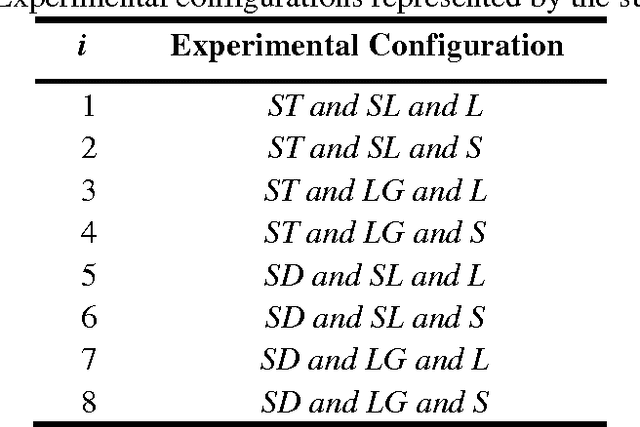
Abstract:This paper presents our work on relationship of evaluation results between virtual environment (VE) and realistic environment (RE) for assembling tasks. Evaluation results consist of subjective results (BPD and RPE) and objective results (posture and physical performance). Same tasks were performed with same experimental configurations and evaluation results were measured in RE and VE respectively. Then these evaluation results were compared. Slight difference of posture between VE and RE was found but not great difference of effect on people according to conventional ergonomics posture assessment method. Correlation of BPD and performance results between VE and RE are found by linear regression method. Moreover, results of BPD, physical performance, and RPE in VE are higher than that in RE with significant difference. Furthermore, these results indicates that subjects feel more discomfort and fatigue in VE than RE because of additional effort required in VE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge