Weiheng Liu
DiffuDepGrasp: Diffusion-based Depth Noise Modeling Empowers Sim2Real Robotic Grasping
Nov 17, 2025



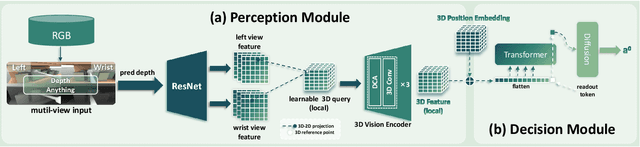
Abstract:Transferring the depth-based end-to-end policy trained in simulation to physical robots can yield an efficient and robust grasping policy, yet sensor artifacts in real depth maps like voids and noise establish a significant sim2real gap that critically impedes policy transfer. Training-time strategies like procedural noise injection or learned mappings suffer from data inefficiency due to unrealistic noise simulation, which is often ineffective for grasping tasks that require fine manipulation or dependency on paired datasets heavily. Furthermore, leveraging foundation models to reduce the sim2real gap via intermediate representations fails to mitigate the domain shift fully and adds computational overhead during deployment. This work confronts dual challenges of data inefficiency and deployment complexity. We propose DiffuDepGrasp, a deploy-efficient sim2real framework enabling zero-shot transfer through simulation-exclusive policy training. Its core innovation, the Diffusion Depth Generator, synthesizes geometrically pristine simulation depth with learned sensor-realistic noise via two synergistic modules. The first Diffusion Depth Module leverages temporal geometric priors to enable sample-efficient training of a conditional diffusion model that captures complex sensor noise distributions, while the second Noise Grafting Module preserves metric accuracy during perceptual artifact injection. With only raw depth inputs during deployment, DiffuDepGrasp eliminates computational overhead and achieves a 95.7% average success rate on 12-object grasping with zero-shot transfer and strong generalization to unseen objects.Project website: https://diffudepgrasp.github.io/.
Survey of Vision-Language-Action Models for Embodied Manipulation
Aug 21, 2025Abstract:Embodied intelligence systems, which enhance agent capabilities through continuous environment interactions, have garnered significant attention from both academia and industry. Vision-Language-Action models, inspired by advancements in large foundation models, serve as universal robotic control frameworks that substantially improve agent-environment interaction capabilities in embodied intelligence systems. This expansion has broadened application scenarios for embodied AI robots. This survey comprehensively reviews VLA models for embodied manipulation. Firstly, it chronicles the developmental trajectory of VLA architectures. Subsequently, we conduct a detailed analysis of current research across 5 critical dimensions: VLA model structures, training datasets, pre-training methods, post-training methods, and model evaluation. Finally, we synthesize key challenges in VLA development and real-world deployment, while outlining promising future research directions.
FetchBot: Object Fetching in Cluttered Shelves via Zero-Shot Sim2Real
Feb 25, 2025

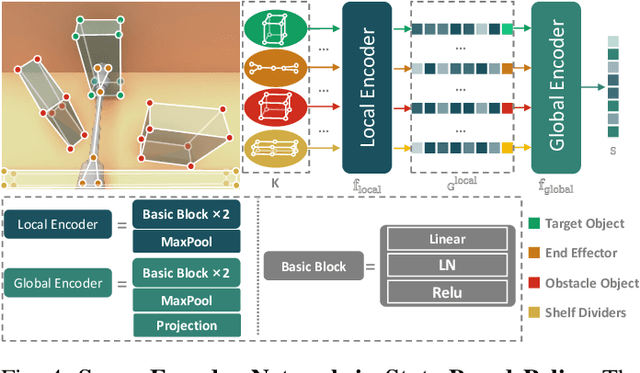
Abstract:Object fetching from cluttered shelves is an important capability for robots to assist humans in real-world scenarios. Achieving this task demands robotic behaviors that prioritize safety by minimizing disturbances to surrounding objects, an essential but highly challenging requirement due to restricted motion space, limited fields of view, and complex object dynamics. In this paper, we introduce FetchBot, a sim-to-real framework designed to enable zero-shot generalizable and safety-aware object fetching from cluttered shelves in real-world settings. To address data scarcity, we propose an efficient voxel-based method for generating diverse simulated cluttered shelf scenes at scale and train a dynamics-aware reinforcement learning (RL) policy to generate object fetching trajectories within these scenes. This RL policy, which leverages oracle information, is subsequently distilled into a vision-based policy for real-world deployment. Considering that sim-to-real discrepancies stem from texture variations mostly while from geometric dimensions rarely, we propose to adopt depth information estimated by full-fledged depth foundation models as the input for the vision-based policy to mitigate sim-to-real gap. To tackle the challenge of limited views, we design a novel architecture for learning multi-view representations, allowing for comprehensive encoding of cluttered shelf scenes. This enables FetchBot to effectively minimize collisions while fetching objects from varying positions and depths, ensuring robust and safety-aware operation. Both simulation and real-robot experiments demonstrate FetchBot's superior generalization ability, particularly in handling a broad range of real-world scenarios, includ
Can Large Language Model Predict Employee Attrition?
Nov 02, 2024Abstract:Employee attrition poses significant costs for organizations, with traditional statistical prediction methods often struggling to capture modern workforce complexities. Machine learning (ML) advancements offer more scalable and accurate solutions, but large language models (LLMs) introduce new potential in human resource management by interpreting nuanced employee communication and detecting subtle turnover cues. This study leverages the IBM HR Analytics Attrition dataset to compare the predictive accuracy and interpretability of a fine-tuned GPT-3.5 model against traditional ML classifiers, including Logistic Regression, k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Decision Tree, Random Forest, AdaBoost, and XGBoost. While traditional models are easier to use and interpret, LLMs can reveal deeper patterns in employee behavior. Our findings show that the fine-tuned GPT-3.5 model outperforms traditional methods with a precision of 0.91, recall of 0.94, and an F1-score of 0.92, while the best traditional model, SVM, achieved an F1-score of 0.82, with Random Forest and XGBoost reaching 0.80. These results highlight GPT-3.5's ability to capture complex patterns in attrition risk, offering organizations improved insights for retention strategies and underscoring the value of LLMs in HR applications.
ConvNext Based Neural Network for Anti-Spoofing
Sep 15, 2022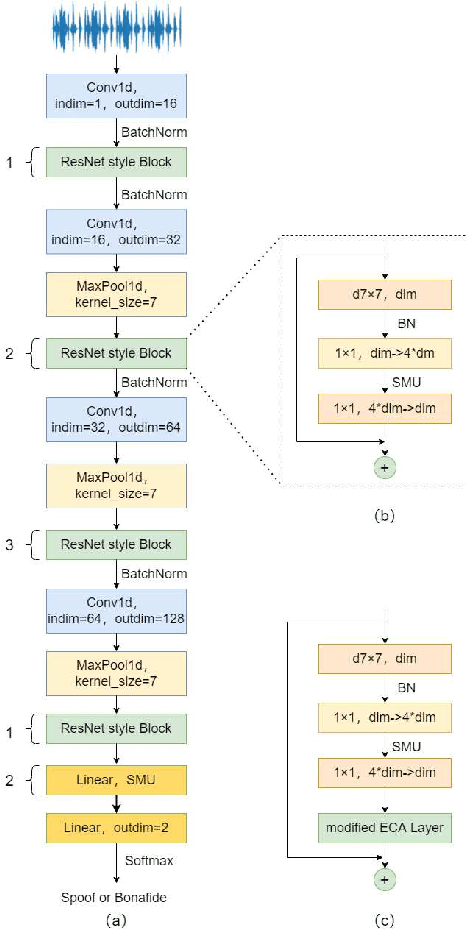
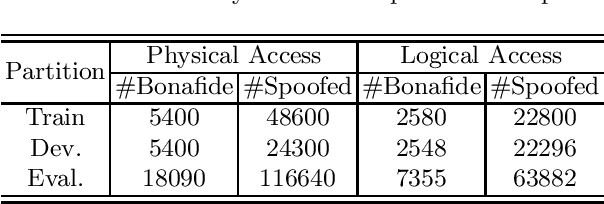
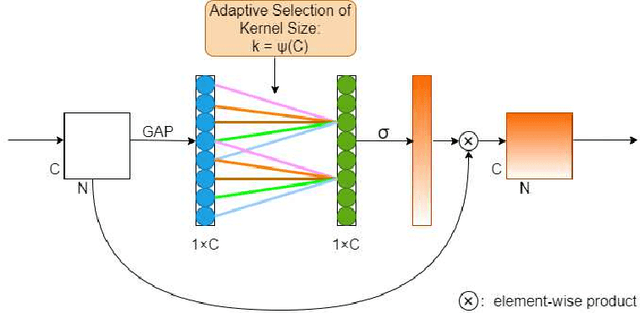
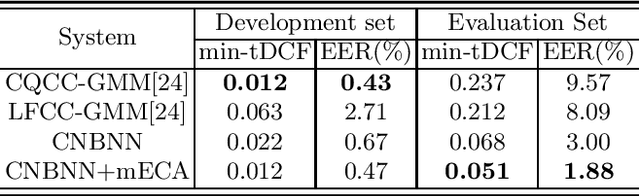
Abstract:Automatic speaker verification (ASV) has been widely used in the real life for identity authentication. However, with the rapid development of speech conversion, speech synthesis algorithms and the improvement of the quality of recording devices, ASV systems are vulnerable for spoof attacks. In recent years, there have many works about synthetic and replay speech detection, researchers had proposed a number of anti-spoofing methods based on hand-crafted features to improve the accuracy and robustness of synthetic and replay speech detection system. However, using hand-crafted features rather than raw waveform would lose certain information for anti-spoofing, which will reduce the detection performance of the system. Inspired by the promising performance of ConvNext in image classification tasks, we extend the ConvNext network architecture accordingly for spoof attacks detection task and propose an end-to-end anti-spoofing model. By integrating the extended architecture with the channel attention block, the proposed model can focus on the most informative sub-bands of speech representations to improve the anti-spoofing performance. Experiments show that our proposed best single system could achieve an equal error rate of 1.88% and 2.79% for the ASVSpoof 2019 LA evaluation dataset and PA evaluation dataset respectively, which demonstrate the model's capacity for anti-spoofing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge