François Guillaume
IRCCyN
Determination of subject-specific muscle fatigue rates under static fatiguing operations
Feb 07, 2014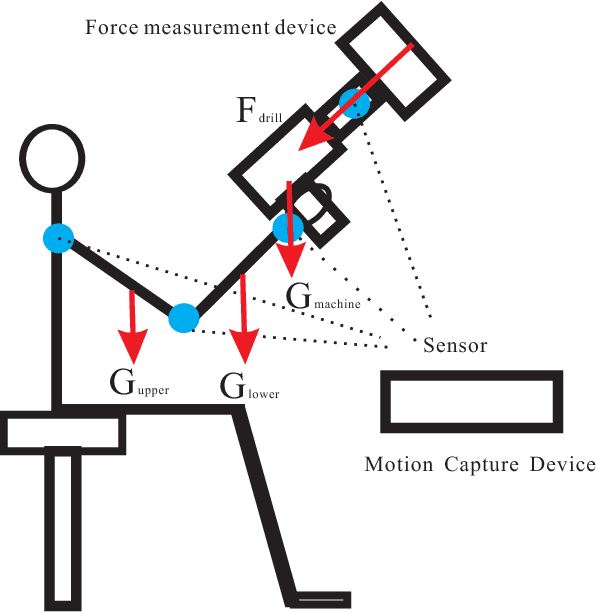


Abstract:Cumulative local muscle fatigue may lead to potential musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) risks {\color{red}, and subject-specific muscle fatigability needs to be considered to reduce potential MSD risks.} This study was conducted to determine local muscle fatigue rate at shoulder joint level based on an exponential function derived from a muscle fatigue model. Forty male subjects participated in a fatiguing operation under a static posture with a range of relative force levels (14% - 33%). Remaining maximum muscle strengths were measured after different fatiguing sessions. The time course of strength decline was fitted to the exponential function. Subject-specific fatigue rates of shoulder joint moment strength were determined. Good correspondence ($R^2>0.8$) was found in the regression of the majority (35 out of 40 subjects). Substantial inter-individual variability in fatigue rate was found and discussed.
A novel approach for determining fatigue resistances of different muscle groups in static cases
Apr 06, 2011
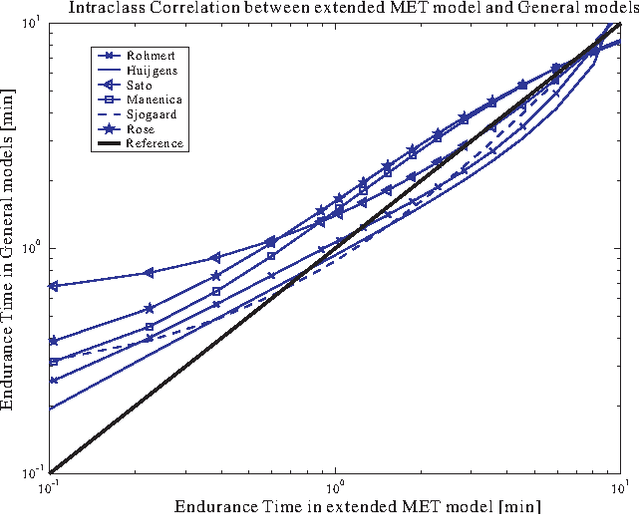
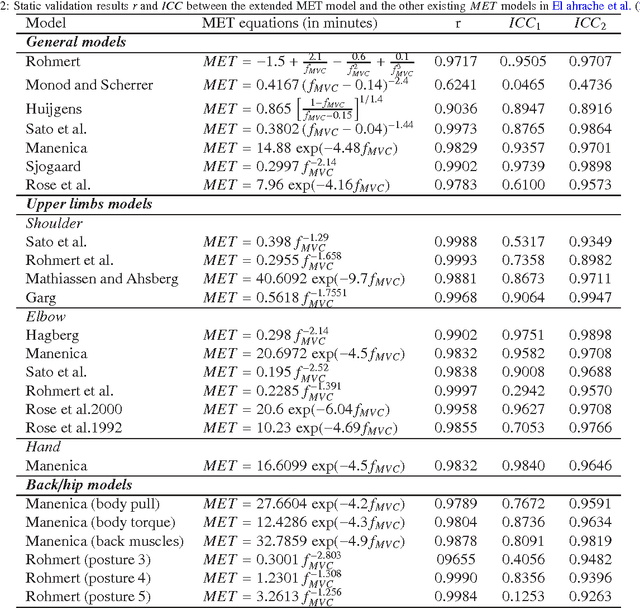
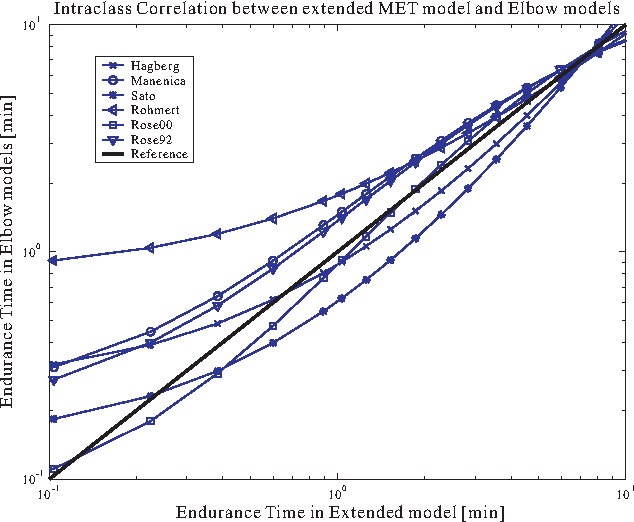
Abstract:In ergonomics and biomechanics, muscle fatigue models based on maximum endurance time (MET) models are often used to integrate fatigue effect into ergonomic and biomechanical application. However, due to the empirical principle of those MET models, the disadvantages of this method are: 1) the MET models cannot reveal the muscle physiology background very well; 2) there is no general formation for those MET models to predict MET. In this paper, a theoretical MET model is extended from a simple muscle fatigue model with consideration of the external load and maximum voluntary contraction in passive static exertion cases. The universal availability of the extended MET model is analyzed in comparison to 24 existing empirical MET models. Using mathematical regression method, 21 of the 24 MET models have intraclass correlations over 0.9, which means the extended MET model could replace the existing MET models in a general and computationally efficient way. In addition, an important parameter, fatigability (or fatigue resistance) of different muscle groups, could be calculated via the mathematical regression approach. Its mean value and its standard deviation are useful for predicting MET values of a given population during static operations. The possible reasons influencing the fatigue resistance were classified and discussed, and it is still a very challenging work to find out the quantitative relationship between the fatigue resistance and the influencing factors.
A new muscle fatigue and recovery model and its ergonomics application in human simulation
Oct 28, 2010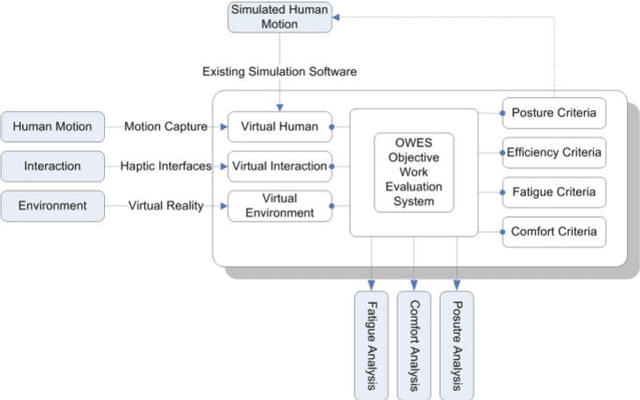
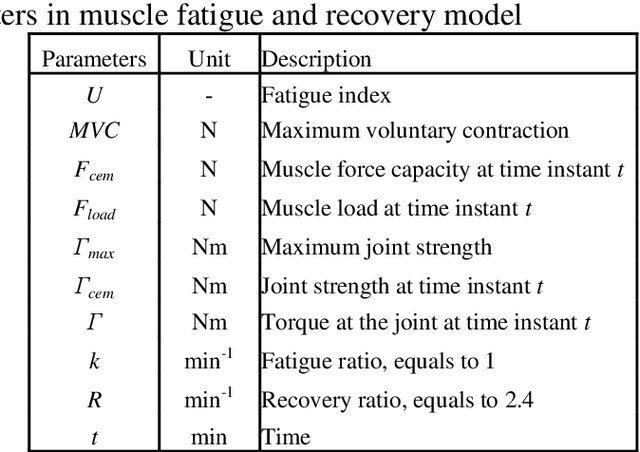
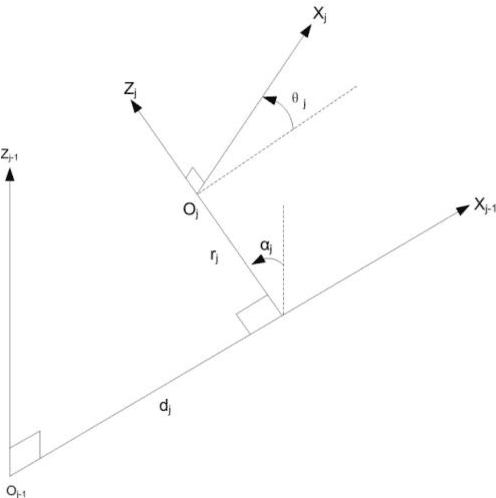
Abstract:Although automatic techniques have been employed in manufacturing industries to increase productivity and efficiency, there are still lots of manual handling jobs, especially for assembly and maintenance jobs. In these jobs, musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are one of the major health problems due to overload and cumulative physical fatigue. With combination of conventional posture analysis techniques, digital human modelling and simulation (DHM) techniques have been developed and commercialized to evaluate the potential physical exposures. However, those ergonomics analysis tools are mainly based on posture analysis techniques, and until now there is still no fatigue index available in the commercial software to evaluate the physical fatigue easily and quickly. In this paper, a new muscle fatigue and recovery model is proposed and extended to evaluate joint fatigue level in manual handling jobs. A special application case is described and analyzed by digital human simulation technique.
Fatigue evaluation in maintenance and assembly operations by digital human simulation
Jun 30, 2010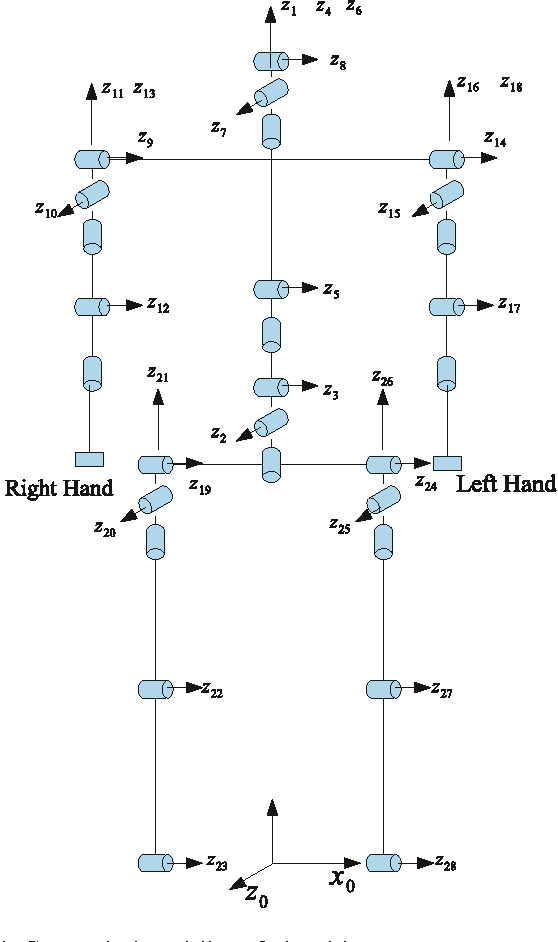
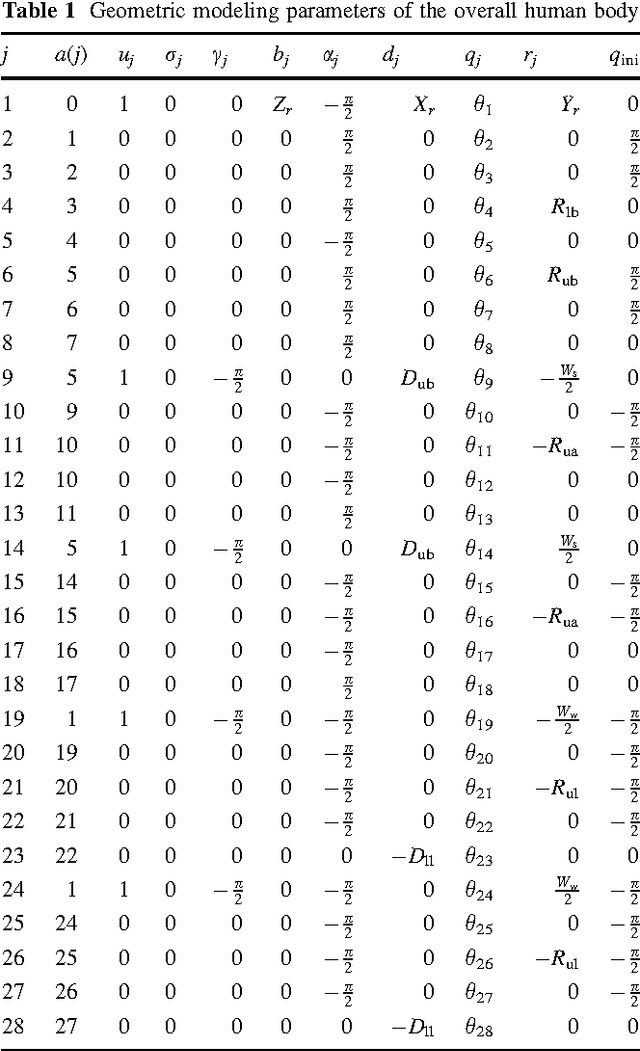


Abstract:Virtual human techniques have been used a lot in industrial design in order to consider human factors and ergonomics as early as possible. The physical status (the physical capacity of virtual human) has been mostly treated as invariable in the current available human simulation tools, while indeed the physical capacity varies along time in an operation and the change of the physical capacity depends on the history of the work as well. Virtual Human Status is proposed in this paper in order to assess the difficulty of manual handling operations, especially from the physical perspective. The decrease of the physical capacity before and after an operation is used as an index to indicate the work difficulty. The reduction of physical strength is simulated in a theoretical approach on the basis of a fatigue model in which fatigue resistances of different muscle groups were regressed from 24 existing maximum endurance time (MET) models. A framework based on digital human modeling technique is established to realize the comparison of physical status. An assembly case in airplane assembly is simulated and analyzed under the framework. The endurance time and the decrease of the joint moment strengths are simulated. The experimental result in simulated operations under laboratory conditions confirms the feasibility of the theoretical approach.
Multi-Objective Optimisation Method for Posture Prediction and Analysis with Consideration of Fatigue Effect and its Application Case
Nov 09, 2009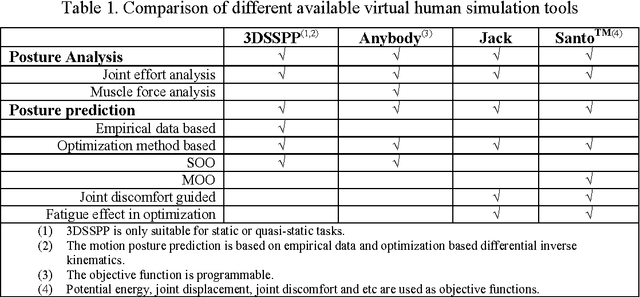
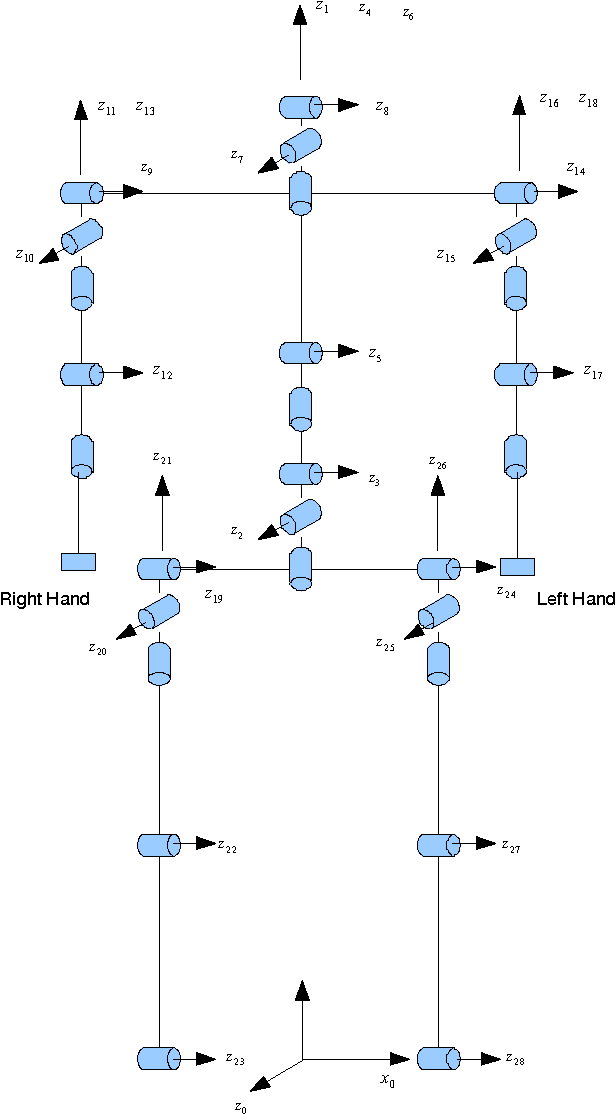

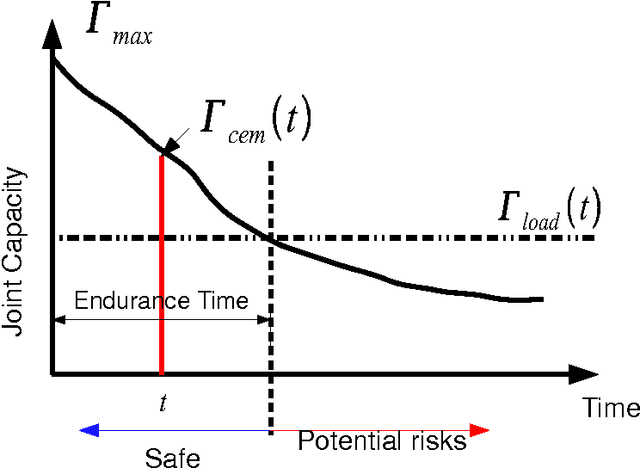
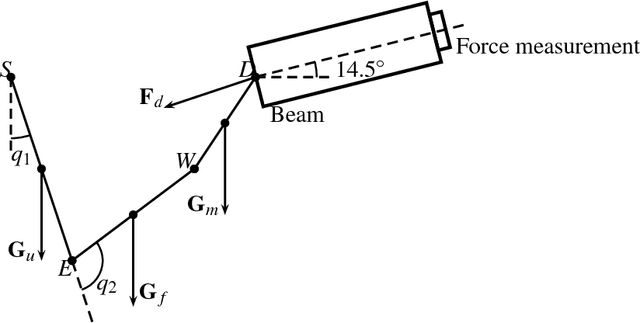
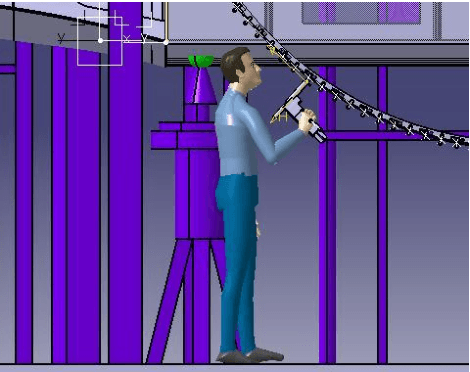
Abstract:Automation technique has been widely used in manufacturing industry, but there are still manual handling operations required in assembly and maintenance work in industry. Inappropriate posture and physical fatigue might result in musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) in such physical jobs. In ergonomics and occupational biomechanics, virtual human modelling techniques have been employed to design and optimize the manual operations in design stage so as to avoid or decrease potential MSD risks. In these methods, physical fatigue is only considered as minimizing the muscle or joint stress, and the fatigue effect along time for the posture is not considered enough. In this study, based on the existing methods and multiple objective optimisation method (MOO), a new posture prediction and analysis method is proposed for predicting the optimal posture and evaluating the physical fatigue in the manual handling operation. The posture prediction and analysis problem is mathematically described and a special application case is demonstrated for analyzing a drilling assembly operation in European Aeronautic Defence & Space Company (EADS) in this paper.
Designing a Virtual Manikin Animation Framework Aimed at Virtual Prototyping
Sep 05, 2007Abstract:In the industry, numerous commercial packages provide tools to introduce, and analyse human behaviour in the product's environment (for maintenance, ergonomics...), thanks to Virtual Humans. We will focus on control. Thanks to algorithms newly introduced in recent research papers, we think we can provide an implementation, which even widens, and simplifies the animation capacities of virtual manikins. In order to do so, we are going to express the industrial expectations as for Virtual Humans, without considering feasibility (not to bias the issue). The second part will show that no commercial application provides the tools that perfectly meet the needs. Thus we propose a new animation framework that better answers the problem. Our contribution is the integration - driven by need ~ of available new scientific techniques to animate Virtual Humans, in a new control scheme that better answers industrial expectations.
Balanced Virtual Humans Interacting with their Environment
Jul 24, 2007



Abstract:The animation of human avatars seems very successful; the computer graphics industry shows outstanding results in films everyday, the game industry achieves exploits... Nevertheless, the animation and control processes of such manikins are very painful. It takes days to a specialist to build such animated sequences, and it is not adaptive to any type of modifications. Our main purpose is the virtual human for engineering, especially virtual prototyping. As for this domain of activity, such amounts of time are prohibitive.
Integration of a Balanced Virtual Manikin in a Virtual Reality Platform aimed at Virtual Prototyping
Jul 24, 2007



Abstract:The work presented here is aimed at introducing a virtual human controller in a virtual prototyping framework. After a brief introduction describing the problem solved in the paper, we describe the interest as for digital humans in the context of concurrent engineering. This leads us to draw a control architecture enabling to drive virtual humans in a real-time immersed way, and to interact with the product, through motion capture. Unfortunately, we show this control scheme can lead to unfeasible movements because of the lack of balance control. Introducing such a controller is a problem that was never addressed in the context of real-time. We propose an implementation of a balance controller, that we insert into the previously described control scheme. Next section is dedicated to show the results we obtained. Finally, we propose a virtual reality platform into which the digital character controller is integrated.
Passive Control Architecture for Virtual Humans
Jul 16, 2007



Abstract:In the present paper, we introduce a new control architecture aimed at driving virtual humans in interaction with virtual environments, by motion capture. It brings decoupling of functionalities, and also of stability thanks to passivity. We show projections can break passivity, and thus must be used carefully. Our control scheme enables task space and internal control, contact, and joint limits management. Thanks to passivity, it can be easily extended. Besides, we introduce a new tool as for manikin's control, which makes it able to build passive projections, so as to guide the virtual manikin when sharp movements are needed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge