Sensitivity Analysis of the Orthoglide, a 3-DOF Translational Parallel Kinematic Machine
Paper and Code
Dec 04, 2013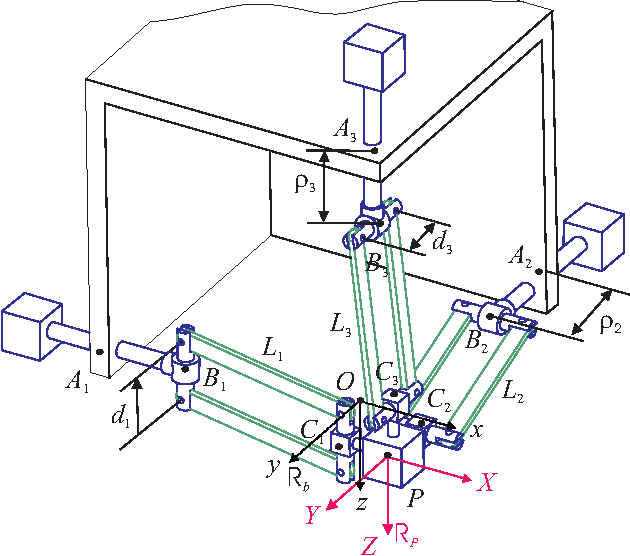
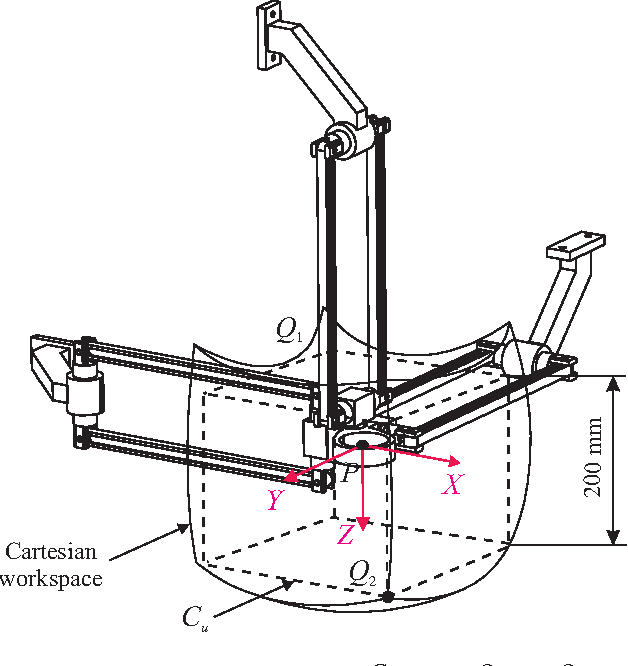

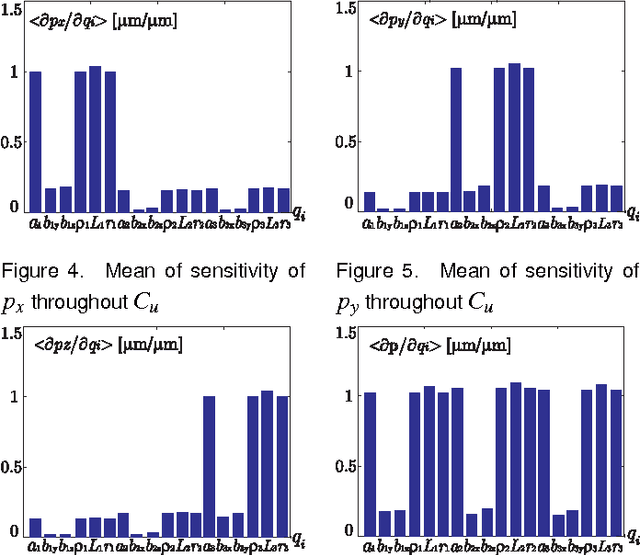
This paper presents a sensitivity analysis of the Orthoglide, a 3-DOF translational Parallel Kinematic Machine. Two complementary methods are developed to analyze its sensitivity to its dimensional and angular variations. First, a linkage kinematic analysis method is used to have a rough idea of the influence of the dimensional variations on the location of the end-effector. Besides, this method shows that variations in the design parameters of the same type from one leg to the other have the same influence on the end-effector. However, this method does not take into account the variations in the parallelograms. Thus, a differential vector method is used to study the influence of the dimensional and angular variations in the parts of the manipulator on the position and orientation of the end-effector, and particularly the influence of the variations in the parallelograms. It turns out that the kinematic isotropic configuration of the manipulator is the least sensitive one to its dimensional and angular variations. On the contrary, the closest configurations to its kinematic singular configurations are the most sensitive ones to geometrical variations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge