Wei-Peng Chen
TabGLM: Tabular Graph Language Model for Learning Transferable Representations Through Multi-Modal Consistency Minimization
Feb 26, 2025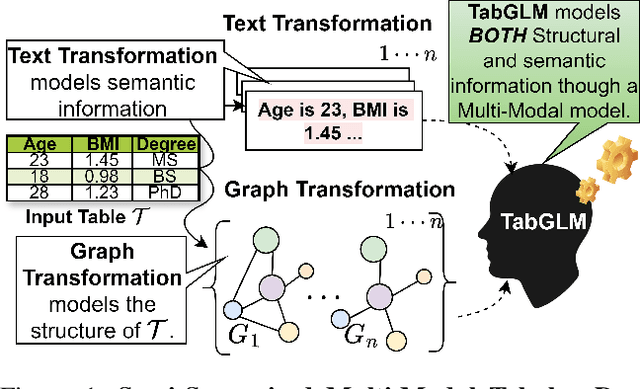
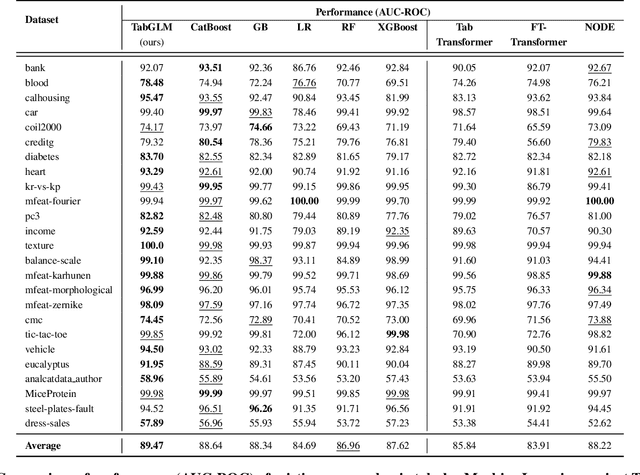
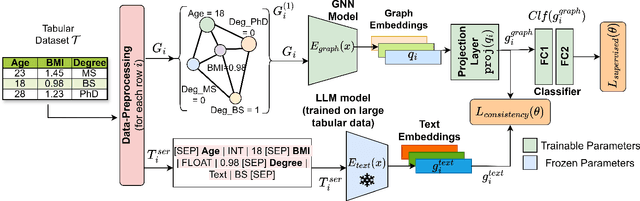
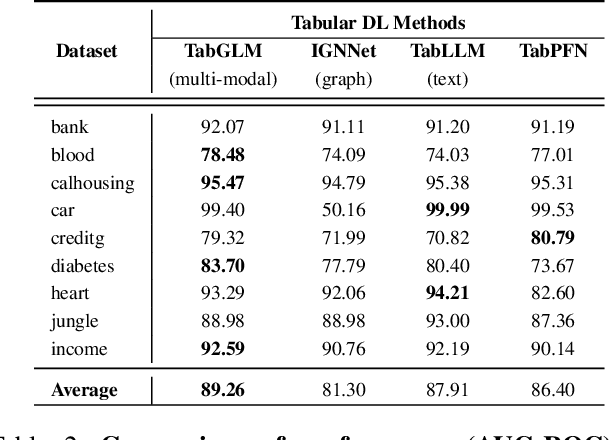
Abstract:Handling heterogeneous data in tabular datasets poses a significant challenge for deep learning models. While attention-based architectures and self-supervised learning have achieved notable success, their application to tabular data remains less effective over linear and tree based models. Although several breakthroughs have been achieved by models which transform tables into uni-modal transformations like image, language and graph, these models often underperform in the presence of feature heterogeneity. To address this gap, we introduce TabGLM (Tabular Graph Language Model), a novel multi-modal architecture designed to model both structural and semantic information from a table. TabGLM transforms each row of a table into a fully connected graph and serialized text, which are then encoded using a graph neural network (GNN) and a text encoder, respectively. By aligning these representations through a joint, multi-modal, self-supervised learning objective, TabGLM leverages complementary information from both modalities, thereby enhancing feature learning. TabGLM's flexible graph-text pipeline efficiently processes heterogeneous datasets with significantly fewer parameters over existing Deep Learning approaches. Evaluations across 25 benchmark datasets demonstrate substantial performance gains, with TabGLM achieving an average AUC-ROC improvement of up to 5.56% over State-of-the-Art (SoTA) tabular learning methods.
AugmentedCode: Examining the Effects of Natural Language Resources in Code Retrieval Models
Oct 16, 2021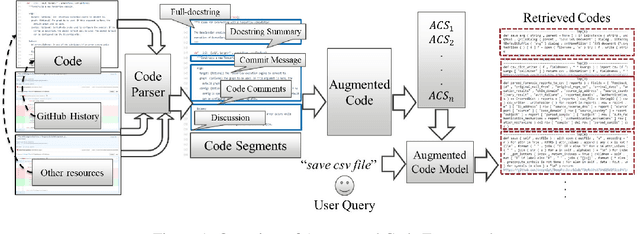
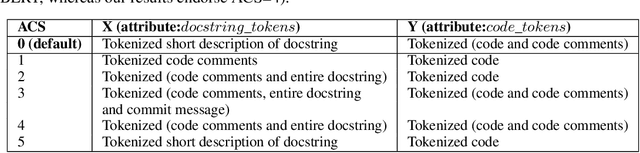
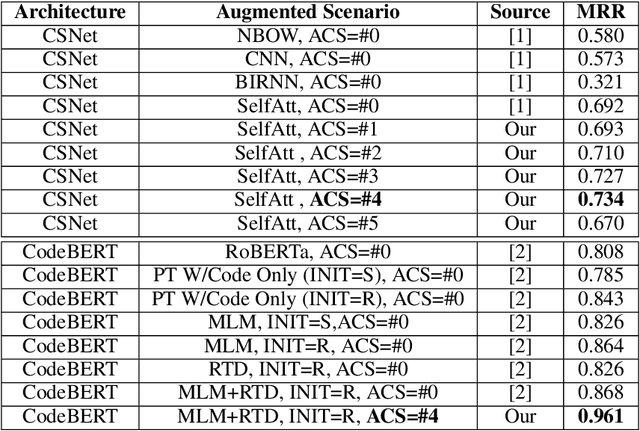
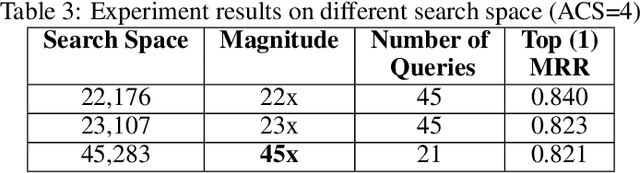
Abstract:Code retrieval is allowing software engineers to search codes through a natural language query, which relies on both natural language processing and software engineering techniques. There have been several attempts on code retrieval from searching snippet codes to function codes. In this paper, we introduce Augmented Code (AugmentedCode) retrieval which takes advantage of existing information within the code and constructs augmented programming language to improve the code retrieval models' performance. We curated a large corpus of Python and showcased the the framework and the results of augmented programming language which outperforms on CodeSearchNet and CodeBERT with a Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR) of 0.73 and 0.96, respectively. The outperformed fine-tuned augmented code retrieval model is published in HuggingFace at https://huggingface.co/Fujitsu/AugCode and a demonstration video is available at: https://youtu.be/mnZrUTANjGs .
A Systematic Investigation of KB-Text Embedding Alignment at Scale
Jun 03, 2021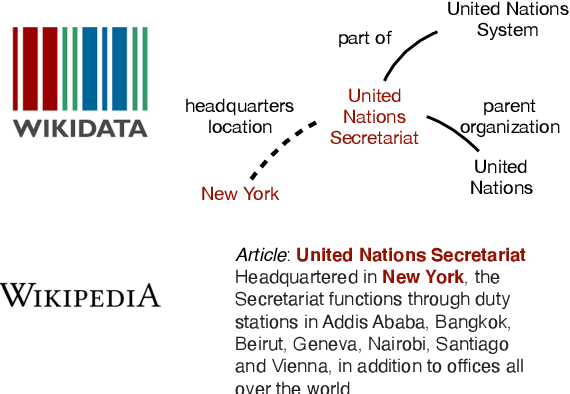
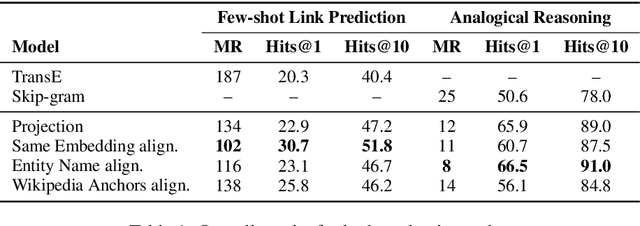
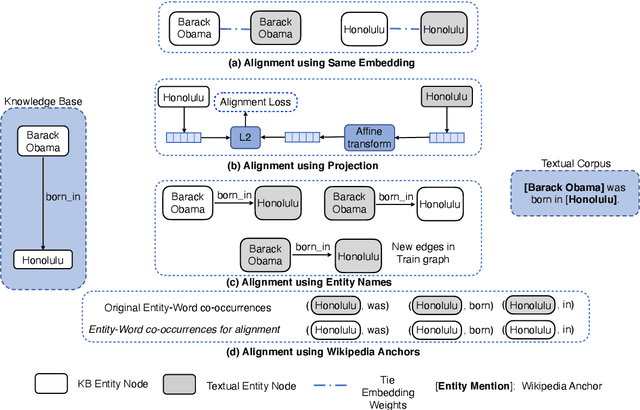
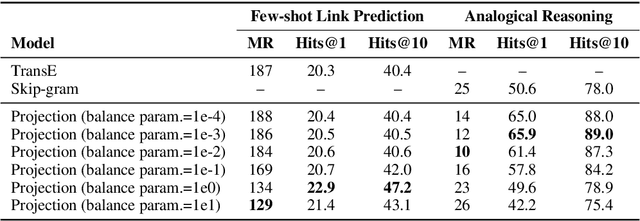
Abstract:Knowledge bases (KBs) and text often contain complementary knowledge: KBs store structured knowledge that can support long range reasoning, while text stores more comprehensive and timely knowledge in an unstructured way. Separately embedding the individual knowledge sources into vector spaces has demonstrated tremendous successes in encoding the respective knowledge, but how to jointly embed and reason with both knowledge sources to fully leverage the complementary information is still largely an open problem. We conduct a large-scale, systematic investigation of aligning KB and text embeddings for joint reasoning. We set up a novel evaluation framework with two evaluation tasks, few-shot link prediction and analogical reasoning, and evaluate an array of KB-text embedding alignment methods. We also demonstrate how such alignment can infuse textual information into KB embeddings for more accurate link prediction on emerging entities and events, using COVID-19 as a case study.
StaQC: A Systematically Mined Question-Code Dataset from Stack Overflow
Mar 26, 2018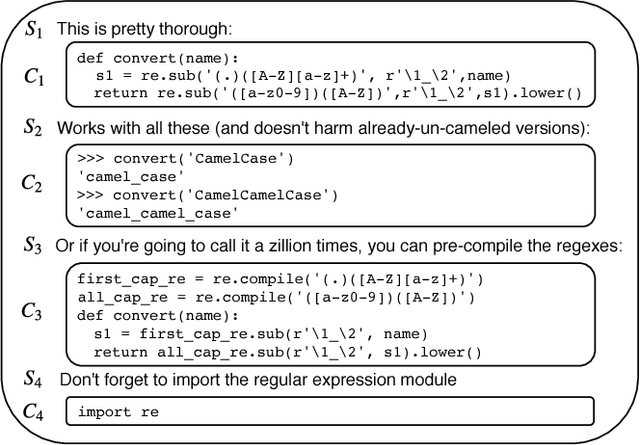
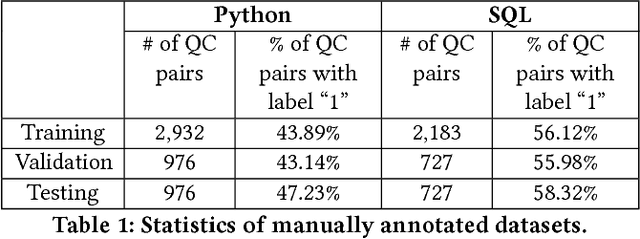
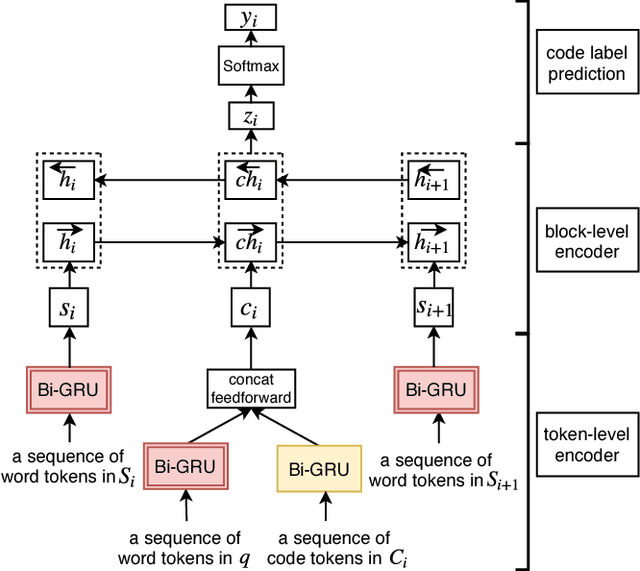
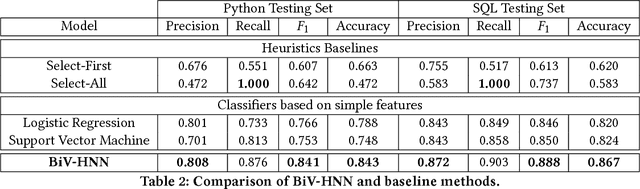
Abstract:Stack Overflow (SO) has been a great source of natural language questions and their code solutions (i.e., question-code pairs), which are critical for many tasks including code retrieval and annotation. In most existing research, question-code pairs were collected heuristically and tend to have low quality. In this paper, we investigate a new problem of systematically mining question-code pairs from Stack Overflow (in contrast to heuristically collecting them). It is formulated as predicting whether or not a code snippet is a standalone solution to a question. We propose a novel Bi-View Hierarchical Neural Network which can capture both the programming content and the textual context of a code snippet (i.e., two views) to make a prediction. On two manually annotated datasets in Python and SQL domain, our framework substantially outperforms heuristic methods with at least 15% higher F1 and accuracy. Furthermore, we present StaQC (Stack Overflow Question-Code pairs), the largest dataset to date of ~148K Python and ~120K SQL question-code pairs, automatically mined from SO using our framework. Under various case studies, we demonstrate that StaQC can greatly help develop data-hungry models for associating natural language with programming language.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge