Wenbo Cui
Staggered Batch Scheduling: Co-optimizing Time-to-First-Token and Throughput for High-Efficiency LLM Inference
Dec 18, 2025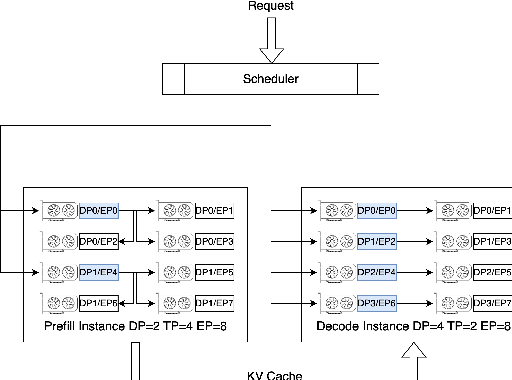
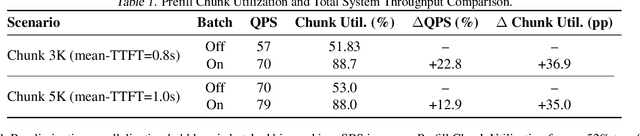
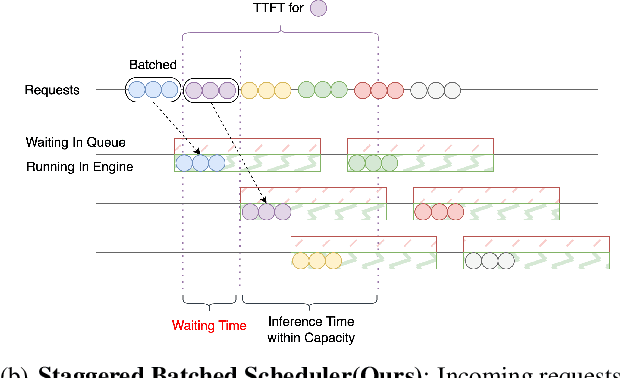
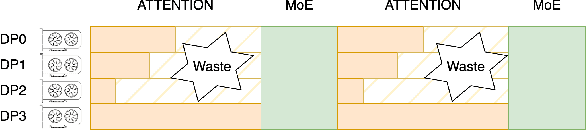
Abstract:The evolution of Large Language Model (LLM) serving towards complex, distributed architectures--specifically the P/D-separated, large-scale DP+EP paradigm--introduces distinct scheduling challenges. Unlike traditional deployments where schedulers can treat instances as black boxes, DP+EP architectures exhibit high internal synchronization costs. We identify that immediate request dispatching in such systems leads to severe in-engine queuing and parallelization bubbles, degrading Time-to-First-Token (TTFT). To address this, we propose Staggered Batch Scheduling (SBS), a mechanism that deliberately buffers requests to form optimal execution batches. This temporal decoupling eliminates internal queuing bubbles without compromising throughput. Furthermore, leveraging the scheduling window created by buffering, we introduce a Load-Aware Global Allocation strategy that balances computational load across DP units for both Prefill and Decode phases. Deployed on a production H800 cluster serving Deepseek-V3, our system reduces TTFT by 30%-40% and improves throughput by 15%-20% compared to state-of-the-art immediate scheduling baselines.
DiffuDepGrasp: Diffusion-based Depth Noise Modeling Empowers Sim2Real Robotic Grasping
Nov 17, 2025



Abstract:Transferring the depth-based end-to-end policy trained in simulation to physical robots can yield an efficient and robust grasping policy, yet sensor artifacts in real depth maps like voids and noise establish a significant sim2real gap that critically impedes policy transfer. Training-time strategies like procedural noise injection or learned mappings suffer from data inefficiency due to unrealistic noise simulation, which is often ineffective for grasping tasks that require fine manipulation or dependency on paired datasets heavily. Furthermore, leveraging foundation models to reduce the sim2real gap via intermediate representations fails to mitigate the domain shift fully and adds computational overhead during deployment. This work confronts dual challenges of data inefficiency and deployment complexity. We propose DiffuDepGrasp, a deploy-efficient sim2real framework enabling zero-shot transfer through simulation-exclusive policy training. Its core innovation, the Diffusion Depth Generator, synthesizes geometrically pristine simulation depth with learned sensor-realistic noise via two synergistic modules. The first Diffusion Depth Module leverages temporal geometric priors to enable sample-efficient training of a conditional diffusion model that captures complex sensor noise distributions, while the second Noise Grafting Module preserves metric accuracy during perceptual artifact injection. With only raw depth inputs during deployment, DiffuDepGrasp eliminates computational overhead and achieves a 95.7% average success rate on 12-object grasping with zero-shot transfer and strong generalization to unseen objects.Project website: https://diffudepgrasp.github.io/.
Survey of Vision-Language-Action Models for Embodied Manipulation
Aug 21, 2025Abstract:Embodied intelligence systems, which enhance agent capabilities through continuous environment interactions, have garnered significant attention from both academia and industry. Vision-Language-Action models, inspired by advancements in large foundation models, serve as universal robotic control frameworks that substantially improve agent-environment interaction capabilities in embodied intelligence systems. This expansion has broadened application scenarios for embodied AI robots. This survey comprehensively reviews VLA models for embodied manipulation. Firstly, it chronicles the developmental trajectory of VLA architectures. Subsequently, we conduct a detailed analysis of current research across 5 critical dimensions: VLA model structures, training datasets, pre-training methods, post-training methods, and model evaluation. Finally, we synthesize key challenges in VLA development and real-world deployment, while outlining promising future research directions.
GAPartManip: A Large-scale Part-centric Dataset for Material-Agnostic Articulated Object Manipulation
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:Effectively manipulating articulated objects in household scenarios is a crucial step toward achieving general embodied artificial intelligence. Mainstream research in 3D vision has primarily focused on manipulation through depth perception and pose detection. However, in real-world environments, these methods often face challenges due to imperfect depth perception, such as with transparent lids and reflective handles. Moreover, they generally lack the diversity in part-based interactions required for flexible and adaptable manipulation. To address these challenges, we introduced a large-scale part-centric dataset for articulated object manipulation that features both photo-realistic material randomizations and detailed annotations of part-oriented, scene-level actionable interaction poses. We evaluated the effectiveness of our dataset by integrating it with several state-of-the-art methods for depth estimation and interaction pose prediction. Additionally, we proposed a novel modular framework that delivers superior and robust performance for generalizable articulated object manipulation. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our dataset significantly improves the performance of depth perception and actionable interaction pose prediction in both simulation and real-world scenarios.
D3RoMa: Disparity Diffusion-based Depth Sensing for Material-Agnostic Robotic Manipulation
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Depth sensing is an important problem for 3D vision-based robotics. Yet, a real-world active stereo or ToF depth camera often produces noisy and incomplete depth which bottlenecks robot performances. In this work, we propose D3RoMa, a learning-based depth estimation framework on stereo image pairs that predicts clean and accurate depth in diverse indoor scenes, even in the most challenging scenarios with translucent or specular surfaces where classical depth sensing completely fails. Key to our method is that we unify depth estimation and restoration into an image-to-image translation problem by predicting the disparity map with a denoising diffusion probabilistic model. At inference time, we further incorporated a left-right consistency constraint as classifier guidance to the diffusion process. Our framework combines recently advanced learning-based approaches and geometric constraints from traditional stereo vision. For model training, we create a large scene-level synthetic dataset with diverse transparent and specular objects to compensate for existing tabletop datasets. The trained model can be directly applied to real-world in-the-wild scenes and achieve state-of-the-art performance in multiple public depth estimation benchmarks. Further experiments in real environments show that accurate depth prediction significantly improves robotic manipulation in various scenarios.
RoboGPT: an intelligent agent of making embodied long-term decisions for daily instruction tasks
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:Robotic agents must master common sense and long-term sequential decisions to solve daily tasks through natural language instruction. The developments in Large Language Models (LLMs) in natural language processing have inspired efforts to use LLMs in complex robot planning. Despite LLMs' great generalization and comprehension of instruction tasks, LLMs-generated task plans sometimes lack feasibility and correctness. To address the problem, we propose a RoboGPT agent\footnote{our code and dataset will be released soon} for making embodied long-term decisions for daily tasks, with two modules: 1) LLMs-based planning with re-plan to break the task into multiple sub-goals; 2) RoboSkill individually designed for sub-goals to learn better navigation and manipulation skills. The LLMs-based planning is enhanced with a new robotic dataset and re-plan, called RoboGPT. The new robotic dataset of 67k daily instruction tasks is gathered for fine-tuning the Llama model and obtaining RoboGPT. RoboGPT planner with strong generalization can plan hundreds of daily instruction tasks. Additionally, a low-computational Re-Plan module is designed to allow plans to flexibly adapt to the environment, thereby addressing the nomenclature diversity challenge. The proposed RoboGPT agent outperforms SOTA methods on the ALFRED daily tasks. Moreover, RoboGPT planner exceeds SOTA LLM-based planners like ChatGPT in task-planning rationality for hundreds of unseen daily tasks, and even other domain tasks, while keeping the large model's original broad application and generality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge